Types of pump | Working methods
Summary
TLDRThis video provides an in-depth exploration of pumps, detailing their purpose, components, and classifications. Pumps are essential devices used to move liquids and gases across systems, with two main categories: Dynamic Pressure Pumps, which use rotating impellers to accelerate fluid, and Positive Displacement Pumps, which trap and force a fixed volume of fluid. The video further breaks down these categories into subtypes like centrifugal, diaphragm, and gear pumps, explaining their operations and applications. It also covers key components, such as impellers, motors, and valves, while highlighting the importance of specifications and energy sources for pump systems.
Takeaways
- 😀 Pumps are essential for transferring and distributing fluids or gases through mechanical action.
- 😀 The two main purposes of pumps are to transfer liquids between locations and to circulate liquids within systems, such as cooling and lubricants.
- 😀 A pumping system typically consists of components like pump casing, impellers, prime movers (e.g., motors, engines), piping, valves, and control instrumentation.
- 😀 Pumps are broadly classified into Dynamic Pressure Pumps and Positive Displacement Pumps based on their operating principles.
- 😀 Dynamic Pressure Pumps, such as centrifugal pumps, use rotational energy from impellers to accelerate fluids, typically in systems with low to moderate pressure and viscosity.
- 😀 Centrifugal pumps are the most common type of dynamic pressure pump and work by converting kinetic energy into hydrodynamic energy.
- 😀 Positive Displacement Pumps trap a fixed amount of fluid and force it through the system, providing consistent flow regardless of pressure changes.
- 😀 Reciprocating Positive Displacement Pumps use pistons, plungers, or diaphragms to move fluid, often used in high-pressure, small-volume applications.
- 😀 Rotary Positive Displacement Pumps, like gear pumps and screw pumps, use rotating elements to transfer fluid, commonly seen in hydraulic systems and metering applications.
- 😀 Specific types of pumps like jet pumps and electromagnetic pumps use unique mechanisms, such as high-speed jets or electromagnetic fields, for fluid movement in specialized applications.
- 😀 Different types of pumps are suited for specific tasks, such as centrifugal pumps for low-viscosity fluids and positive displacement pumps for high-viscosity, high-pressure fluids.
Q & A
What are the two main purposes of a pump?
-The two main purposes of a pump are to transfer liquids or gases from one place to another and to circulate fluids around a system, such as cooling water or lubricants in machinery.
What are the primary components of a pumping system?
-A typical pumping system consists of a pump casing, impellers, prime movers (like electric motors or diesel engines), piping, valves, and other fittings for flow control and instrumentation.
How are pumps broadly classified?
-Pumps are broadly classified into two categories: Dynamic Pressure Pumps and Positive Displacement Pumps.
What is the operating principle of dynamic pressure pumps?
-Dynamic pressure pumps work by imparting tangential force through rotating impellers, which accelerates the fluid, creating motion that drives the fluid from the pump.
What are the main types of centrifugal pumps?
-Centrifugal pumps are divided into three main types: Axial Flow, Mixed Flow, and Peripheral Centrifugal Pumps.
How does a mixed flow centrifugal pump differ from an axial flow pump?
-A mixed flow centrifugal pump combines characteristics of both axial and radial flow pumps, with impeller blades that send liquid at an angle larger than 90 degrees from the pump shaft, unlike axial flow pumps which move fluid in a straight path along the axis.
What are special effect pumps, and how do they work?
-Special effect pumps, like jet and electromagnetic pumps, use principles other than centrifugal force. Jet pumps create a high-speed fluid jet to induce flow, while electromagnetic pumps use electromagnetism to move conductive liquids like molten metal.
What distinguishes positive displacement pumps from dynamic pressure pumps?
-Positive displacement pumps move fluid by trapping a set volume and forcing it through the system, providing consistent flow regardless of pressure. In contrast, dynamic pressure pumps accelerate fluid using impellers and vary their flow based on system pressure.
What are the key types of reciprocating pumps?
-The main types of reciprocating pumps are piston pumps, plunger pumps, and diaphragm pumps, each utilizing different mechanisms like pistons or diaphragms to move fluid.
How do rotary pumps differ from reciprocating pumps?
-Rotary pumps use rotating elements (such as gears or screws) to continuously move fluid, while reciprocating pumps use back-and-forth motion (e.g., pistons or diaphragms) to create fluid flow.
What are the main types of rotary pumps and their applications?
-The main types of rotary pumps are gear pumps, screw pumps, lobe pumps, and vane pumps. Gear pumps are commonly used in hydraulic systems, screw pumps are suitable for metering, lobe pumps are used in applications requiring precise flow, and vane pumps are used in high-pressure systems.
What specifications are used to rate pumps?
-Pumps are typically rated by their volumetric flow rate, horsepower, suction head, discharge pressure, and energy source, which may include wind power, manual operation, electricity, or engines.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Centrifugal Pump Basics I Definition I Working I Velocity Triangle I Work Done I Head I Efficiency

