Bagaimana sih intepretasi hasil Hasil Laboratorium Liver Function Test? #yourstudybuddy
Summary
TLDRThe transcript discusses the importance of liver function tests (LFTs) in assessing liver health, focusing on bilirubin metabolism and enzyme levels. It explains the differences between indirect and direct bilirubin, the significance of elevated SGOT (AST) and SGPT (ALT) in diagnosing liver damage, and the implications of albumin and coagulation factors. Additionally, it highlights how urinary bilirubin and urobilinogen can indicate liver obstruction or hemolysis. Overall, understanding these markers is crucial for appropriate diagnosis and referral in cases of liver dysfunction.
Takeaways
- 😀 Liver function tests are crucial for assessing liver health, particularly for bilirubin excretion.
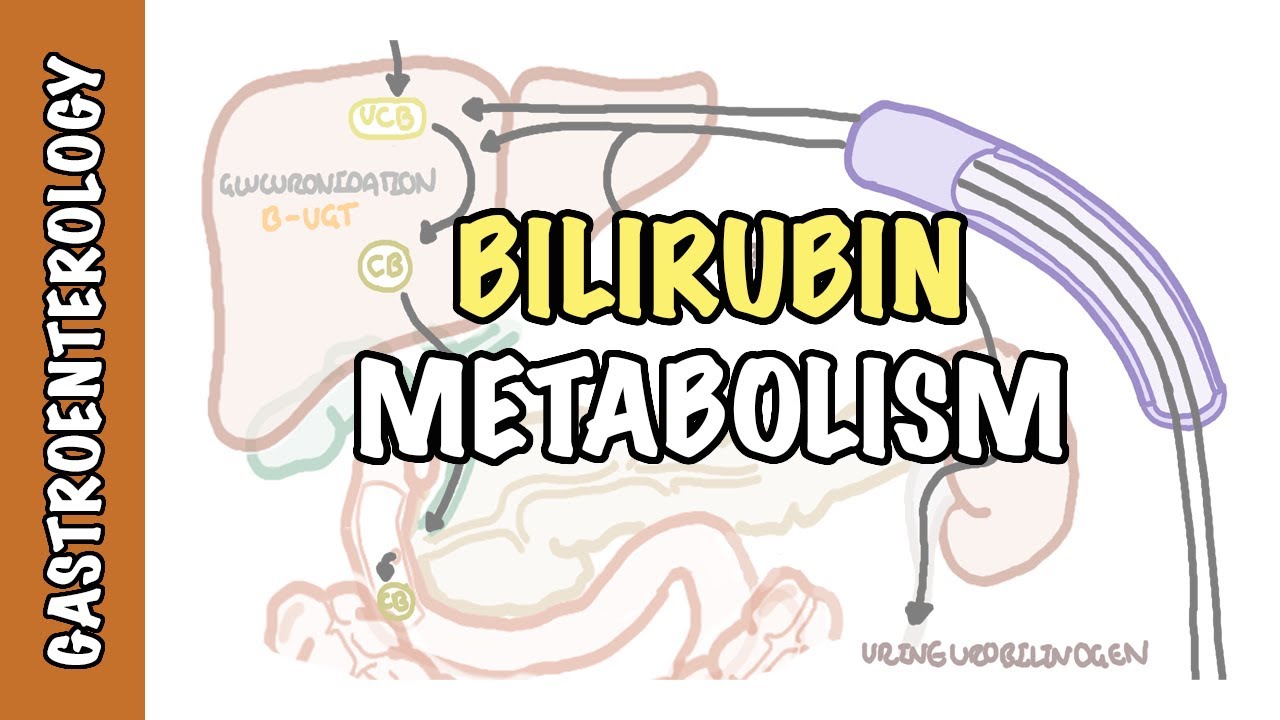
- 😀 Bilirubin is produced from the breakdown of hemoglobin and exists in direct and indirect forms.
- 😀 Indirect bilirubin increases in conditions like hemolytic anemia, while direct bilirubin can indicate liver dysfunction.
- 😀 Urobilin is a breakdown product of bilirubin that provides color to urine and feces, and its levels can indicate liver health.
- 😀 Liver enzyme levels, such as SGOT and SGPT, help identify liver cell damage and its severity.
- 😀 SGOT (AST) is found in muscle tissues, whereas SGPT (ALT) is specific to the liver; their ratios can indicate different conditions.
- 😀 A rise in alkaline phosphatase (ALP) suggests obstruction in bile flow, which can lead to elevated bilirubin levels.
- 😀 The presence of bilirubin in urine indicates that it bypasses the liver due to obstruction.
- 😀 Understanding bilirubin pathways aids in diagnosing liver issues and guiding appropriate referrals to specialists.
- 😀 Familiarity with these metabolic pathways is essential for medical professionals in evaluating and managing liver-related conditions.
Q & A
What is the primary role of the liver in excreting bilirubin?
-The liver excretes bilirubin, which is produced from the breakdown of hemoglobin in aged erythrocytes, by converting it into a water-soluble form that can be eliminated from the body.
What are the two types of bilirubin mentioned in the transcript?
-The two types of bilirubin are direct (conjugated) bilirubin, which is water-soluble and can be excreted, and indirect (unconjugated) bilirubin, which is not water-soluble and remains in the bloodstream until it is processed by the liver.
How does bilirubin direct increase indicate liver function issues?
-An increase in direct bilirubin suggests liver dysfunction or obstruction since it indicates that the liver's ability to process and excrete bilirubin is impaired.
What does a rise in SGOT (AST) and SGPT (ALT) levels indicate?
-Elevated levels of SGOT and SGPT indicate liver cell damage, with SGPT being more specific to liver injury.
What can cause hypoproteinemia in patients with liver issues?
-Hypoproteinemia, specifically low albumin levels, can occur due to liver dysfunction, such as cirrhosis or chronic hepatitis, which affects the liver's ability to synthesize proteins.
What does the presence of bilirubin in urine signify?
-The presence of bilirubin in urine indicates that there is an obstruction in the bile duct, causing bilirubin to bypass the liver and enter the bloodstream, ultimately being filtered out by the kidneys.
What role do urobilins play in diagnostics?
-Urobilins, derived from the breakdown of bilirubin in the intestines, provide diagnostic clues; increased urobilin levels may indicate hemolytic processes.
How can understanding bilirubin metabolism aid in diagnosing liver conditions?
-By understanding the pathways of bilirubin metabolism, healthcare providers can differentiate between obstructive jaundice and hepatocellular damage, leading to appropriate diagnoses.
What is the significance of comparing SGOT and SGPT levels?
-Comparing SGOT and SGPT levels helps to identify the source of liver damage; a predominance of SGOT over SGPT may suggest conditions involving the heart or muscles rather than the liver.
What are the key indicators of liver function discussed in the transcript?
-Key indicators of liver function include bilirubin levels, albumin levels, and the activity of liver enzymes such as ALT and AST.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Enzim Hepar dan Tes Faal Hepar 3 (Materi Kuliah Analis Kesehatan Kimia Klinik)

Demystifying Liver Function Tests | Easy Algorithm for Medical Practitioners
Bilirubin Metabolism - unconjugated and conjugated bilirubin

Dokter 24 : Cara Pemeriksaan/Diagnosa Hepatitis (1)

SINAIS DE QUE SEU FÍGADO ESTÁ AFETANDO A SUA SAÚDE MENTAL (DEPRESSÃO E ANSIEDADE)

Interpretation of LFTs (Liver Function Tests)
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)