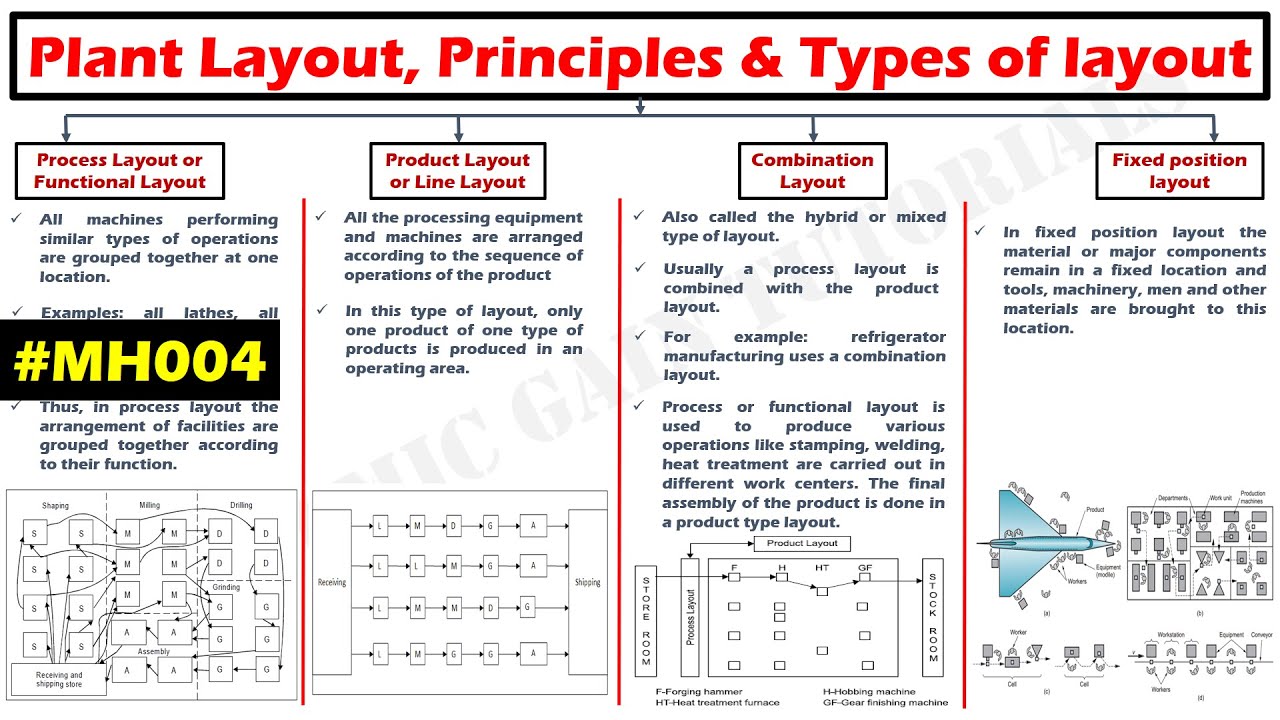
LO007: 6a Warehouse Layout
Summary
TLDRThis video lecture covers essential concepts in warehouse layout design, focusing on optimizing space utilization and material handling efficiency. The dedicated storage method is explored, emphasizing the assignment of specific storage locations for each product to maximize storage and improve operational speed. The video also delves into calculations for space requirements, material handling throughput, and the distance between storage blocks and entry/exit points, providing practical examples. These strategies aim to minimize costs, improve efficiency, and ensure effective warehouse operations, ultimately enhancing service speed and reducing handling time.
Takeaways
- 😀 Efficient warehouse layout is essential for minimizing costs, increasing operational speed, and improving customer service.
- 😀 Dedicated storage method assigns specific locations to each product, ensuring each storage block is optimized for only one type of product.
- 😀 The space requirement for storing products is calculated based on the average reception of the product and the block's storage capacity.
- 😀 Throughput (Thruput) measures the efficiency of warehouse operations, factoring in both reception and shipping activities for material handling.
- 😀 Proper warehouse layout can reduce material handling costs by optimizing storage and minimizing travel distances.
- 😀 The formula for calculating storage capacity in a block includes the number of rows, stacks, and the capacity per pallet or box.
- 😀 Comparing throughput per specific storage (TPS) helps determine the most efficient product placement in a warehouse, prioritizing high-TPS products near entry and exit points.
- 😀 The distance between storage blocks and entry/exit points is crucial for minimizing travel time in the warehouse, and it is calculated using the Euclidean distance formula.
- 😀 Total travel distance for products can be calculated by factoring in both receiving and shipping throughput, helping to optimize warehouse operations.
- 😀 Effective warehouse design requires evaluating throughput, space requirements, and travel distances to create an efficient and cost-effective system.
- 😀 Proper planning and calculation, such as determining TPS and block-specific storage, can significantly improve warehouse workflow and operational effectiveness.
Q & A
What is the focus of this lecture on warehouse layout?
-The lecture focuses on a quantitative approach to warehouse layout, including determining space requirements, calculating throughput, and assessing the effectiveness of warehouse storage configurations to optimize space utilization and reduce costs.
What is meant by 'space requirements' in warehouse layout?
-Space requirements refer to the amount of storage space needed to accommodate the inventory, determined by factors such as product volume, storage method (e.g., pallets, boxes), and the layout of the warehouse.
What is the dedicated storage method in warehouse layout?
-The dedicated storage method involves assigning specific locations for each product in the warehouse. Each location is reserved for a single product type, which ensures that storage is organized and optimized for each item.
How is the storage capacity for a block in the warehouse determined?
-Storage capacity for a block is calculated by multiplying the number of stacks by the number of layers per stack, and then multiplying by the capacity of each pallet or box used for storage.
What is throughput (or 'thruput') in the context of warehouse operations?
-Throughput refers to the rate at which items are stored and retrieved in a warehouse. It is calculated by measuring the number of items received and shipped during a given period and dividing that by the capacity of the handling equipment (e.g., forklifts).
Why is the comparison of throughput to specific space important in warehouse management?
-Comparing throughput to specific storage space (referred to as TPS or throughput-specific storage) helps identify the most efficient storage locations for products. Products with higher throughput are placed closer to entry/exit points to reduce handling time and improve overall efficiency.
What is the formula used to calculate space requirements for a dedicated storage method?
-The formula for space requirements (denoted as SC) is the average receipt of products per day divided by the storage capacity of a block. The storage capacity of a block is calculated by multiplying the number of stacks, layers, and pallet capacity (or box capacity).
How is the distance for material handling in the warehouse calculated?
-The distance for material handling is calculated using the Manhattan method, where the distance between two points (e.g., a block and the entrance/exit) is determined by the sum of the absolute differences in the X and Y coordinates of the two points.
How does calculating travel distance contribute to warehouse efficiency?
-Calculating travel distance helps in optimizing the placement of products in relation to entrance/exit points. By minimizing the travel distance for high-turnover items, overall material handling time can be reduced, improving the efficiency of warehouse operations.
What factors influence the decision of where to place products in the warehouse?
-The decision on product placement is influenced by factors such as throughput rates (how quickly products are received and shipped), space utilization, and the distance from entry/exit points. Products with higher throughput should be placed closer to these points to minimize handling time.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)