Teori Pergerakan Lempeng Tektonik di Indonesia. Selalu Ada Kemudahan Setelah Kesulitan
Summary
TLDRSoutheast Asia's unique geography is shaped by geological processes over millions of years, as discussed in research by a team from Oxford University. The region, comprising islands like Sumatra and Papua, was once part of a larger landmass that gradually submerged and emerged due to tectonic activity. Around 10 million years ago, it began to resemble its current form, but the seas were different 18,000 to 20,000 years ago when the Sunda Shelf connected several islands. This transformation was driven by climatic changes and geological forces, influencing both the land and the migration of early human civilizations in the area.
Takeaways
- 🌏 Southeast Asia is characterized by its unique geological formation, including the Malay Peninsula and the Nusantara archipelago.
- 📜 The region's current shape is the result of geological processes occurring over hundreds of millions of years.
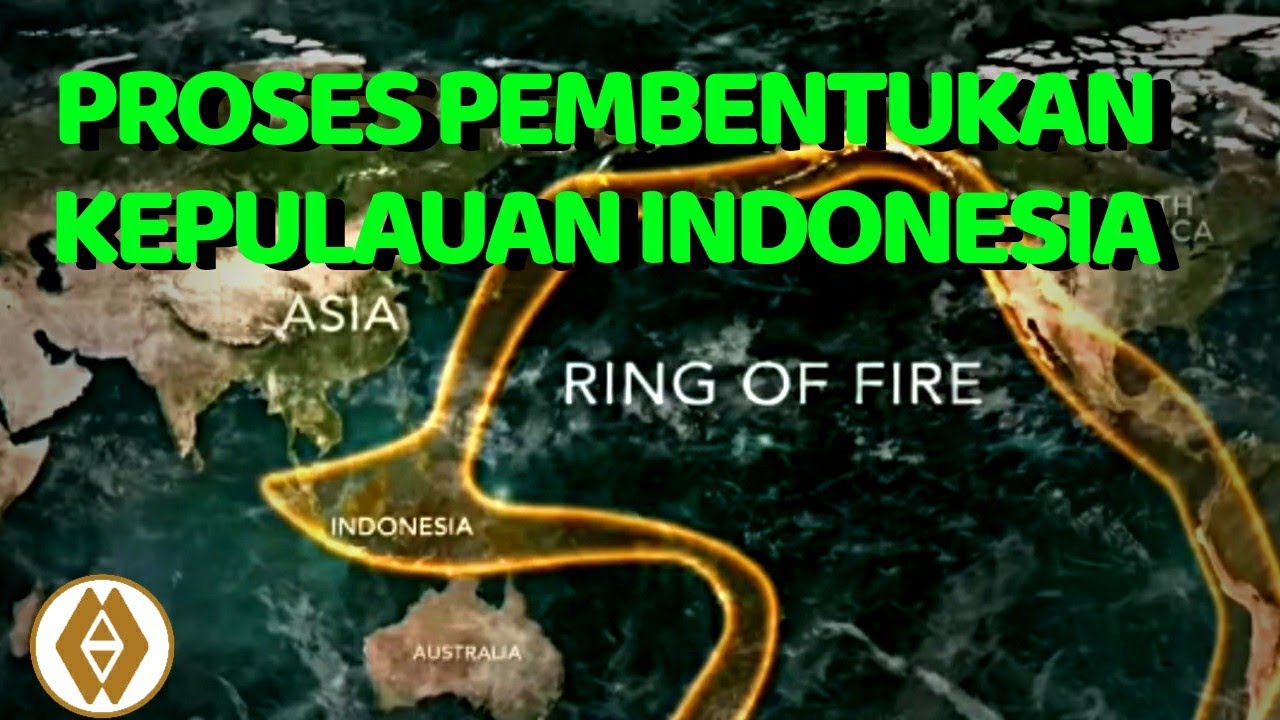
- 🔍 Research from Oxford University outlines how plate tectonics have shaped Southeast Asia's landscape.
- 🦖 Fossil discoveries in the region mostly reveal ancient marine species rather than terrestrial dinosaurs, due to its geological evolution.
- 🌊 The Sundaland Shelf, which once connected islands like Borneo and Java, submerged around 18,000 to 20,000 years ago as sea levels rose.
- 🏞️ During the Ice Age, a cooler climate led to lower sea levels and the emergence of ancient rivers on the Sundaland Shelf.
- 👣 Human migration into Southeast Asia was facilitated by land bridges formed during lower sea levels in ancient times.
- 🌡️ The region's current geography has been influenced by both natural earth processes and climatic changes over millennia.
- 🔄 Plate tectonics continue to play a vital role in the ongoing geological evolution of Southeast Asia.
- 🌊 Understanding paleogeology and paleoclimatology is essential to comprehending the region's natural history and formation.
Q & A
What geological processes shaped Southeast Asia's unique structure?
-The unique structure of Southeast Asia was shaped by geological processes involving the movement of tectonic plates over hundreds of millions of years.
How does the position of Southeast Asia relate to the equator?
-Southeast Asia is located under the equator due to the geological movements of the Earth's plates, which have altered its position over time.
What significant geological event occurred around 410 million years ago?
-Around 410 million years ago, during the Paleozoic era, tectonic plates began to move, leading to the gradual formation of what we now recognize as Southeast Asia.
Why is it difficult to find dinosaur fossils in Southeast Asia?
-Dinosaur fossils are hard to find in Southeast Asia because the region has undergone significant geological changes, with landmasses rising and sinking over millions of years.
What evidence do archaeologists find in Southeast Asia instead of dinosaur fossils?
-Archaeologists mainly find ancient marine species' fossils, such as the Megalodon, instead of terrestrial dinosaur fossils.
What role did the Sunda Shelf play in human migration?
-The Sunda Shelf, which connected several landmasses during periods of lower sea levels, facilitated human migration and the development of civilizations in Southeast Asia.
How did climate changes affect the Sunda Shelf?
-Climate changes during glacial periods caused lower sea levels, exposing the Sunda Shelf, which eventually submerged again as the Earth warmed.
What are some of the ancient rivers that existed on the Sunda Shelf?
-Ancient rivers on the Sunda Shelf flowed from various mountain ranges and emptied into the surrounding seas, such as the Natuna Sea and the Malacca Strait.
What natural forces contribute to the geological evolution of Southeast Asia?
-Natural forces such as tectonic plate movement and climatic conditions, including variations in solar intensity, contribute to the geological evolution of Southeast Asia.
When did Southeast Asia start to resemble its current geological form?
-Southeast Asia began to take on its current geological form approximately 10 million years ago, although its marine geography was different until more recent climate changes.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)