Kelarutan dan Hasil Kali Kelarutan (Ksp) Kimia Kelas 11 • Part 1: Konsep, Hubungan Kelarutan dan Ksp
Summary
TLDRIn this educational video, viewers are introduced to the concepts of solubility and the solubility product constant (Ksp). The presenter explains how solubility refers to the maximum amount of a substance that can dissolve in a solvent, exemplified by sodium chloride (NaCl). The video also distinguishes between soluble and insoluble compounds and details the calculations involved in determining Ksp using specific examples, such as barium sulfate and calcium phosphate. Through clear explanations and practical examples, the video aims to enhance understanding of these fundamental chemistry topics.
Takeaways
- 😀 Solubility refers to the maximum amount of a substance that can dissolve in a specific amount of solvent.
- 🌊 Sodium chloride (NaCl) has a solubility of 36 grams per 100 grams of water.
- 🔄 A saturated solution contains the maximum amount of solute that can dissolve; any additional solute will not dissolve.
- 📉 Solubility limits differ for substances; more soluble substances have higher limits, while less soluble substances have lower limits.
- 🔬 The solubility product constant (Ksp) is the equilibrium constant for the solubility of sparingly soluble salts.
- ⚖️ Ksp is calculated from the concentrations of the ions in a saturated solution, raised to the power of their coefficients in the balanced equation.
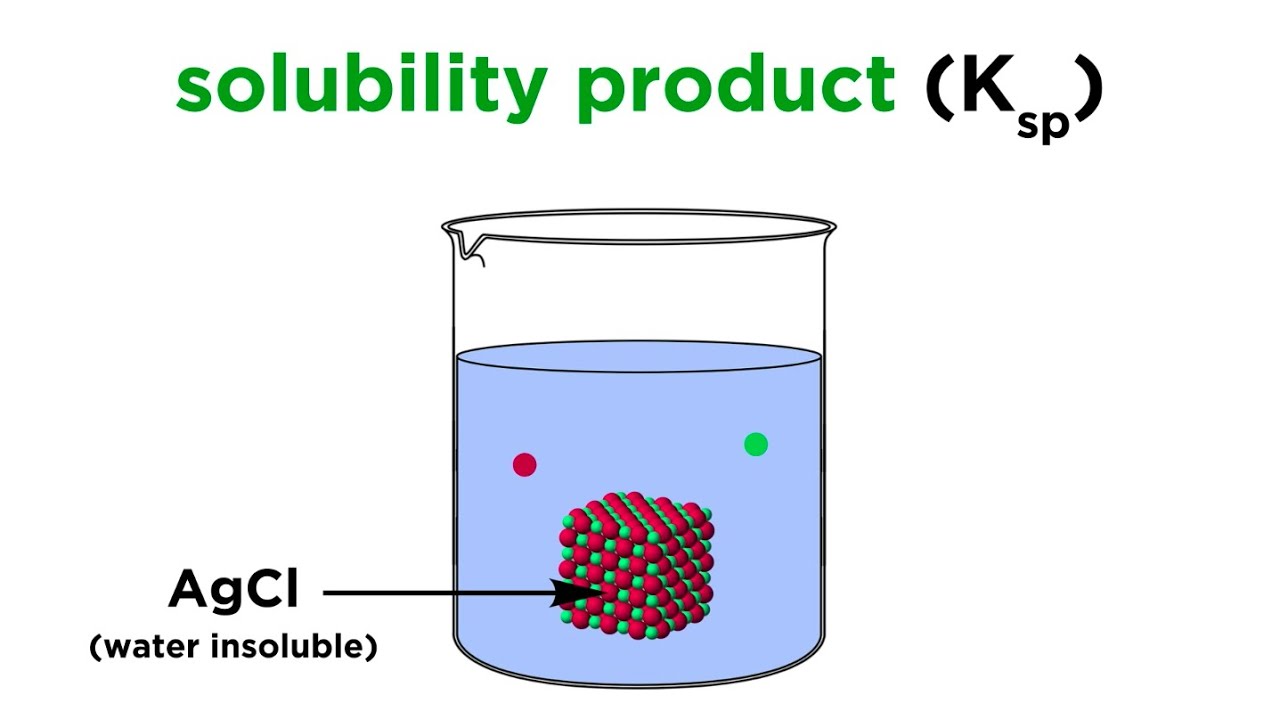
- ⚗️ Examples of soluble compounds include NaCl, while silver chloride (AgCl) is an example of a sparingly soluble compound.
- 🧪 The relationship between solubility (s) and Ksp can be used to determine the Ksp value of a compound from its solubility.
- 📏 The formula for solubility can be expressed as S = n/V, where S is solubility, n is the number of moles of solute, and V is the volume of solvent.
- 📝 Understanding the difference between soluble and insoluble compounds is essential for predicting their behavior in solutions.
Q & A
What is solubility?
-Solubility is the maximum amount of a substance that can dissolve in a specific amount of solvent at a given temperature.
What is the solubility of sodium chloride (NaCl) in water?
-The solubility of sodium chloride in water is 36 g per 100 g of water.
What is a saturated solution?
-A saturated solution is one where no additional solute can dissolve in the solvent, meaning it has reached its maximum solubility.
How does solubility vary among different compounds?
-Compounds can be classified as soluble or insoluble based on their ability to dissolve in water; soluble compounds have higher solubility, while insoluble compounds have very low solubility.
What is the significance of the solubility product constant (Ksp)?
-The Ksp is an equilibrium constant that indicates the extent to which a sparingly soluble compound can dissolve in water, providing insight into its solubility.
How is Ksp calculated for a compound?
-Ksp is calculated as the product of the molar concentrations of the ions in a saturated solution, each raised to the power of their coefficients in the balanced dissociation equation.
Why are solids not included in the Ksp expression?
-Solids are not included in the Ksp expression because their concentration remains constant in a saturated solution, making them irrelevant for calculating the equilibrium constant.
Can you provide an example of calculating Ksp?
-For barium sulfate (BaSO₄), if its solubility is S, the Ksp is given by Ksp = [Ba²⁺][SO₄²⁻] = S × S = S².
What happens to the solubility of a compound as the solution becomes saturated?
-Once a solution becomes saturated, no more solute can dissolve, and any additional solute will remain undissolved.
What distinguishes soluble compounds from insoluble ones in terms of their solubility limits?
-Soluble compounds have higher solubility limits, meaning they can dissolve in larger amounts in a solvent, while insoluble compounds have low solubility limits, indicating they dissolve only in minimal amounts.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)