Risorgimento - Die Einigung Italiens 1
Summary
TLDRThis video explores the history of Italy's unification, focusing on the period from 1815 to 1870, known as the Risorgimento. It details the fragmented state of Italy before unification, describing the different regions controlled by foreign powers. The key figures in this movement include Camillo di Cavour, who led Sardinia-Piedmont, Giuseppe Mazzini, a revolutionary advocating for a democratic republic, and Giuseppe Garibaldi, a military leader who played a pivotal role in the Italian unification wars. The video highlights the internal and external struggles, including battles against Austria and local monarchies, and sets the stage for future episodes on the unification wars.
Takeaways
- 😀 Italy's Independence Day, celebrating the country's unification, is only observed every 50 years, most recently during the 150th anniversary in 2011.
- 😀 Since the fall of the Roman Empire, Italy had been divided into small kingdoms and principalities, mostly under foreign rule.
- 😀 The only independent region in Italy in the 19th century was Sardinia-Piedmont, with its capital in Turin, led by the House of Savoy.
- 😀 The Papal States, governed by the Pope, were a significant power in central Italy, unlike the modern-day Vatican City.
- 😀 Nationalism began to rise in Italy, driven by the idea of creating a unified nation with a common culture and language, first inspired by Napoleon's conquests.
- 😀 The period from 1815 to 1870 is known as the Risorgimento, or 'resurrection,' marking Italy's struggle for unification and independence.
- 😀 Camillo di Cavour, the Prime Minister of Sardinia-Piedmont, played a key role in Italy's unification, advocating for a monarchy with the King of Sardinia as the head of the new nation.
- 😀 Giuseppe Mazzini, a revolutionary figure, founded the secret society 'Young Italy' and pushed for a republic, although his ideas initially failed to gain widespread support.
- 😀 Giuseppe Garibaldi, a key military leader, led guerrilla campaigns in South America before returning to Italy to fight for unification, earning fame for his 'Redshirts' army.
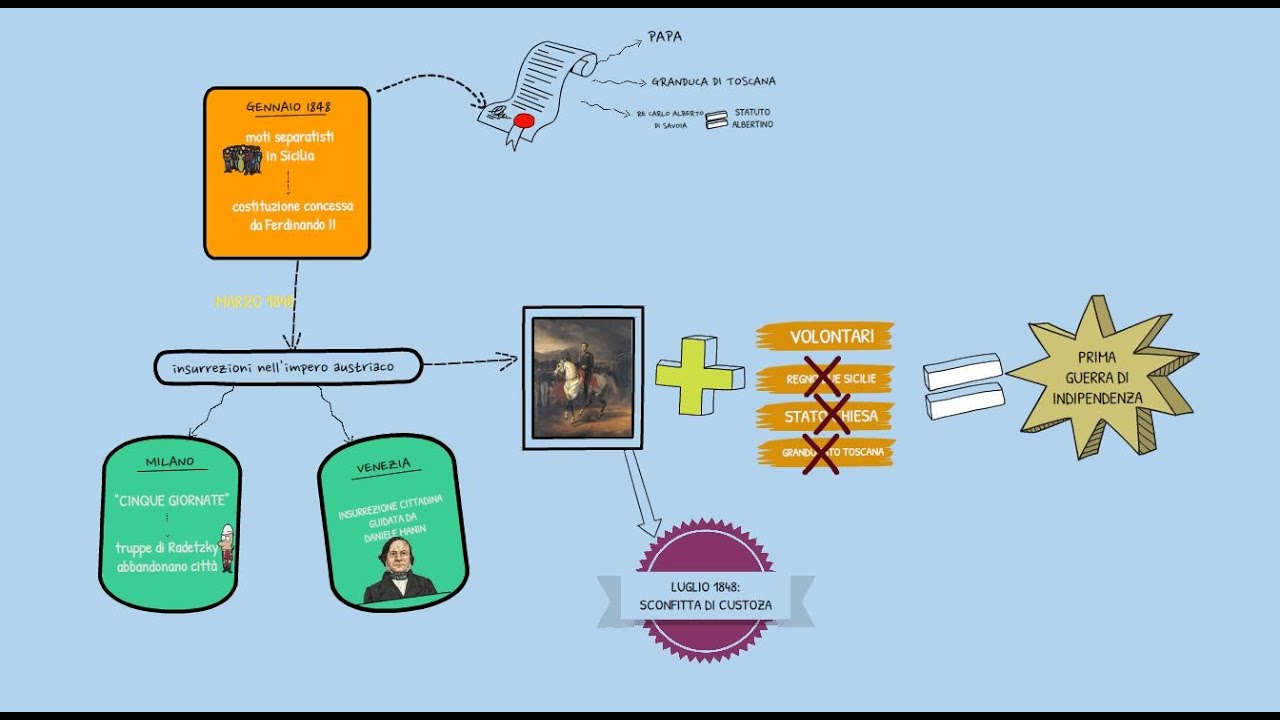
- 😀 Despite internal divisions, revolutions in 1848 across Europe spurred hopes for freedom and democratic reforms, with Italy experiencing uprisings that were eventually suppressed by Austrian forces.
- 😀 Cavour’s strategic diplomacy with France and Britain helped Sardinia-Piedmont gain important allies and secure Italy's unification through a combination of military and political efforts.
Q & A
What is the significance of March 17th, 2021 in the video?
-March 17th, 2021 marks the beginning of the research for the video, coinciding with the 160th anniversary of Italy's declaration of independence and unification.
Why is Italy's Independence Day only celebrated every 50 years?
