Sistema Excretor (URINÁRIO) - Aula 30 - Módulo 7: Fisiologia Humana
Summary
TLDRThis video delves into the fascinating workings of the human urinary system, focusing on how the kidneys filter blood, regulate pH, and maintain fluid and electrolyte balance. It explains the role of nephrons in waste excretion, reabsorption, and hormone regulation, such as aldosterone and ADH. Additionally, the video touches on how urine color can indicate health status. With a final reflective note encouraging viewers to embrace new experiences in life, the video combines educational insights with a motivational message, making complex biological processes more relatable and engaging.
Takeaways
- 😀 The main focus of the video is on understanding the urinary system, particularly the role of the nephron in filtering and reabsorbing substances from the blood.
- 😀 The nephron is composed of several segments, each playing a unique role in filtration and reabsorption, including the proximal convoluted tubule, loop of Henle, distal convoluted tubule, and collecting duct.
- 😀 The proximal convoluted tubule (PCT) is where the majority of nutrient reabsorption occurs, especially glucose, amino acids, and essential ions like sodium.
- 😀 The loop of Henle plays a critical role in water reabsorption and establishing a concentration gradient in the kidney, helping to maintain water balance in the body.
- 😀 The distal convoluted tubule (DCT) is involved in regulating electrolyte balance, including the reabsorption of sodium and potassium.
- 😀 In the DCT and the collecting duct, the excretion of excess hydrogen ions (H+) helps to regulate blood pH, maintaining homeostasis.
- 😀 Hormonal regulation within the nephron is crucial, particularly through aldosterone, which helps with sodium reabsorption, and ADH (antidiuretic hormone), which plays a role in water retention.
- 😀 The final composition of urine includes water, urea, excess salts, hydrogen ions (H+), and various metabolites that the body needs to eliminate.
- 😀 The importance of maintaining pH balance in the blood is emphasized, as excessive H+ in the blood indicates acidosis, which the body combats by excreting H+ ions in the urine.
- 😀 The script encourages taking time to break from routine and explore new experiences to refresh and reignite curiosity, similar to how children experience life with wonder and discovery.
Q & A
What is the primary function of the renal tubules?
-The primary function of the renal tubules is to filter and reabsorb substances from the blood, while also secreting unwanted metabolites and maintaining fluid and electrolyte balance.
What happens in the proximal convoluted tubule?
-In the proximal convoluted tubule, the majority of the filtered nutrients, such as glucose, amino acids, and electrolytes, are reabsorbed into the bloodstream.
What role does the loop of Henle play in urine formation?
-The loop of Henle plays a critical role in concentrating urine by creating a high osmolarity in the medulla of the kidney, allowing for water reabsorption in the collecting ducts.
How does the distal convoluted tubule contribute to maintaining blood pH?
-The distal convoluted tubule helps regulate blood pH by secreting hydrogen ions (H+) into the urine, thus reducing the acidity of the blood when necessary.
What is the function of aldosterone in the renal system?
-Aldosterone is a hormone that promotes the reabsorption of sodium (Na+) and water in the kidneys, which helps regulate blood pressure and fluid balance.
How does antidiuretic hormone (ADH) affect water reabsorption in the kidneys?
-ADH promotes the reabsorption of water from the filtrate in the collecting ducts, which helps to conserve water in the body, especially when dehydrated.
What substances are typically found in urine?
-Urine typically contains water, urea (a nitrogenous waste), hydrogen ions (H+), various metabolites, and excess salts or electrolytes that the body needs to excrete.
What is the significance of the 'countercurrent multiplier' system in the kidneys?
-The countercurrent multiplier system, particularly in the loop of Henle, creates a concentration gradient that allows for efficient water reabsorption and helps produce concentrated urine.
What metabolic byproducts might be found in urine as a result of medications?
-Medications like antibiotics or alcohol can lead to the production of metabolic byproducts, which may be excreted in the urine as waste products.
How do the kidneys contribute to maintaining the body's electrolyte balance?
-The kidneys help maintain electrolyte balance by selectively reabsorbing or excreting sodium, potassium, calcium, and other ions, depending on the body's needs.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
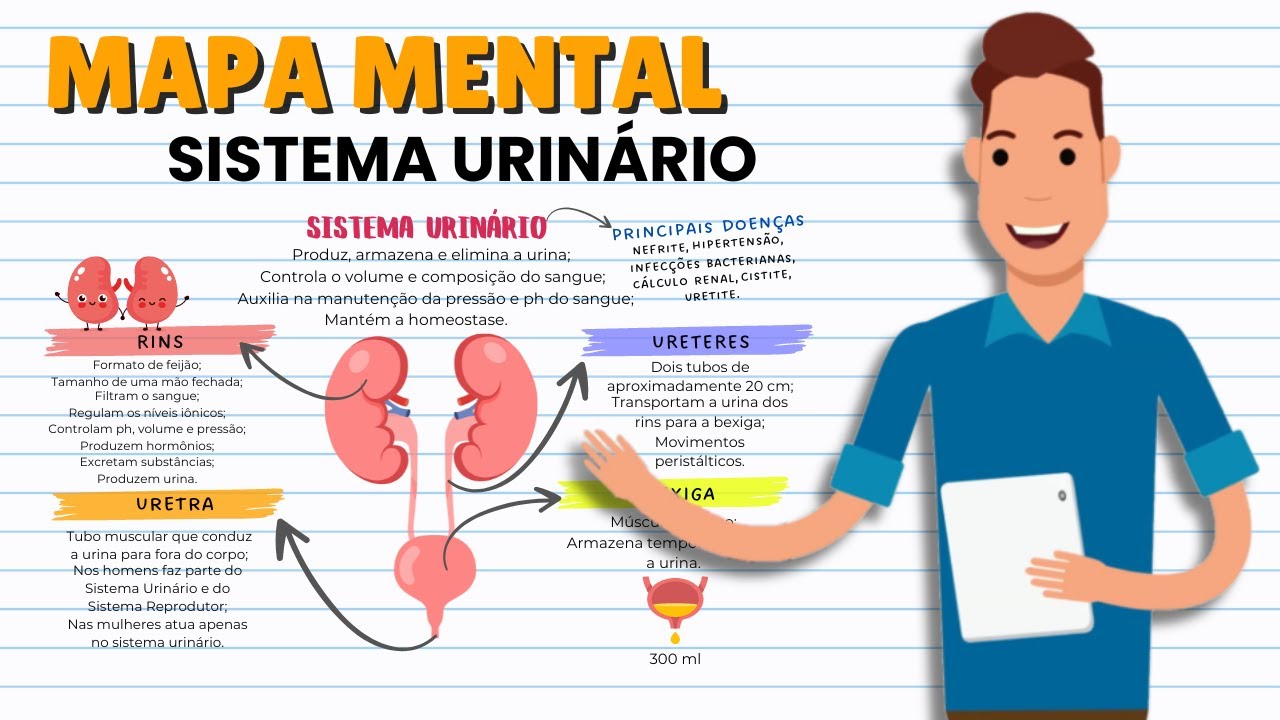
MAPA MENTAL SIMPLIFICADO DO SISTEMA URINÁRIO

