Google Compute Engine Tutorial | Google Compute Services Overview | GCP Training | Edureka
Summary
TLDRThis video presents an overview of Google Cloud's Compute Engine, a key infrastructure as a service (IaaS) component of the Google Cloud Platform (GCP). The session explores the benefits of GCP, including cost-effectiveness and efficient data management. It highlights the Compute Engine's capabilities for launching virtual machines, its applications in genomics data processing, and virtual machine migration. Key features like machine types, local SSDs, and global load balancing are discussed. The tutorial also provides a practical demonstration on how to use the Compute Engine, emphasizing its user-friendly interface and robust performance for various cloud computing needs.
Takeaways
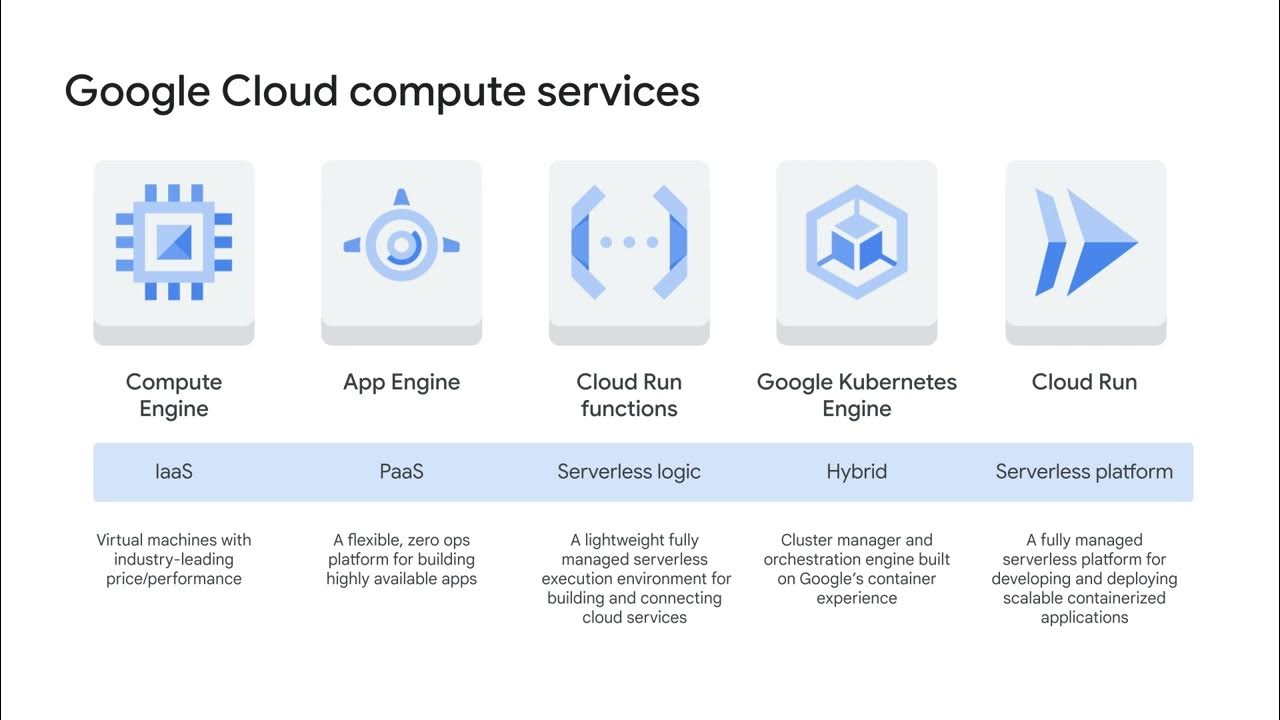
- 😀 Google Compute Engine is part of Google Cloud Platform, providing Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) built on Google's robust global infrastructure.
- 😀 IaaS allows users to manage virtual machines and resources in the cloud without needing physical server hardware.
- 😀 Google Cloud Platform offers a range of services, including computing, data storage, analytics, and machine learning, with competitive pricing compared to AWS.
- 😀 Users can launch virtual machines on Google Compute Engine using standard or custom images, requiring authentication via OAuth 2.0.
- 😀 Key applications of Google Compute Engine include virtual machine migration, genomics data processing, and support for bring your own license (BYOL) models.
- 😀 Google Compute Engine features predefined and custom machine types, allowing for flexible configurations based on user needs.
- 😀 Persistent disks in Google Compute Engine support durable storage options, including SSDs, and can retain data even if virtual machines are deleted.
- 😀 The platform offers advanced capabilities such as GPU accelerators for computationally intensive tasks and global load balancing for performance optimization.
- 😀 Key advantages of Google Compute Engine include high storage capacity, cost-effectiveness, stability through live migration, and strong security measures.
- 😀 The session includes a practical demonstration of launching virtual machines on Google Cloud, highlighting the ease of use and available configurations.
Q & A
What is Google Compute Engine?
-Google Compute Engine is an Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) component of the Google Cloud Platform, allowing users to run virtual machines on Google's global infrastructure.
How does Google Cloud Platform differ from AWS?
-Google Cloud Platform offers computing services that are generally cheaper than AWS, particularly in data storage, while both provide robust cloud solutions.
What are the key components of Infrastructure as a Service?
-IaaS provides high-level APIs to manage low-level details such as physical computing resources, security, and storage, often using cloud orchestration technologies.
What is the role of authentication in Google Compute Engine?
-Users must authenticate using OAuth 2.0 before launching virtual machines, which allows secure access without sharing passwords.
What are some applications of Google Compute Engine?
-Applications include virtual machine migration, genomics data processing, and running licensed Windows applications in the cloud.
What types of machine configurations does Google Compute Engine offer?
-Google Compute Engine offers predefined machine types optimized for various workloads, as well as custom machine types that allow users to select the number of CPUs and memory.
How does Google Compute Engine handle storage?
-It provides persistent storage options, including local SSDs and high-performance block storage that can be retained even if the virtual machine is terminated.
What are some key features of Google Compute Engine?
-Key features include machine types, local SSD storage, GPU accelerators for intensive workloads, image management, and global load balancing.
What advantages does Google Compute Engine offer?
-Advantages include cost-effectiveness, high storage capacity, stability through live migration, and robust security measures.
What should users do to avoid losing data on their virtual machines?
-Users should create snapshots of their virtual machines to retain data, which can be restored even after the instance is deleted.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)