KEHIDUPAN MANUSIA PURBA DAN ASAL USUL NENEK MOYANG - SEJARAH INDONESIA KELAS X
Summary
TLDRThis video lesson provides an in-depth exploration of early human life in Indonesia, focusing on prehistoric humans and the origins of the Indonesian people. It covers various types of prehistoric humans, such as Meganthropus Paleojavanicus, Pithecanthropus, and Homo sapiens, alongside their physical and cultural characteristics. The video also delves into the origins of the Indonesian ancestors, discussing theories from scholars about their migration and the cultural significance of the Austronesian people. Key insights include the development of early tools, languages, and maritime culture in Southeast Asia, highlighting the importance of this knowledge in understanding modern Indonesia.
Takeaways
- 😀 Prehistoric humans in Indonesia are studied through fossils and artifacts like tools, weapons, and jewelry.
- 😀 The goal of the lesson is to compare prehistoric humans' physical and non-physical characteristics and understand the origins of Indonesia's ancestors.
- 😀 Fossils provide insights into prehistoric humans, including Meganthropus Paleojavanicus, Pithecanthropus, and various Homo species.
- 😀 Meganthropus Paleojavanicus, found in Java, is the oldest and largest prehistoric human species, with distinct physical features like a massive jaw and large teeth.
- 😀 Pithecanthropus Erectus, discovered by Eugène Dubois in 1891, is considered a significant species in the development of modern humans.
- 😀 Homo Wajakensis, Homo Soloensis, and Homo Sapiens represent more recent stages of human evolution, with larger brain volumes and features resembling modern humans.
- 😀 Theories about the origins of Indonesia's ancestors include the Austronesian theory (Sangkot Marzuki), the Asia Central theory (Van Heine-Golden), and the Indian theory (Mayundar).
- 😀 The Austronesian theory suggests that the ancestors of the Indonesian people came from the Austronesian region and spread through Southeast Asia.
- 😀 Proto-Malayans, the early wave of Malay people, arrived in Indonesia around 1500 BCE, bringing Neolithic culture with tools made from polished stone.
- 😀 Deutro-Malayans, the second wave of Malay migrants, came around 400-300 BCE, bringing more advanced cultural artifacts, such as bronze and iron tools.
- 😀 Before the arrival of Malayans, early primitive groups like the Wedoid and Negroid lived in Indonesia with simple cultures and nomadic lifestyles.
Q & A
What are the two main methods used to discover prehistoric human life in Indonesia?
-The two main methods are: 1) through fossils of humans, plants, and animals that have fossilized over time, and 2) through artifacts such as tools, household items, buildings, and weapons left by prehistoric humans.
What is the significance of the discovery of Meganthropus Paleojavanicus?
-Meganthropus Paleojavanicus, discovered between 1936-1941, is significant because it represents one of the earliest forms of human-like species in Indonesia, with large jaws, thick skulls, and a robust chewing structure.
What are the physical characteristics of Pithecanthropus Mojokertensis?
-Pithecanthropus Mojokertensis is characterized by a thick and prominent brow, no chin, and strong jawbones. Its fossils were discovered in 1891 by Eugene Dubois.
How does Homo sapiens differ from earlier prehistoric human species in terms of physical and cultural development?
-Homo sapiens, the modern human species, differs by having a much larger brain volume (1300-1600 cc), a more advanced body structure, and higher cognitive abilities. They developed complex tools, art, and culture, unlike earlier species such as Pithecanthropus and Meganthropus, which had simpler tools and less advanced physical traits.
What is the theory of Austronesian migration and how does it relate to the origins of the Indonesian people?
-The theory of Austronesian migration, proposed by Professor Sangkot Marzuki, suggests that the ancestors of the Indonesian people came from the Austronesian homeland in Sunda Land, based on DNA fossil studies. This theory challenges the earlier belief that Indonesians originated from Yunnan.
What is the main idea behind the theory proposed by Van Heine Golden regarding the origins of the Indonesian people?
-Van Heine Golden's theory suggests that the Indonesian people originated from Central Asia, supported by cultural similarities in artifacts found in both Indonesia and Central Asia. He believes that the ancient people from this region migrated to Southeast Asia and the Indonesian archipelago.
What evidence supports the theory that Indonesian ancestors came from India?
-The theory proposed by Mayundar states that the Indonesian ancestors originated from India, based on linguistic evidence, particularly the Austronesian languages, which are considered a young language family in Eastern India. This theory suggests that the migration happened through Indochina to the Indonesian islands.
Who are the Proto-Malay and Deutero-Malay, and how do they differ?
-The Proto-Malay, or 'Old Malay' people, were the first to migrate to the Indonesian archipelago and arrived around 1511 CE. They brought with them a Neolithic culture, characterized by stone tools. The Deutero-Malay, or 'New Malay', arrived later, around 400-300 BCE, and brought advanced metallurgy, such as the production of bronze and iron tools.
How did early human migration patterns affect the development of the Indonesian culture?
-Early human migrations, particularly the movements of Proto-Malay and Deutero-Malay groups, led to the spread of different cultural practices, technologies, and languages throughout the Indonesian archipelago. These migrations facilitated the development of a diverse yet interconnected cultural heritage, seen in the distinct but related linguistic, agricultural, and metallurgical advancements.
What evidence do we have of primitive human groups, like the Wedoid and Negroid, in Indonesia?
-The Wedoid group, which still exists in regions like Siak and Jambi, practiced a simple culture based on foraging and gathering forest products. The Negroid group, which no longer exists in Indonesia, is believed to have contributed to the early human populations of Southeast Asia, with surviving descendants in Malaysia and the Philippines, such as the Semang and Negrito tribes.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

