Rotary Drilling Fluids, Part II Water Base Muds
Summary
TLDRThis video script explains the fundamentals of rotary drilling fluids, focusing on water-based muds. It covers the composition and types of drilling fluids, including water, active solids (like bentonite), and inert solids (like barite), and their roles in maintaining viscosity, gel strength, and filtration control. The script also discusses the impact of various water types, such as fresh, hard, and saltwater, on mud properties. Further, it addresses the chemistry of clay hydration, the use of additives to manage drilling conditions, and methods to keep solids content low, ensuring effective and stable drilling operations.
Takeaways
- 😀 Drilling fluids, also known as drilling muds, are essential for rotary drilling, performing tasks like cooling the bit, stabilizing the hole, and carrying away cuttings.
- 😀 Water-based muds (WBMs) are the most common type, consisting of three phases: water, active solids, and inert solids.
- 😀 Active solids like bentonite react with water to increase viscosity and provide suspension properties in the mud.
- 😀 Inert solids, such as barite, are used to increase the mud's density but do not react chemically with the water.
- 😀 Freshwater, seawater, and hard water are the primary types of water used in drilling fluids, each affecting the mud properties differently.
- 😀 Saltwater muds are used in specific conditions, like drilling in salt zones, where they prevent clay swelling and maintain hole stability.
- 😀 Freshwater muds can be untreated (spud muds), chemically treated, or calcium-treated, with each type serving different purposes based on the formation and drilling environment.
- 😀 Bentonite clay swells in freshwater to form a viscous gel, but calcium-based clays, like montmorillonite, do not swell as much, resulting in lower viscosity.
- 😀 Flocculants and large settling pits are used to keep water-based muds with low solids content, facilitating better drilling and hole stability.
- 😀 Proper management of mud properties like viscosity, gel strength, and filtration control is critical for efficient drilling and maintaining both hole and mud stability.
Q & A
What are the primary components of water-based mud in drilling?
-Water-based muds consist of three main components: the water phase, active solids (like bentonite), and inert solids (such as barite). These elements work together to create a stable drilling fluid that aids in the drilling process.
How does the type of water used affect the mud properties?
-The type of water used significantly affects mud properties like viscosity and filtration control. Freshwater, seawater, and saltwater differ in their composition and the way they hydrate clay, impacting the mud's performance during drilling.
What is the role of active solids in water-based mud?
-Active solids, such as bentonite, are responsible for building viscosity and gel strength in the mud. They react with the water phase, creating a thickening effect that helps carry cuttings to the surface and provides stability during drilling.
Why is barite used in drilling fluids?
-Barite is used in drilling fluids to increase the density of the mud. It is a heavy inert solid that doesn't react chemically with the other components but helps adjust the mud weight, which is crucial for controlling pressure in the well.
What are the differences between saltwater muds and freshwater muds?
-Saltwater muds are used when drilling in formations with high salt content. They have inhibitive properties due to dissolved salts that prevent clay swelling. Freshwater muds, on the other hand, may require chemical treatments for effective performance in various formation types.
What is the function of calcium compounds in water-based mud?
-Calcium compounds, particularly calcium chloride, are added to freshwater muds to inhibit the swelling of clay particles. This is particularly important in preventing issues when drilling through shale or other formations that contain reactive clays.
How do flocculants and settling pits help in low solids mud?
-Flocculants are chemicals added to low solids mud to encourage the clumping together of fine solids, making them easier to settle in large settling pits. This helps maintain a low solids content in the mud, ensuring efficient drilling and proper mud properties.
What is the role of shale inhibitors in water-based mud?
-Shale inhibitors, like calcium compounds, are used to prevent the hydration and swelling of shale formations that may be encountered while drilling. These inhibitors help maintain wellbore stability and prevent the mud from losing its effectiveness in challenging formations.
What is the significance of viscosity in drilling fluids?
-Viscosity is crucial in drilling fluids as it determines the fluid's ability to carry cuttings to the surface. Higher viscosity helps suspend solid particles, while lower viscosity ensures the mud flows smoothly and circulates effectively in the wellbore.
What is the importance of selecting the right mud type for drilling operations?
-Choosing the right mud type is essential for maintaining wellbore stability, controlling pressure, and ensuring efficient cuttings removal. The mud must be able to adapt to different formation types and conditions, ensuring that drilling can be done safely and at minimal cost.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Rotary Drilling Fluids, Part III Oil Muds

