Floods, heavy rain, extreme weather - Why we need to build differently | DW Documentary
Summary
TLDRThe video explores how cities worldwide are adapting to the impacts of climate change, particularly extreme weather events like heat, flooding, and heavy rain. It highlights innovative solutions for creating climate-resilient cities, focusing on projects like ‘HeatResilientCity.’ The video emphasizes the importance of proactive planning, both in small cities like Dresden and large megacities such as Bangkok, showing that cities can adapt to and mitigate the challenges posed by a changing climate, making urban areas more livable despite extreme conditions.
Takeaways
- 😀 Climate change is causing extreme weather events like heatwaves, heavy rain, and flooding, which urban areas must adapt to.
- 🌍 Research projects like 'HeatResilientCity' demonstrate that cities worldwide can still take action to prepare for climate challenges.
- 🏙️ In Dresden, Germany, urban heat islands are being targeted through research and data-driven approaches to increase resilience against heat.
- 🌡️ The 2003 European heatwave serves as a reminder of the deadly impacts of high temperatures, prompting proactive measures for the future.
- 🌿 In Bangkok, Thailand, integrating green spaces and porous surfaces helps manage flooding and reduce the risks posed by heavy rainfall.
- 💧 Bangkok's geographical challenge of being built on floodplains requires innovative solutions to prevent flooding and manage water efficiently.
- 🌳 Nature-based solutions like increasing green infrastructure are essential for cities to coexist with water and extreme weather conditions.
- 💡 New technologies such as AI and temperature sensors are being used to predict and manage urban heat spots more effectively.
- 🏗️ Sustainable construction materials, like loam, are being utilized in Germany to create buildings that are more energy-efficient and climate-resilient.
- ⏳ There is still time to act and adapt to the effects of climate change through smart urban planning and collaboration across cities globally.
Q & A
What is the main focus of the research being conducted in Dresden, Germany?
-The main focus of the research in Dresden is to identify urban heat islands and develop effective heat protection measures for buildings in response to increasing heatwaves and climate change.
How does the project 'HeatResilientCity' contribute to climate adaptation?
-'HeatResilientCity' is a prize-winning research project that demonstrates how cities, both small and large, can adapt to extreme weather, such as heat, flooding, and heavy rainfall, by using innovative urban planning and design solutions.
What specific measures are being implemented in Dresden to manage urban heat?
-In Dresden, researchers are using heat sensors to monitor temperatures and implementing heat-resistant building materials and designs to protect residents from extreme heat, which became especially critical after the 2003 heatwave.
What role does Kotchakorn Voraakhom play in Bangkok's climate adaptation efforts?
-Kotchakorn Voraakhom is a landscape architect leading the initiative to redesign Bangkok's urban landscape by incorporating green, porous spaces that absorb water, reduce flooding, and improve urban resilience to extreme weather events like flooding.
How does Bangkok's approach to water management differ from its past practices?
-Historically, Bangkok thrived on its canals and water systems, but rapid urbanization has led to challenges in water management. Now, the city is revitalizing old canals and creating green spaces that act as water reservoirs to address these issues.
Why is the use of green roofs important in Bangkok’s climate adaptation?
-Green roofs in Bangkok help absorb water, reduce the urban heat island effect, and create more green spaces, which improve both water management and the overall livability of the city in response to climate change.
What is the significance of using loam in building construction in Germany?
-Loam is a natural, eco-friendly building material that is energy-efficient, recyclable, and capable of regulating indoor temperatures. It offers a sustainable alternative to concrete, contributing to environmental sustainability in urban development.
How do the projects in Dresden and Bangkok reflect global trends in climate adaptation?
-Both Dresden and Bangkok are adopting nature-based solutions, such as green spaces and sustainable materials, to adapt to the effects of climate change. These strategies reflect a growing global focus on resilience, environmental sustainability, and the integration of nature into urban planning.
What is the main challenge that Bangkok faces due to its rapid urbanization?
-The main challenge Bangkok faces is inadequate water management due to rapid urbanization, which has led to increased flooding and a loss of the city's historical water circulation systems.
How can urban environments globally learn from the initiatives in Dresden and Bangkok?
-Cities worldwide can learn from Dresden and Bangkok by implementing green, porous infrastructure, using sustainable materials, and developing heat and water management systems to better cope with extreme weather events brought on by climate change.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

