Ecuaciones factorizables
Summary
Please replace the link and try again.
Takeaways
- 😀 Factorizing equations involves identifying multiple factors within an equation that can be multiplied together.
- 😀 To factorize an equation, it must be equal to zero, which is essential for graphing the equation properly.
- 😀 The first step in factorization is recognizing if the equation can be expressed as a difference of squares or other common factoring forms.
- 😀 A common factoring case is the difference of squares, where terms like x^2 - y^2 can be factored into (x + y)(x - y).
- 😀 Once the equation is factored, it can be split into separate equations, each of which is set to zero to solve for the variable.
- 😀 Graphing is possible by using the factored terms and understanding where each factor equals zero on a Cartesian plane.
- 😀 Equations can be factored into forms like trinomials, as seen in examples with x^4 and x^2 terms.
- 😀 To factor more complex terms like x^4, it's often necessary to apply square roots and break the equation down into simpler parts.
- 😀 The process of factoring can also include adding or subtracting specific terms to balance the equation, as in the case of completing a square.
- 😀 Once the equation is fully factored, it generates two separate equations, each of which can be graphed to visualize the overall solution.
Please replace the link and try again.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

0. ¿Qué es una Ecuación Diferencial? Tipos de ecuaciones diferenciales, solución de ED

Sistema de Ecuaciones 2x2 - Método de Eliminación o Reducción

DEFINICIÓN DE SISTEMAS DE ECUACIONES LINEALES
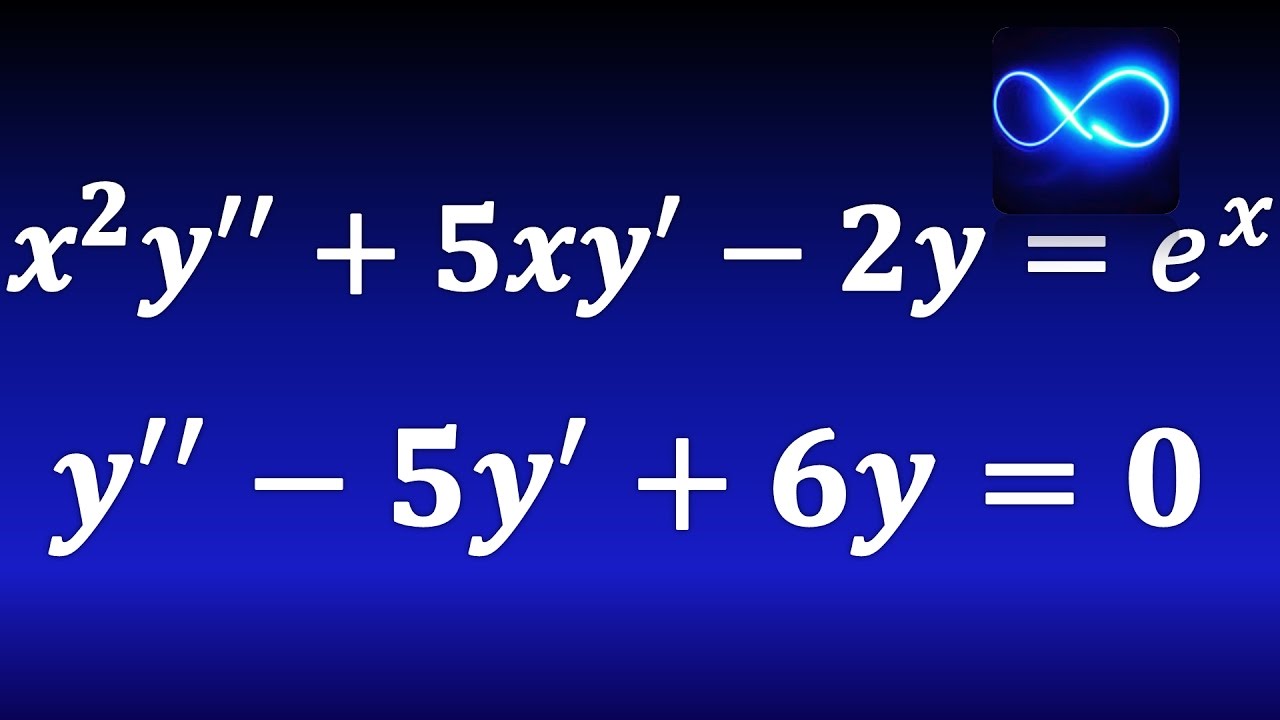
78. Qué son las ecuaciones de segundo orden, ecuaciones homogéneas y de coeficientes constantes

¿Qué aprenderás en el curso de ecuaciones polinómicas?

Las 8 ecuaciones más importantes de la Física

Sistema de 3x3. MÉTODO DE SUSTITUCIÓN. Ejemplo 1 de 3
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)