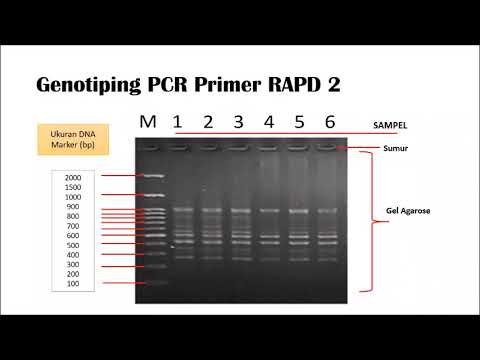
Allele Specific PCR (AS-PCR) / Amplification Refractory Mutation System (ARMS) - Genotyping PCR
Summary
TLDRThis video introduces Allele-Specific PCR (AS-PCR), a technique for detecting specific DNA mutations using tailored primers. Known for its sensitivity and specificity, AS-PCR is instrumental in genetic testing, diagnosing disorders, and population studies. The method differentiates between alleles by employing various detection strategies, including TaqMan probes, melting curve analysis, restriction fragment length polymorphism, and probe-based approaches. Each strategy offers unique advantages, making AS-PCR a vital tool in research and clinical applications focused on identifying genetic variations.
Takeaways
- 😀 AS-PCR stands for allele-specific polymerase chain reaction, a technique for detecting DNA mutations.
- 🔬 This method targets single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) to identify specific genetic variations.
- 🧬 Primers are specifically designed to amplify either a mutated or a wild-type allele during the PCR process.
- 👩⚕️ AS-PCR is widely used in genetic testing, diagnosis of genetic disorders, and population genetics research.
- ⚗️ Detection strategies for AS-PCR include TaqMan probes, melting curve analysis, RFLP, and probe-based methods.
- 📈 TaqMan probes use fluorescent signals to indicate the presence of mutations in the target DNA.
- 🌡️ Melting curve analysis relies on different melting temperatures between wild-type and mutant alleles to differentiate them.
- 🔍 RFLP involves digesting PCR products with restriction enzymes to analyze fragment lengths for mutation detection.
- 📐 The design of primers is crucial, with specific mismatches at the three-prime end enhancing specificity.
- 📋 The choice of AS-PCR strategy depends on the research needs, focusing on sensitivity, visibility, and user-friendliness.
Q & A
What is allele-specific PCR (AS-PCR)?
-AS-PCR is a technique used to detect specific variations or mutations in DNA by amplifying particular alleles.
What are the common names for AS-PCR?
-AS-PCR is also known as the amplification refractory mutation system (ARMS).
How are primers designed in AS-PCR?
-Primers in AS-PCR are specifically designed to recognize and amplify either the normal or mutated allele, allowing for differentiation.
What applications is AS-PCR commonly used for?
-AS-PCR is used in genetic testing, diagnosing genetic disorders, and conducting population genetic studies.
What is the significance of the three-prime end of the primer in AS-PCR?
-The three-prime end of the primer must perfectly complement the target sequence to ensure successful amplification of the desired allele.
What are some detection strategies used in AS-PCR?
-Detection strategies include TaqMan probes, melting curve analysis, restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLP), and probe-based methods.
How does the TaqMan probe method work?
-TaqMan probes use fluorescent labels that bind to the target DNA and are cleaved during amplification if there is a perfect match with the mutant primer.
What does melting curve analysis reveal?
-Melting curve analysis shows the differing melting temperatures of amplified DNA fragments from wild-type and mutant alleles, aiding in genotype differentiation.
What is the role of restriction enzymes in RFLP?
-Restriction enzymes cut specific DNA sequences, allowing for comparison of fragment lengths between normal and mutated sequences.
What factors should be considered when choosing an AS-PCR detection strategy?
-Factors include the sensitivity required, the visibility of results, and the ease of use for specific research or clinical applications.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)