-Italy's Independence Day is only celebrated every 50 years to commemorate significant anniversaries, such as the 150th anniversary celebration in 2011.
What was the political situation in Italy before its unification?
-Before unification, Italy was divided into multiple kingdoms and territories, many of which were under foreign control, such as Sardinia-Piedmont in the northwest, the Papal States in central Italy, and Austrian-occupied Lombardy-Venetia in the north.
Who was Camillo Benso di Cavour and what was his role in Italy's unification?
-Camillo Benso di Cavour was the Prime Minister of Sardinia-Piedmont and played a crucial role in Italy's unification by advocating for a monarchy-led kingdom, reforming the state, and securing alliances with France and Great Britain.
What was Giuseppe Mazzini's vision for Italy?
-Giuseppe Mazzini envisioned a unified, independent, and democratic Italy, without a king, where the people, particularly workers and craftsmen, would drive the revolution for a republic.
What military tactics did Giuseppe Garibaldi employ during the unification efforts?
-Giuseppe Garibaldi employed guerrilla warfare tactics, leading his 'Redshirts' against larger, better-equipped armies, using small but strategically effective military units.
What role did the 1848 revolutions play in Italy's path to unification?
-The 1848 revolutions, part of a broader European wave of uprisings, expressed widespread discontent with monarchies and foreign control. In Italy, they led to increased demands for a unified, constitutional Italy.
How did the Congress of Vienna impact Italy's political situation?
-The Congress of Vienna in 1815 aimed to restore pre-Napoleonic monarchies, stoking resentment in Italy due to the restoration of foreign powers like Austria and suppressing nationalistic movements.
What was the significance of the first and second Italian wars of independence?
-The first and second Italian wars of independence were crucial military campaigns in the unification process. The first war was an early, unsuccessful attempt to expel Austrian influence, while the second saw more strategic involvement from Sardinia-Piedmont and France.
How did Cavour's reforms contribute to the unification of Italy?
-Cavour's reforms modernized the economy through agricultural improvements, the expansion of the railway system, and trade agreements with France and Britain, strengthening Sardinia-Piedmont's political and economic influence, which helped propel the unification of Italy.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
Il Risorgimento italiano. Parte 1: dal congresso di Vienna alla prima guerra di Indipendenza

How did Italy Become a Country? | Animated History

GIUSEPPE MAZZINI e l’INIZIO del RISORGIMENTO

Episodio 0, In principio era una lupa (riassunto anni 32 AC-305 AD).

Comment l'Italie est-elle parvenue à s'unifier ?

What Caused Italian Unification?
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)