IPB Podcast: Perubahan Iklim dan Kontribusi Masyarakat dalam Menghadapinya
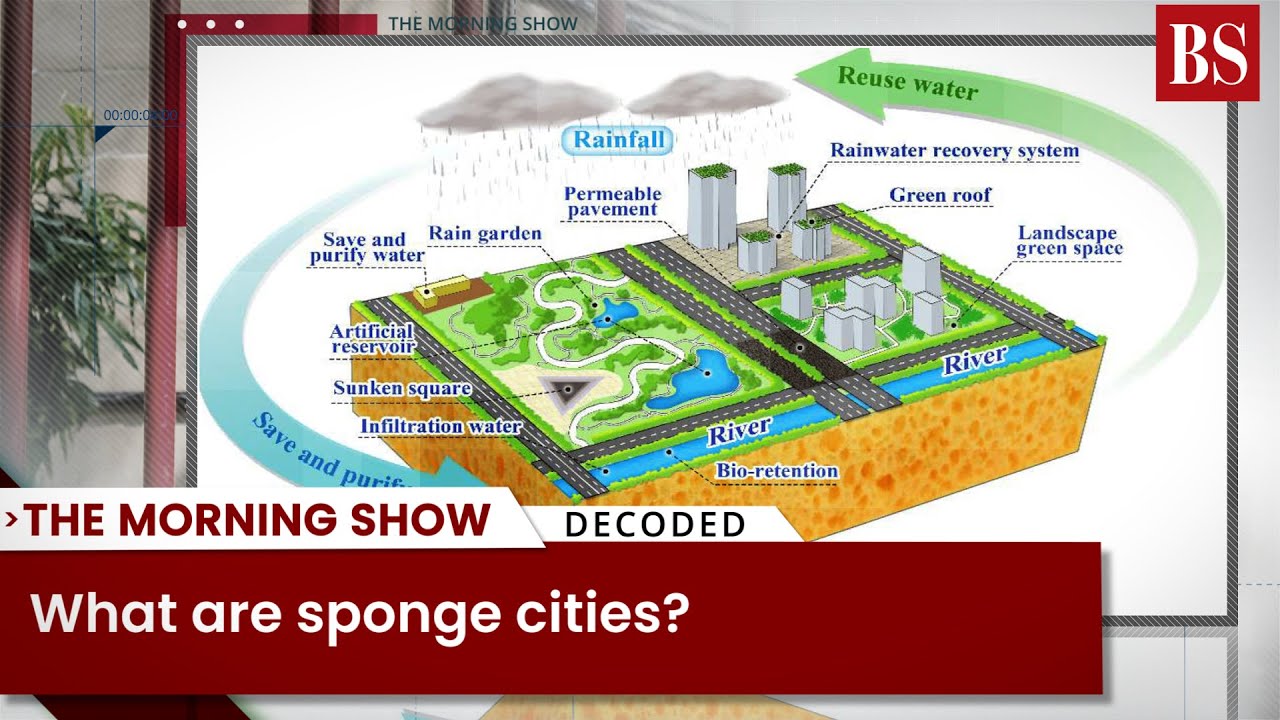
What are sponge cities?

Flooded By Climate Change: Will India Sink Or Swim? | Insight | Full Episode

Cuaca Ekstrim Melanda Amerika: Los Angeles Kebakaran, Kota Lain Tertutup Salju | Liputan 6

How I Think About Climate Change

Crise climática: até onde vamos aguentar?
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)