Introdução aos Estudos Epidemiológicos - Resumo - Epidemiologia
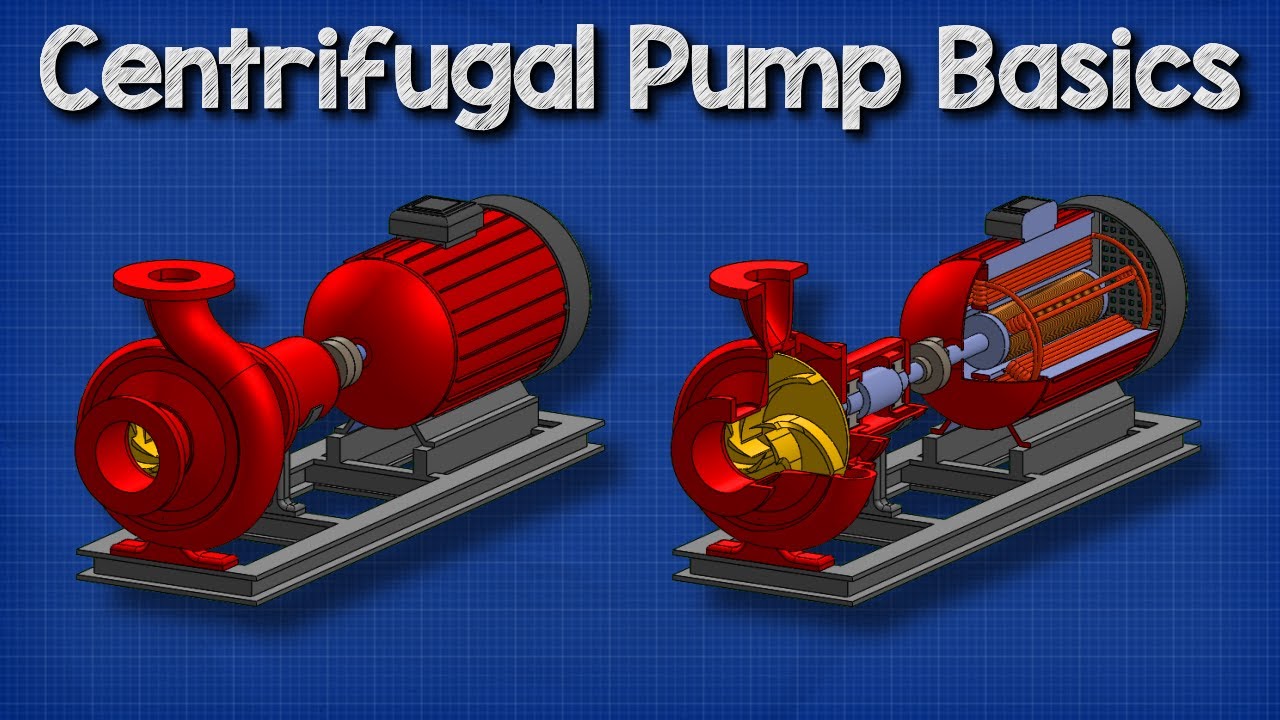
Centrifugal Pump Basics - How centrifugal pumps work working principle hvacr

26. CAMBRIDGE IGCSE (0478-0984) 3.1 Purpose of the components in a CPU

What is Research ? - Nature, Definition and Concept of Research - Practical Research Guide

Cargo Handling & Stowage | Cargo Crane
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)