JENIS-JENIS MANUSIA PURBA || SEJARAH INDONESIA KELAS 10 (SEPULUH) #4

Penelitian Manusia, Budaya, dan Lingkungan pada Masa Prasejarah di Gua Lawa, Sampung, Jawa Timur
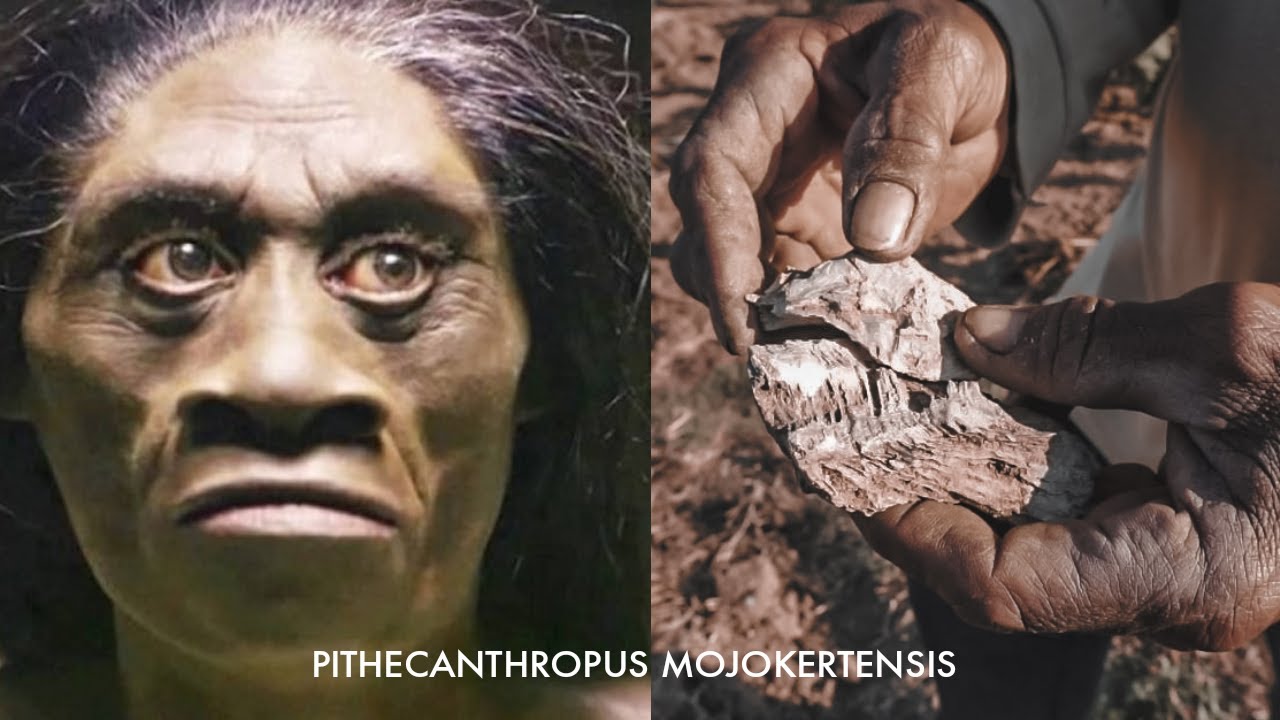
Ternyata Begini Jejak Manusia Purba PITHECANTHROPUS MOJOKERTENSIS Manusia Kera Dari Mojokerto

Kelas X - Manusia Purba di Indonesia | Sejarah Indonesia

Materi Masa Berburu dan Mengumpulkan Makanan / Sejarah Indonesia

Prehistory in India : Palaeolithic Period - I
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)