All of AQA BIOLOGY Paper 1 in 25 minutes - GCSE Science Revision
Summary
TLDRThis video provides a comprehensive overview of key concepts in AQA GCSE Biology, covering cell structure, organization, and processes such as respiration and photosynthesis. It explains the differences between eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells, the role of enzymes, and the importance of diffusion, osmosis, and active transport. The video also discusses the human circulatory and respiratory systems, infection responses, and the impact of pathogens. Additionally, it addresses topics like metabolism, the significance of stem cells, and the effects of lifestyle on health, making it an essential resource for students preparing for their exams.
Takeaways
- 😀 Vaccines stimulate immunity by using dead or inactive pathogens, while mRNA vaccines introduce genetic material to produce antigens.
- 💊 Antibiotics target bacteria specifically and are ineffective against viruses; overuse can lead to antibiotic resistance.
- 🧪 Drug development involves multiple trial phases: lab tests, animal studies, and human trials, often employing blind and double-blind methods to eliminate bias.
- 🧬 Monoclonal antibodies are engineered to produce specific antibodies for treatment and diagnostics, but they may have unexpected side effects.
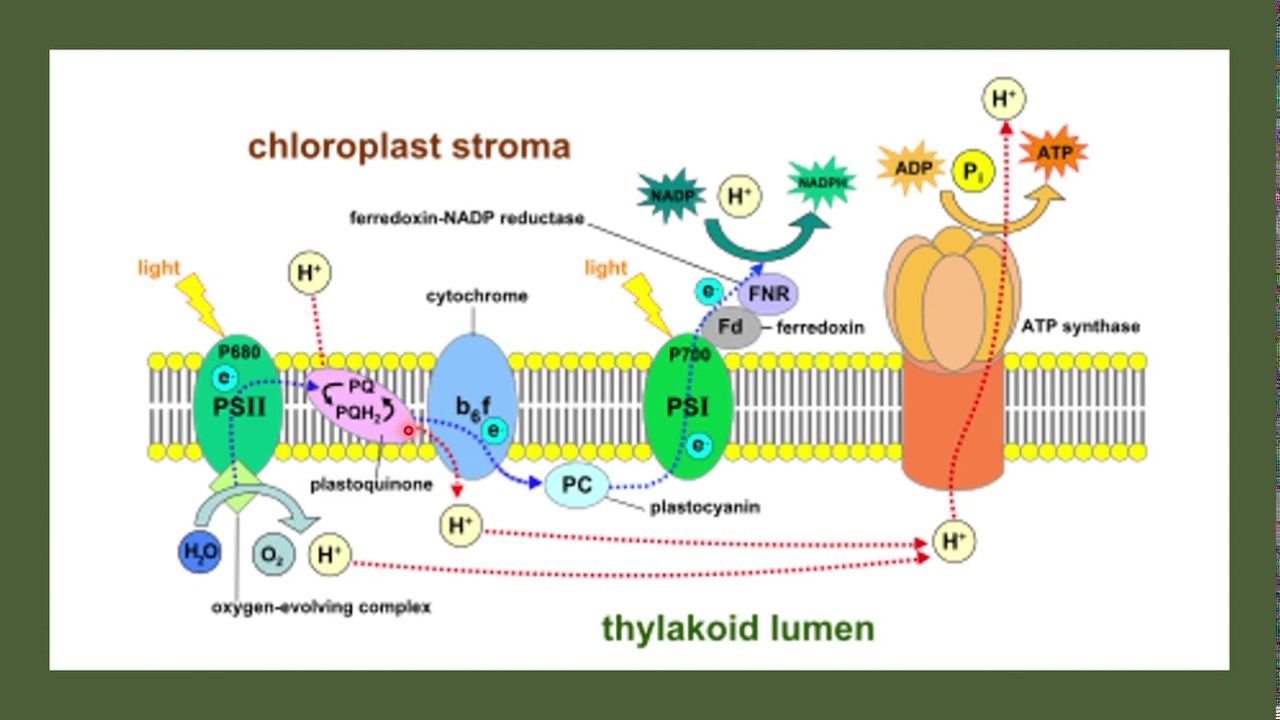
- 🌱 Photosynthesis occurs in chloroplasts, converting light energy, carbon dioxide, and water into glucose, with limiting factors being light intensity, temperature, and CO2 concentration.
- 💨 Aerobic respiration occurs with oxygen, while anaerobic respiration (e.g., during intense exercise) produces lactic acid and creates an oxygen debt.
- 🍞 Yeast ferments sugars into alcohol and carbon dioxide, which is utilized in baking and brewing processes.
- ⚛️ Metabolism encompasses all biochemical reactions in a cell, including the synthesis and breakdown of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats.
- 📈 The rate of photosynthesis can be measured by the volume of oxygen produced or the number of bubbles from submerged pondweed.
- 💡 Understanding these biological processes is crucial for exams and provides foundational knowledge for further studies in biology.
Q & A
What are the two main types of cells, and how do they differ?
-The two main types of cells are eukaryotic and prokaryotic. Eukaryotic cells have a nucleus where their DNA is stored, such as plant and animal cells, while prokaryotic cells do not have a nucleus and contain DNA in a ring form called a plasmid.
What is the role of mitochondria in cells?
-Mitochondria are the sites of respiration in cells, where energy is released for the cell to function.
How do stem cells differ from specialized cells?
-Stem cells are unspecialized cells that have the potential to develop into various types of cells, while specialized cells have distinct structures and functions tailored to their roles in the body.
What is osmosis, and how does it differ from diffusion?
-Osmosis is specifically the diffusion of water across a semi-permeable membrane, while diffusion refers to the movement of any molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration.
What is the purpose of a vaccine?
-A vaccine is designed to expose the immune system to a dead or inactive version of a pathogen, enabling it to produce antibodies without causing disease, thus providing immunity against future infections.
What is the significance of the double circulatory system in humans?
-The double circulatory system allows blood to be pumped twice through the heart: once to the lungs for oxygenation and again to the rest of the body to deliver oxygen and nutrients.
What factors can affect the rate of photosynthesis?
-The rate of photosynthesis can be influenced by temperature, light intensity, and carbon dioxide concentration. Each can act as a limiting factor.
What is the function of enzymes in biological reactions?
-Enzymes are biological catalysts that speed up chemical reactions by lowering the activation energy required for the reaction to occur.
How do monoclonal antibodies work in medical treatments?
-Monoclonal antibodies are produced from a single clone of cells and can target specific antigens on pathogens or diseased cells, allowing for targeted treatment or diagnostic purposes.
What are the consequences of antibiotic resistance?
-Antibiotic resistance occurs when bacteria mutate and become resistant to the effects of antibiotics, making infections harder to treat and increasing the risk of spreading resistant strains.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
AP Biology Unit 3: Cellular Energetics Complete Review

SEL : STRUKTUR DASAR DAN FUNGSI ORGANEL - BIOLOGI 11 SMA

All of BIOLOGY PAPER 1 in 20 mins - GCSE Science Revision Mindmap 9-1 AQA

Kisi Kisi OSN BIOLOGI 2025

Top 40 biology MCQ | biology mcq for all competitive exam | biology Mcq 2025 | neet biology

Struktur dan Fungsi Sel Tumbuhan (Animasi) | Bagian-bagian sel tumbuhan
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)