Plant Life Cycles
Summary
TLDRThis educational video explores the life cycle of plants, detailing how seeds germinate and grow into mature plants. It explains the importance of water, light, and temperature in seed development and highlights the roles of flowers and pollination in seed production. Viewers learn how various plants, including sunflowers and pumpkins, produce seeds and fruit, ensuring the continuation of their species. The cycle of growth, reproduction, and renewal is emphasized, showcasing the remarkable processes that enable plants to thrive and perpetuate life.
Takeaways
- 🌱 Seeds are essential for plant reproduction, containing tiny plants (embryos) inside.
- 💧 For a seed to germinate, it needs the right amount of water, temperature, light, and air.
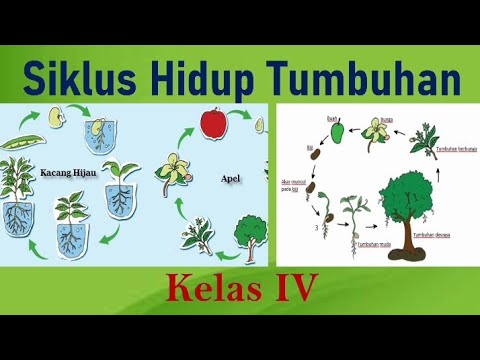
- 🌻 The life cycle of a plant includes stages: seed, seedling, mature plant, flowering, and seed production.
- 🍂 Germination begins when the seed coat splits, allowing the root to grow down and the stem to grow up.
- 🌼 Flowers are crucial for pollination, which is necessary for seed formation in many plants.
- 🍉 Fruits protect the seeds and are important for plant reproduction.
- 🌳 Different types of seeds have varying requirements for germination, some needing specific conditions like cold or heat.
- 🐝 Pollinators like bees play a vital role in transferring pollen between flowers, facilitating the pollination process.
- 🔄 The life cycle of plants is cyclical, allowing for continuous growth and reproduction across generations.
- 🌲 Some plants, like conifers, produce seeds in cones instead of flowers, demonstrating diverse reproductive strategies.
Q & A
What is the life cycle of a plant?
-The life cycle of a plant includes the stages of seed, germination, seedling, mature plant, flowering, and seed production.
What conditions are necessary for a seed to germinate?
-Seeds need the right amount of water, temperature, light, and air to germinate.
What is the function of the seed coat?
-The seed coat protects the seed and its embryo from external conditions.
What happens during germination?
-During germination, the seed absorbs water, swells, and the seed coat splits open, allowing the tiny plant to emerge.
What are seed leaves?
-Seed leaves, or cotyledons, are the first leaves that appear on a seedling, providing food as it begins to grow.
How do flowers contribute to the life cycle of a plant?
-Flowers produce seeds through pollination, which is essential for plant reproduction.
What is pollination?
-Pollination is the process of transferring pollen from one flower to another, which is necessary for seed formation.
What is the role of fruit in a plant's life cycle?
-Fruit protects the seeds and aids in their dispersal, ensuring the continuation of the plant's life cycle.
How do coniferous plants reproduce differently from flowering plants?
-Coniferous plants reproduce using cones, with small cones producing pollen and larger cones containing seeds.
Can seeds remain dormant before germination? If so, why?
-Yes, some seeds can remain dormant for months or even years until the right conditions for germination are met.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)