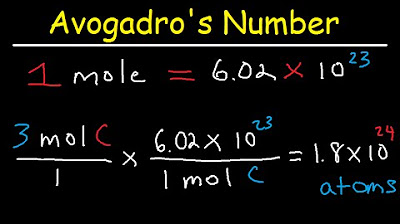Konsep Mol - perhitungan kimia / stoikiometri- kimia SMA kelas 10 semester 2
Summary
TLDRIn this video, the host explains the concept of moles in chemistry, describing it as a unit for quantifying particles. Key relationships between moles, mass, and volume are discussed, with essential formulas such as Avogadro's number (6.02 x 10^23) and the ideal gas law (PV = nRT). The video also addresses conditions for standard temperature and pressure (STP) and provides several calculation examples to illustrate how to determine the number of particles, moles, and mass of various substances. This foundational knowledge is crucial for understanding chemical reactions and stoichiometry.
Takeaways
- 😀 A mole is a unit used in chemistry to express the amount of substance, similar to grams for mass and liters for volume.
- 😀 Avogadro's number (6.02 × 10²³) is used to relate the number of particles to the number of moles.
- 😀 The formula to calculate the number of particles from moles is: Number of particles = Moles × Avogadro's number.
- 😀 Moles are also related to mass, with the formula: Moles = Mass / Molar Mass (Mr).
- 😀 At standard temperature and pressure (STP, 0°C and 1 atm), one mole of an ideal gas occupies 22.4 liters.
- 😀 For gases not at STP, the Ideal Gas Law (PV = nRT) can be used to find volume or moles.
- 😀 It is essential to convert temperature to Kelvin when using gas laws, where Kelvin = Celsius + 273.
- 😀 Calculating moles from mass requires knowing the molar mass of the substance involved.
- 😀 The example problems demonstrate practical applications of mole calculations in determining quantities of various substances.
- 😀 Understanding these concepts is crucial for performing accurate chemical calculations in laboratory and theoretical settings.
Q & A
What is a mole in chemistry?
-A mole is a unit used to express the amount of particles in a substance, similar to how grams measure mass or meters measure length.
How is the number of particles related to moles?
-The number of particles can be calculated using the formula: number of particles = moles × Avogadro's number (6.02 × 10^23).
What is Avogadro's number?
-Avogadro's number is a constant, approximately equal to 6.02 × 10^23, which represents the number of particles in one mole of a substance.
How do you calculate moles from mass?
-Moles can be calculated from mass using the formula: moles = mass / molar mass (M_R).
What does STP stand for, and why is it important?
-STP stands for Standard Temperature and Pressure, defined as 0°C (273.15 K) and 1 ATM. It provides a reference point for gas calculations.
What is the volume of one mole of a gas at STP?
-At STP, one mole of an ideal gas occupies a volume of 22.4 liters.
What is the ideal gas law formula?
-The ideal gas law is expressed as PV = nRT, where P is pressure, V is volume, n is the number of moles, R is the ideal gas constant, and T is temperature in Kelvin.
How do you convert Celsius to Kelvin?
-To convert Celsius to Kelvin, add 273.15 to the Celsius temperature.
What is the molar mass of copper sulfate (CuSO4)?
-The molar mass of copper sulfate (CuSO4) is calculated as 63.5 (Cu) + 32 (S) + 4 × 16 (O) = 159.5 g/mol.
How do you find the volume of a gas under non-STP conditions?
-To find the volume of a gas under non-STP conditions, use the ideal gas law: V = nRT/P, where you need to know the moles, temperature, and pressure.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)