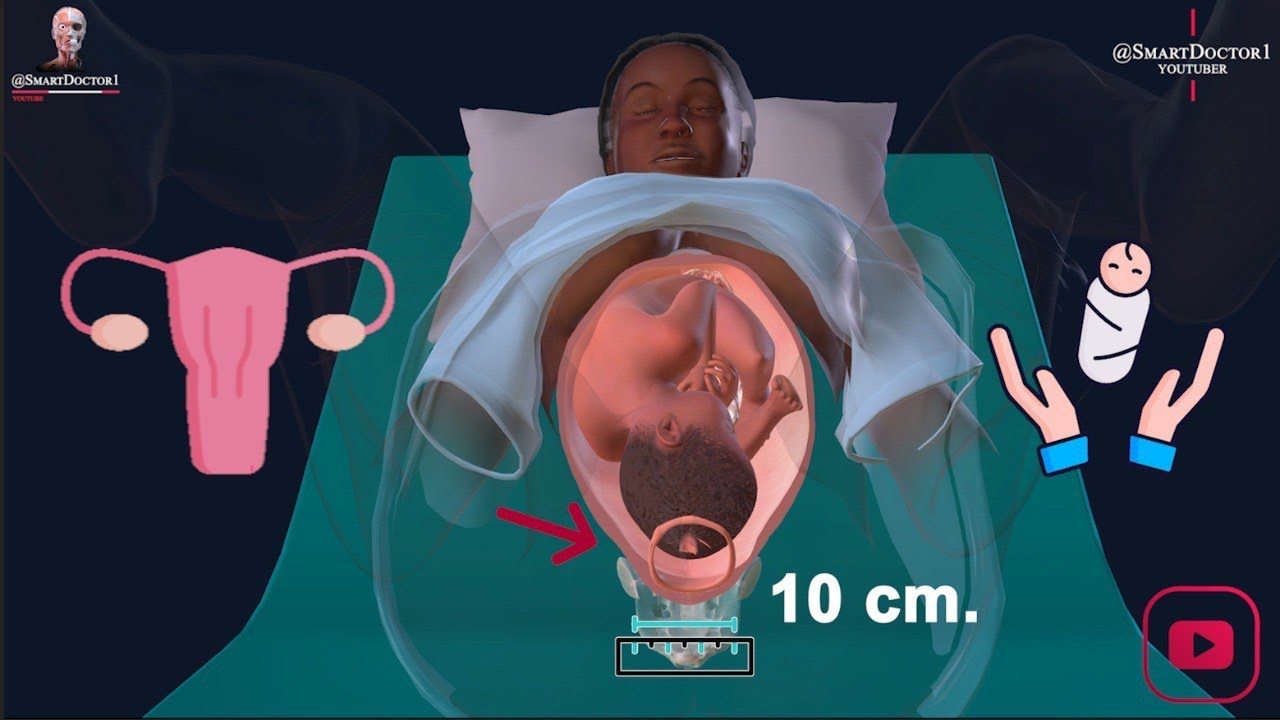
Obstetrics - Stage I of Labour
Summary
TLDRThis video provides an overview of stage one of labor, focusing on the anatomy of the fetus and the cervix, as well as the phases of labor. It explains the role of the amniotic sac, placenta, and umbilical cord, and discusses the process of cervical effacement and dilation. The video also covers spontaneous rupture of membranes (water breaking), artificial rupture, and premature rupture of membranes. It details the phases of labor, the timeline for dilation, and potential complications such as failure to progress, with a focus on differences between first-time and multi-parous women. The content serves as a general guide to the early stages of labor.
Takeaways
- 😀 Stage 1 of labor is divided into two phases: the latent phase (initial) and the active phase.
- 😀 The cervix undergoes effacement (thinning) and dilation during labor, allowing for the passage of the baby.
- 😀 The mucus plug, which forms during pregnancy, usually comes out when labor begins, and this is known as the 'show'.
- 😀 Contractions during labor are regular and painful, contributing to cervical dilation.
- 😀 Spontaneous rupture of membranes (water breaking) happens when the amniotic sac bursts during labor, releasing clear amniotic fluid.
- 😀 If the amniotic fluid is green or smelly, it indicates meconium, which can be harmful if aspirated by the fetus.
- 😀 Artificial rupture of membranes (amniotomy) can be performed by a doctor or midwife to help accelerate labor, but there are contraindications like breach presentation or placenta previa.
- 😀 Premature rupture of membranes (before 37 weeks) can occur and may require early delivery due to risks to the fetus.
- 😀 Crowning occurs when the baby's head is visible at the cervix, signaling the transition from the first to the second stage of labor.
- 😀 The first stage of labor can be long, especially for first-time mothers (nulliparas), and failure to progress may occur if dilation slows or stops.
- 😀 In multiparous women (those who've given birth before), labor tends to progress faster, with a faster rate of cervical dilation compared to first-time mothers.
Q & A
What is the first stage of labor, and how is it divided?
-The first stage of labor is the phase when the cervix dilates to 10 cm in preparation for delivery. It is divided into two phases: the initial (latent) phase and the active phase.
What are the key components of the anatomy of the fetus during pregnancy?
-The fetus is surrounded by the amniotic sac, which contains amniotic fluid. The placenta is connected to the fetus via the umbilical cord, providing nutrients and removing waste.
What role does the amniotic fluid play in pregnancy?
-Amniotic fluid protects the fetus, cushions it, and helps in the development of the lungs. Initially, the placenta produces this fluid, but later, the fetus contributes to it by peeing and swallowing the fluid.
What is the mucus plug, and what is its role during pregnancy?
-The mucus plug forms in the cervix due to estrogen production during pregnancy. It helps protect the uterus by blocking bacteria from entering the cervix.
What is the 'show' in relation to labor, and what does it signify?
-The 'show' refers to the clear, mucoid-like discharge that occurs when the mucus plug is expelled. It is a sign that labor is approaching.
What is the significance of the rupture of membranes during labor?
-The rupture of membranes, or water breaking, happens when the amniotic sac breaks during labor, releasing amniotic fluid. This is a sign that labor is progressing. If the fluid is green or has an odor, it may indicate meconium, which can pose a risk to the fetus.
What is spontaneous rupture of membranes, and what is its potential timing?
-Spontaneous rupture of membranes occurs naturally, either before labor begins or during labor. The amniotic sac bursts, releasing fluid.
What is an artificial rupture of membranes (amniotomy), and when might it be used?
-An amniotomy is the artificial rupture of the amniotic sac by a doctor or midwife using a small hook. It is used to induce or accelerate labor, but it is contraindicated in certain conditions such as breech presentation or placental previa.
What is premature rupture of membranes (PROM), and how does it differ from a typical rupture?
-Premature rupture of membranes occurs when the amniotic sac ruptures before 37 weeks of pregnancy, which can lead to preterm birth. This differs from a typical rupture, which occurs after 37 weeks.
How does the duration of the first stage of labor differ between nulliparous and multiparous women?
-For nulliparous women (first-time mothers), the initial phase of labor should ideally last less than 20 hours, while for multiparous women (those with previous births), it is usually less than 14 hours.
What is failure to progress in labor, and how is it addressed?
-Failure to progress occurs when labor is not advancing as expected, either in cervical dilation or contraction intensity. This can be identified in both the initial and active phases, and interventions may be needed to assist labor, particularly if cervical dilation is too slow.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)