Prototyping and Model Making - Students of Product Design Episode 5
Summary
TLDRThis video emphasizes the importance of prototyping in the design process, highlighting how prototypes help test ideas, uncover problems, and refine concepts. It explores different types of prototypes, including visual appearance models and functional prototypes, and the significance of rapid prototyping. The video also emphasizes that prototyping doesn’t require expensive materials or tools, encouraging creativity with found objects. With personal anecdotes and examples, the speaker stresses the value of testing prototypes early and frequently, learning from mistakes, and being resourceful in the design journey.
Takeaways
- 😀 Prototyping is essential to the design process, as it helps test ideas, prove concepts, and identify problems early.
- 😀 A good prototype is not defined by its aesthetics or quality of construction but by how effectively it answers key questions and advances the project.
- 😀 Prototypes, even if they fail, offer valuable insights that can improve the design and guide future iterations.
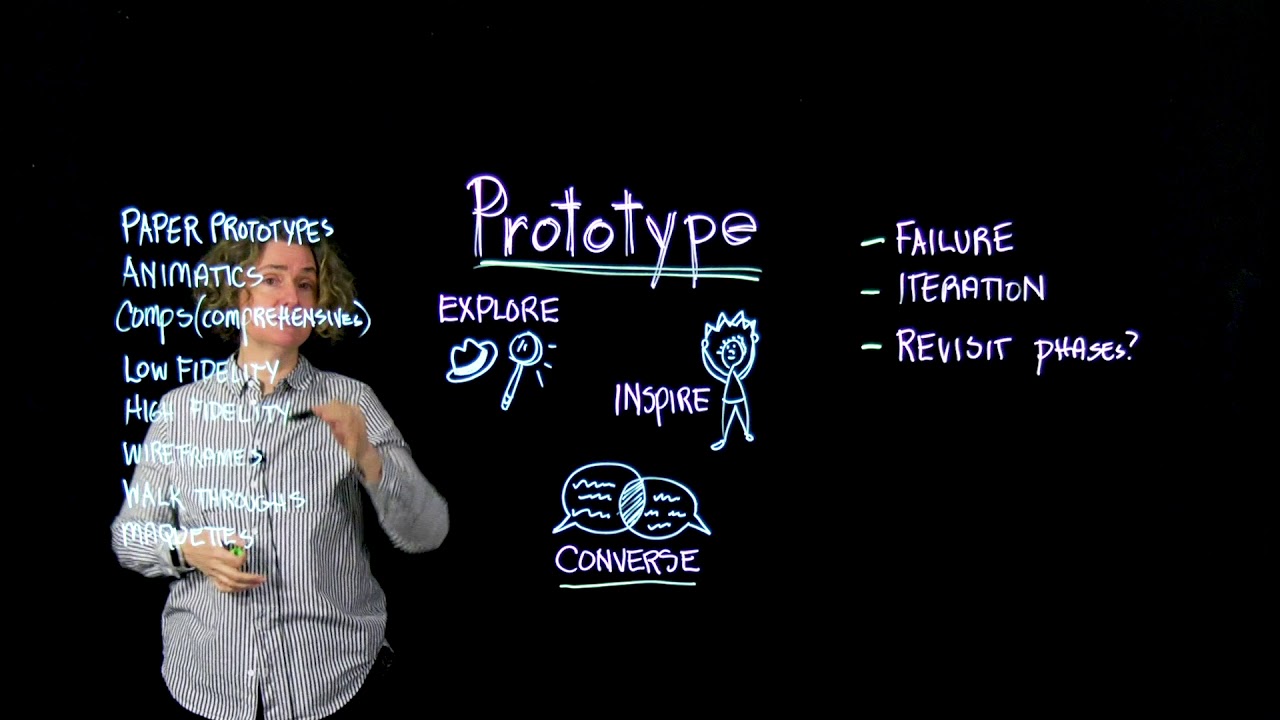
- 😀 There is a difference between a model (a visual representation of a design) and a prototype (a functional test of the design's mechanism). Both are needed in the design process.
- 😀 Rapid prototyping can be a useful tool for creating designs quickly, but it is not always cost-effective or practical for larger projects.
- 😀 The initial prototypes should be simple and quick to create in order to assess whether a concept is worth further development.
- 😀 Using cheap, readily available materials like cardboard, paper, or even everyday objects can help save time and money in early prototyping stages.
- 😀 Salvaging materials from discarded items, like old machines or office supplies, can provide both cost-effective resources and valuable learning opportunities about manufacturing processes.
- 😀 Prototypes should be tested by a variety of users (different ages, sizes, etc.) to uncover usability issues and ensure the design works for a wide audience.
- 😀 Don't be afraid to jump straight into making prototypes—it's an essential part of the design process that often leads to unexpected breakthroughs.
Q & A
Why are prototypes important in design projects?
-Prototypes are crucial because they help designers test ideas, prove concepts, and identify problems early. Without prototypes, it's difficult to assess how a design will function, and issues may not surface until the later stages, potentially causing costly errors or project delays.
What is the difference between a model and a prototype?
-A model primarily represents the visual appearance of a design, often scaled down, while a prototype demonstrates how the design works. Prototypes may not always look like the final product, but they are used to test the functionality and feasibility of the design.
What should designers focus on when creating prototypes?
-Designers should focus on creating prototypes that answer key questions and move the project forward. This includes identifying functional issues, testing user interactions, and exploring different design aspects, rather than solely focusing on aesthetics or perfection.
Why is it important to test prototypes with real users?
-Testing prototypes with a diverse group of real users—different ages, hand sizes, and other variables—helps identify problems and areas for improvement. It's essential because the design is ultimately for the users, not the designer themselves.
What are the two main types of product design positions?
-The two main types of product design positions are in-house designers, who work within companies that manufacture products, and design consultants, who work on a contract basis for various companies.
Why are rapid prototyping methods not always ideal?
-Rapid prototyping is not always cost-effective or practical, especially for large designs. Many companies only have access to small machines, which limits their ability to prototype larger products efficiently. Additionally, the process can be expensive depending on the design.
What is the benefit of using fast and inexpensive materials for early prototypes?
-Using fast and inexpensive materials allows designers to quickly test and validate ideas without investing too much time or money. This approach helps in identifying feasible design directions early, and can save significant resources down the line.
How can taking things apart help in the prototyping process?
-Disassembling old objects can provide valuable materials for prototyping, and offers insights into how things are constructed. This hands-on learning can inform better design choices and enhance a designer's understanding of mechanical systems.
Why is it important to not focus solely on a product's visual appearance in early prototyping?
-Focusing only on appearance in the early stages can lead to overlooking critical functional issues. It’s more important to understand how the product works and behaves before refining its visual details.
What was James Dyson's experience with prototyping, and how does it relate to the prototyping process?
-James Dyson created over 5,000 prototypes before getting his first bagless vacuum cleaner right. His experience highlights the value of persistence and the need for multiple iterations in the prototyping process, where each failure is an opportunity to learn and improve the design.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)