Pemboran Minyak dan Gas Bumi

PENYELIDIKAN TANAH : part2 - Teknik Pengeboran dan Pengambilan Contoh Tanah [masdosen]

Estática de Fluidos - Parte 1
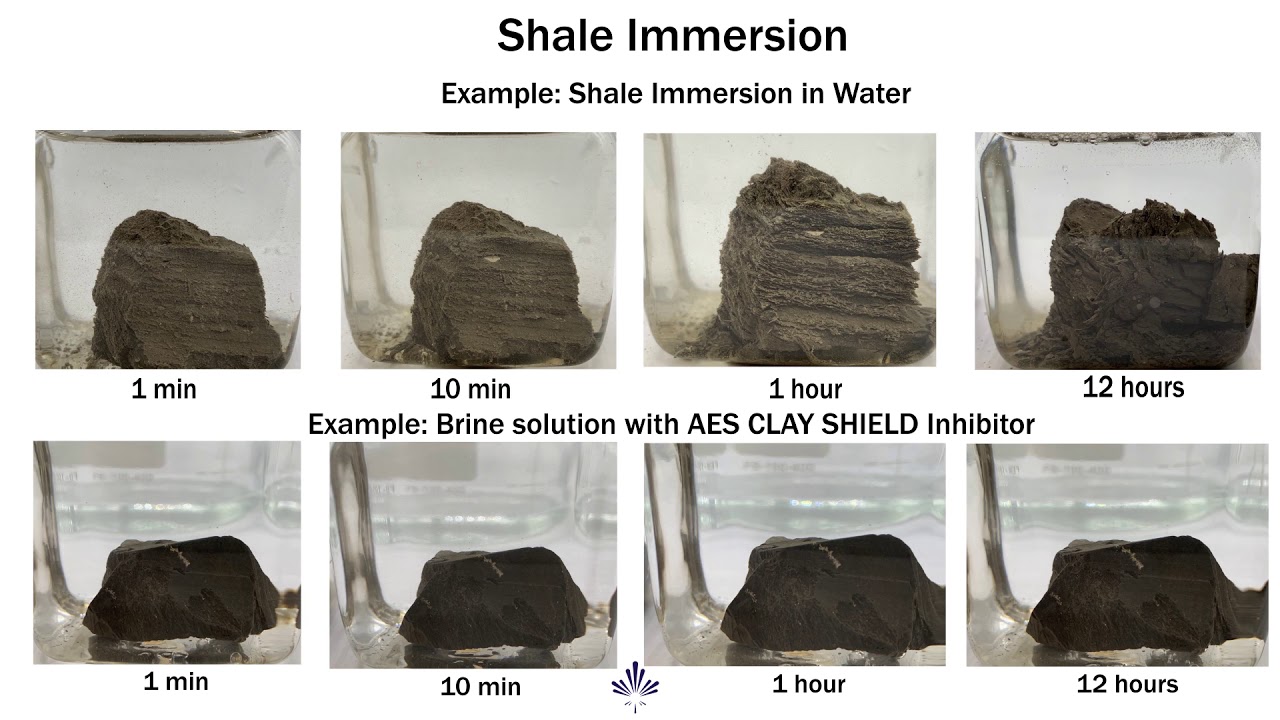
AES Tech Tip 3: Shale Inhibition and Testing

FISIOLOGÍA DE LÍQUIDOS CORPORALES 1: Líquido intracelular y extracelular, osmolaridad y tonicidad
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)