Bagaimana proses terjadinya Replikasi DNA?
Summary
TLDRThis video provides an in-depth look at DNA replication, explaining its fundamental processes and key players. It covers the structure of DNA, the three models of DNA replication (conservative, semi-conservative, and dispersive), and the enzymes involved, such as helicase, primase, and DNA polymerase. The video highlights how DNA is replicated accurately with minimal errors, focusing on the roles of different proteins in the unwinding, copying, and synthesis of new DNA strands. Viewers also learn about the directionality of DNA replication and the mechanisms that ensure the fidelity of the process, ultimately leading to the formation of two identical DNA molecules.
Takeaways
- 😀 Human cells contain 46 chromosomes, each made up of a long double-helix DNA molecule.
- 😀 DNA is composed of base pairs, and each base pair plays a crucial role in genetic information storage.
- 😀 DNA replication is the process of creating an identical copy of DNA, ensuring accurate transmission of genetic material during cell division.
- 😀 The process of DNA replication begins with the separation of DNA strands at the origin of replication, forming a 'replication bubble.'
- 😀 There are three models of DNA replication: conservative, semi-conservative, and dispersive, with the semi-conservative model being proven correct.
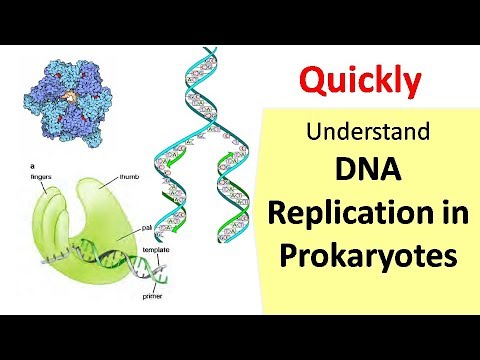
- 😀 In DNA replication, helicase unwinds the DNA double helix at the replication fork, while single-strand binding proteins stabilize the separated strands.
- 😀 Topoisomerase prevents DNA tangling by relieving tension in the DNA ahead of the replication fork.
- 😀 Primase synthesizes a short RNA primer to provide a starting point for DNA polymerase during replication.
- 😀 DNA polymerase adds complementary nucleotides to the growing DNA strand in the 5' to 3' direction, using the original DNA strand as a template.
- 😀 The energy required for DNA polymerization comes from the release of phosphate groups when nucleotides are added to the new DNA strand.
- 😀 DNA replication involves proofreading mechanisms that correct errors, ensuring the new DNA strands are accurate copies of the originals.
Q & A
What is DNA replication?
-DNA replication is the process by which a DNA molecule is copied to produce two identical DNA molecules. This involves the unwinding of the double helix, separating the strands, and synthesizing complementary strands to form two identical copies of the DNA.
What is the role of hydrogen bonds in DNA replication?
-Hydrogen bonds hold the complementary base pairs of the DNA strands together. During replication, these bonds are broken, allowing the two strands of DNA to separate and serve as templates for the synthesis of new complementary strands.
What are the three models of DNA replication?
-The three models of DNA replication are conservative, semi-conservative, and dispersive. In the conservative model, the original double helix remains intact, and a completely new helix is formed. In the semi-conservative model, each original strand serves as a template for a new complementary strand. In the dispersive model, each strand of the new DNA contains segments of both old and new DNA.
Which model of DNA replication was proven to be correct?
-The semi-conservative model of DNA replication was proven to be correct. This was confirmed by the experiments of Meselson and Stahl in the 1950s.
What are the key stages in DNA replication?
-The key stages of DNA replication include the initiation at the origin of replication, the unwinding of the DNA helix by helicase, the synthesis of RNA primers by primase, and the elongation of the new DNA strands by DNA polymerase. Additionally, there are steps for proofreading and repairing the DNA to ensure accuracy.
What is the function of helicase in DNA replication?
-Helicase is an enzyme that unwinds the DNA double helix at the replication fork by breaking the hydrogen bonds between the complementary bases, allowing the two DNA strands to separate.
What role does primase play in DNA replication?
-Primase synthesizes short RNA primers that are necessary for DNA polymerase to begin adding nucleotides. These primers provide the 3' hydroxyl group required for DNA polymerase to initiate DNA synthesis.
How does DNA polymerase contribute to DNA replication?
-DNA polymerase adds nucleotides to the growing DNA strand, matching each nucleotide with its complementary base on the template strand. It catalyzes the formation of phosphodiester bonds between the nucleotides, thus elongating the DNA strand.
What is the significance of the 5' and 3' ends of the DNA strand?
-The 5' and 3' ends refer to the orientation of the DNA strand. The 5' end has a phosphate group attached to the fifth carbon of the sugar ring, while the 3' end has a hydroxyl group attached to the third carbon. DNA polymerase can only add nucleotides to the 3' end, meaning DNA is synthesized in a 5' to 3' direction.
What is the function of topoisomerase in DNA replication?
-Topoisomerase is an enzyme that alleviates the tension in the DNA molecule caused by its unwinding. It does so by making temporary cuts in the DNA strands to relieve supercoiling, and then rejoining the strands.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)