The Fascinating Bitcoin Origin Story
Summary
TLDRThis video delves into the fascinating origin story of Bitcoin, tracing its roots back to earlier digital cash projects like e-gold and the groundbreaking work of the Cypherpunks. It highlights the failures of centralized systems and the rise of decentralized solutions designed to avoid government control. Key technological innovations like public key cryptography, proof of work, and Merkle trees were instrumental in Bitcoin’s creation. Satoshi Nakamoto’s genius lay in perfecting a decentralized currency that couldn't be censored or shut down, offering economic freedom in an increasingly regulated world.
Takeaways
- 😀 Bitcoin did not emerge out of nowhere; it was built on decades of experimentation with digital cash and privacy technology.
- 😀 The story of Bitcoin begins with earlier digital cash projects like e-gold, which were centralized and vulnerable to government intervention.
- 😀 E-gold’s downfall, due to a government crackdown, demonstrated the need for a decentralized digital currency.
- 😀 The Cypherpunks, a group of cryptographic activists, played a key role in pushing for privacy-focused technologies and digital cash systems.
- 😀 The phrase 'Cypherpunks write code' embodied the Cypherpunks' belief in using technology, not politics, to ensure privacy and decentralization.
- 😀 Key technological innovations that led to Bitcoin include public key cryptography, proof of work, and Merkle trees.
- 😀 Bitcoin’s architecture relies on public key cryptography to securely sign transactions and prove ownership without third-party intermediaries.
- 😀 Proof of work, introduced through projects like Hashcash, is the consensus mechanism that ensures the decentralization and security of Bitcoin.
- 😀 Merkle trees, a technology from time-stamping, allow Bitcoin’s blockchain to be tamper-proof by securely hashing data in blocks.
- 😀 Satoshi Nakamoto did not invent Bitcoin’s technologies but effectively combined existing innovations to create a decentralized, unstoppable system.
- 😀 Bitcoin’s rise was fueled by the philosophy of decentralization and privacy, rejecting the need for government approval or control over money.
Q & A
What is the central theme of the video script?
-The central theme of the video is the history and development of Bitcoin, focusing on its creation, the challenges faced in building a decentralized digital currency, and the role of the cypherpunks in shaping its foundation.
How does the script describe the origin of Bitcoin?
-The script explains that Bitcoin did not emerge out of nowhere but was the result of decades of prior work by visionaries and cryptographers. It highlights various digital cash projects that contributed to the development of Bitcoin, culminating in Satoshi Nakamoto’s creation of a decentralized, unstoppable currency.
What role did Douglas Jackson's company e-gold play in the evolution of digital currencies?
-Douglas Jackson’s e-gold was an early attempt at digital currency, using gold-backed tokens. However, the company was shut down by authorities due to concerns over money laundering and illegal activities, demonstrating the risks of centralization in digital cash systems. Bitcoin arose as a decentralized alternative to avoid such risks.
What was the primary issue that led to the downfall of e-gold?
-The primary issue that led to the downfall of e-gold was the government’s crackdown, citing concerns that it facilitated money laundering, fraud, and even the use by criminals. Despite Jackson’s claims of compliance and a solid fraud detection system, the company was targeted by law enforcement.
How does the script describe the influence of cypherpunks on Bitcoin's creation?
-Cypherpunks were crucial in developing the technologies that made Bitcoin possible. Their work on privacy, cryptography, and decentralized systems laid the foundation for Bitcoin, with their ethos of privacy and individual freedom being key influences on Bitcoin’s design.
What technological breakthroughs did Satoshi Nakamoto integrate to create Bitcoin?
-Satoshi Nakamoto combined several key technologies to create Bitcoin: public key cryptography for secure transactions, proof of work for consensus and scarcity, and Merkle trees for efficient data verification. These innovations, built upon earlier ideas, resulted in the creation of an unstoppable digital currency.
What is the significance of public key cryptography in Bitcoin?
-Public key cryptography is essential in Bitcoin for securely signing transactions. It ensures that only the rightful owner of Bitcoin can spend their coins, maintaining the integrity and security of the currency without the need for a trusted third party.
Why is proof of work important in Bitcoin’s operation?
-Proof of work is important in Bitcoin because it serves as both the consensus mechanism for verifying transactions and a way to introduce new coins into circulation. It ensures the network remains decentralized and secure, making it difficult for bad actors to manipulate the system.
What were some key projects that contributed to the development of Bitcoin?
-Key projects that contributed to Bitcoin’s development include eCash (which allowed private transactions), Hashcash (which introduced the concept of digital scarcity and proof of work), B-money (a decentralized currency idea), and Bitgold (a proof of work-based digital gold concept).
How did Bitcoin differ from earlier digital currencies like e-gold?
-Unlike e-gold, which was centralized and vulnerable to government control and shutdown, Bitcoin is decentralized, making it resistant to censorship or regulation. This key difference allowed Bitcoin to remain immune to the issues faced by earlier digital currencies like e-gold.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Where Did Bitcoin Come From? – The True Story

Sejarah Emas sebagai Uang Dunia (ringkasan 2500 tahun)

Origin and Evolution or History of Accounting

30 Fakta Negara Jepang yang perlu kamu ketahui!

Asal Usul Kota Wonogiri: Dari Hutan Belantara Hingga Kota Modern
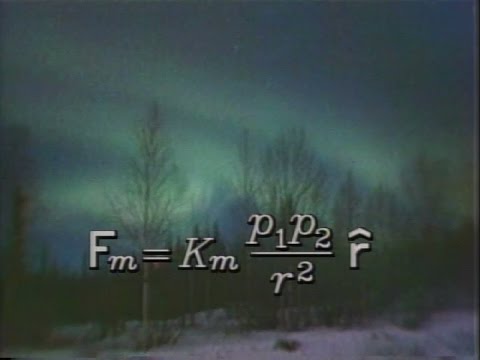
Episode 34: Magnetism - The Mechanical Universe
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)