Trickling Filter at the wastewater treatment plant (utilities)
Summary
TLDRIn this informative video, Bruce the water guy explains the functioning of a trickling filter, an old but effective technology for wastewater treatment. He details how gravity-driven mechanisms distribute water over a rock media, where microorganisms thrive in a biofilm. These microorganisms play a crucial role in breaking down waste products and nutrients. After treatment, the water goes through a clarifier to settle solids before being disinfected and returned to the environment. Bruce emphasizes the system's efficiency, showcasing the importance of such technologies in maintaining clean water standards.
Takeaways
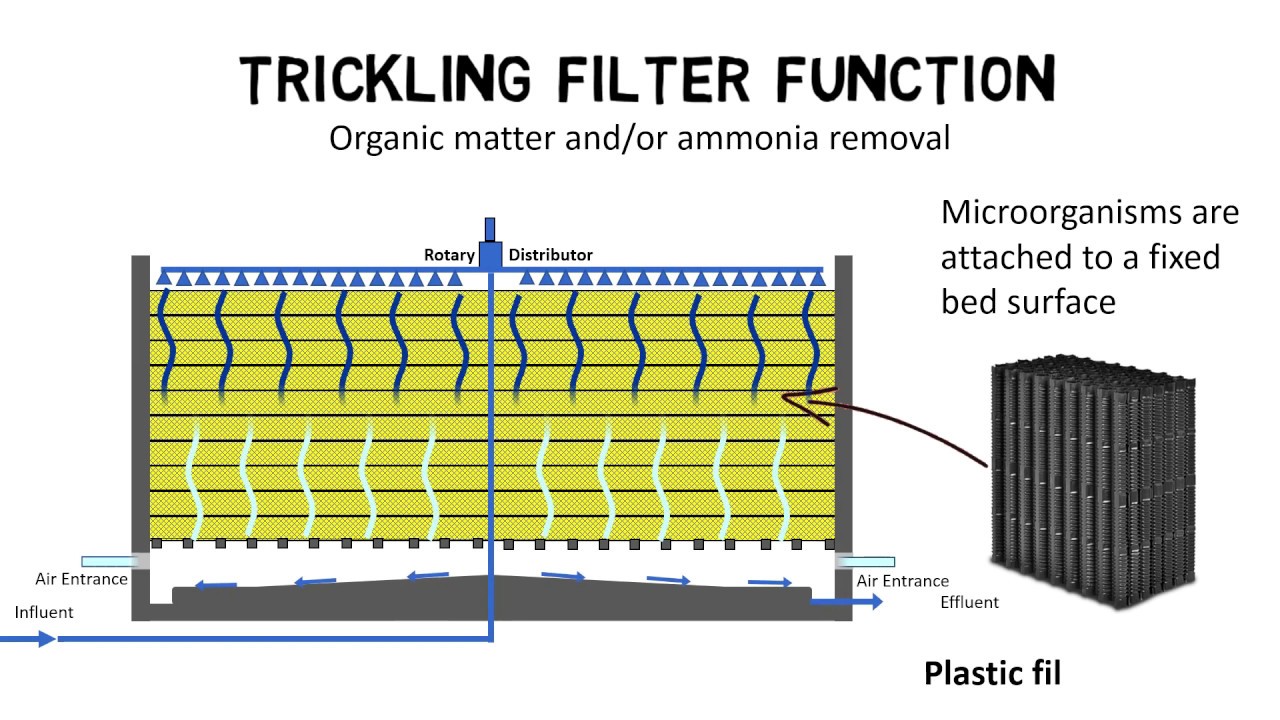
- 😀 A trickling filter is an old wastewater treatment technology that cleans water using gravity-driven distribution.
- 💧 Water is pumped to the end of rotating arms, which then distributes it evenly over a rock media.
- 🌍 The rock media, original from 1963, provides a surface for microorganisms to grow and treat wastewater.
- 🦠 Microorganisms form a biofilm that breaks down waste products, utilizing them as an energy source.
- 📏 The rock media is about six feet deep and offers approximately 11 square feet of growth area per cubic foot.
- ⚙️ After treatment in the trickling filter, the water flows to a clarifier for further processing.
- 🛠️ The clarifier allows solids and microorganisms to settle out of the water before further treatment.
- 🔄 Settled solids are pumped to a primary tank and then sent to a digester system for energy utilization.
- 💧 The end result is clean water, which is disinfected before being returned to the environment.
- 👨🔧 Bruce emphasizes the importance of older treatment systems and their role in sustainable water management.
Q & A
What is the main function of the trickling filter?
-The trickling filter is used to clean wastewater by utilizing microorganisms that break down waste products.
How does the distribution mechanism in the trickling filter work?
-The distribution mechanism operates by gravity, allowing wastewater to be pumped out and evenly distributed over the media.
What material is used as the media in the trickling filter?
-The media consists of rocks, which provide surface area for microbial growth.
When was the trickling filter built?
-The trickling filter was built in 1963.
What role do microorganisms play in the trickling filter?
-Microorganisms grow in a biofilm on the media and are responsible for breaking down waste products and utilizing nutrients for energy.
How deep is the media in the trickling filter?
-The media is about six feet deep.
What happens to the water after it exits the trickling filter?
-After exiting, the water goes to a clarifier where solids and microorganisms settle before being pumped into a primary tank.
What is the purpose of the clarifier in the treatment process?
-The clarifier allows for the settling of solids and microorganisms, ensuring that only clean water is returned to the environment.
How is energy utilized in this wastewater treatment system?
-The solids collected in the primary tank are sent to a digester system, which processes them to generate energy.
What is done to the water before it is returned to the environment?
-The water is disinfected before being released back into the environment.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)