TEAS Science Review: Urinary system [Higher volume]

PROSES BERKEMIH PADA SISTEM PERKEMIHAN MANUSIA

Anatomi Fisiologi Sistem Perkemihan

Hormones in body fluid homestasis (ADH/vasopressin, Aldosterone and Natriuretic peptides)
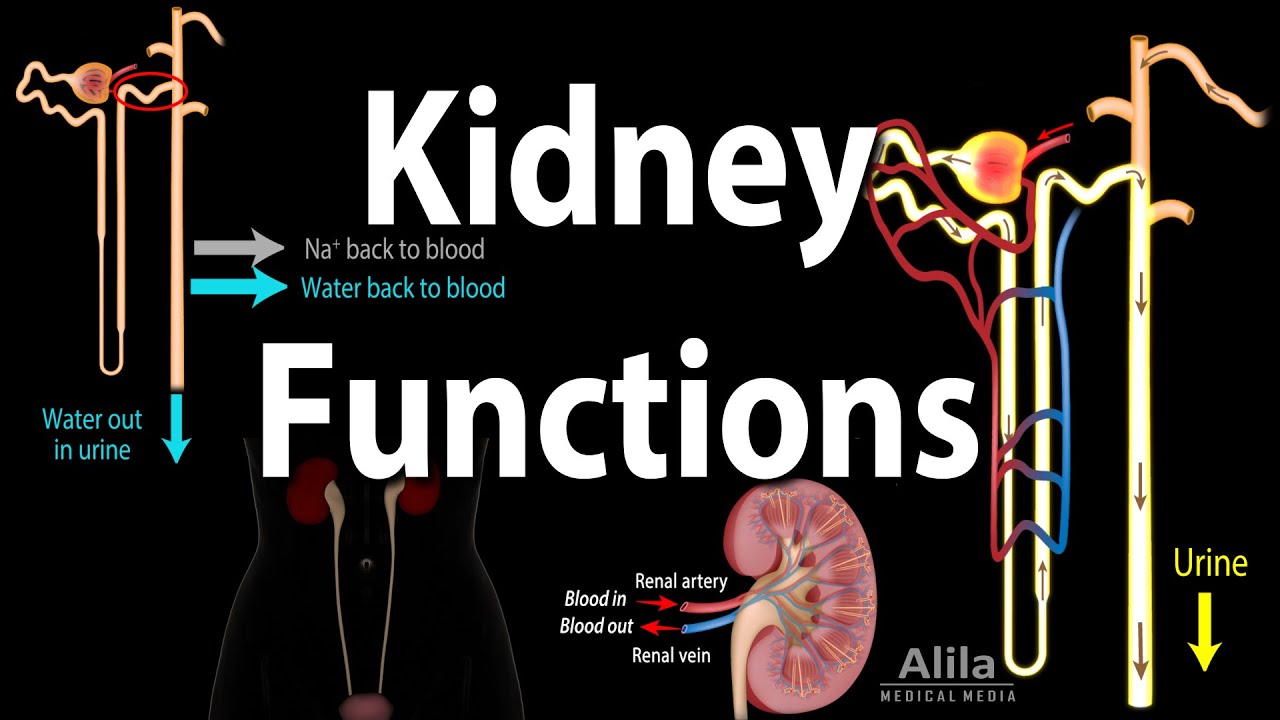
Kidney Homeostatic Functions, Animation
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)