Replicação do DNA
Summary
TLDRThis video provides a detailed explanation of DNA replication, focusing on the roles of key enzymes like DNA polymerase and helicase. The speaker explains how DNA is replicated semi-conservatively, with one old strand serving as a template for a new one. The process involves multiple replication forks to speed up replication, highlighting concepts such as base pairing, energy requirements for nucleotide bonding, and Okazaki fragments. The video concludes with a brief introduction to additional courses offered on biology and study materials for exams like the ENEM.
Takeaways
- 🧬 DNA replication is the process where the DNA molecule duplicates itself, allowing genetic material to be passed on.
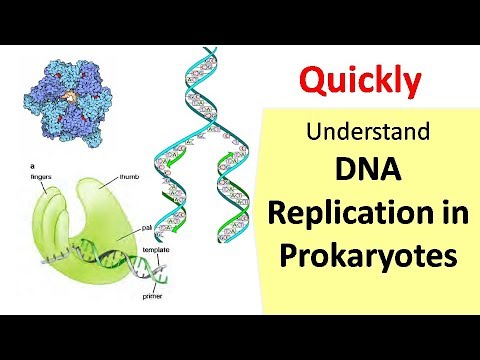
- 🔬 The enzyme DNA polymerase is essential for replication, synthesizing a new strand by following the template of the old strand.
- ✂️ Helicase unwinds the DNA strands by breaking hydrogen bonds, allowing replication to occur.
- ⚡ Replication happens at multiple points simultaneously to speed up the process, forming replication forks.
- 🌀 Replication is semi-conservative, meaning each new DNA molecule contains one old and one new strand.
- 🔗 Hydrogen bonds between bases form spontaneously, but covalent bonding between nucleotides requires energy provided by removing two phosphates from a nucleotide.
- ⏩ DNA polymerase adds nucleotides in the 5' to 3' direction, and replication can only occur in this direction.
- 🔄 DNA polymerase has a proofreading function to minimize errors during replication, significantly reducing mutation rates.
- 📌 Primase initiates replication by adding a small RNA primer, which allows DNA polymerase to begin adding nucleotides.
- 🧩 The lagging strand is synthesized in short segments called Okazaki fragments, which are later joined together.
Q & A
What is the role of DNA polymerase in DNA replication?
-DNA polymerase is the enzyme responsible for synthesizing a new DNA strand based on the template of the old strand. It adds nucleotides to the new strand, following the complementary base-pairing rules.
How does DNA polymerase ensure the accuracy of DNA replication?
-DNA polymerase has a proofreading function. After adding a nucleotide, it moves back to check if the correct base-pairing has occurred. If an error is detected, the enzyme removes the incorrect nucleotide and replaces it with the correct one, ensuring high fidelity in replication.
What is the function of helicase during DNA replication?
-Helicase is the enzyme that unwinds the DNA double helix by breaking the hydrogen bonds between the two strands, allowing the replication machinery to access the DNA template for synthesis.
Why does DNA replication occur at multiple points along the DNA strand?
-If replication started at only one point and proceeded along the entire DNA molecule, it would take too long due to the DNA's length. To speed up the process, replication occurs at multiple points simultaneously, forming replication forks.
What are replication forks, and why are they important?
-Replication forks are areas where the DNA double helix is being unwound by helicase, allowing replication to proceed. Multiple replication forks occur simultaneously, increasing the speed of DNA replication.
What does it mean that DNA replication is semiconservative?
-Semiconservative replication means that each new DNA molecule consists of one original strand (the old strand) and one newly synthesized strand. This ensures that the genetic information is preserved.
How is energy provided for the formation of new DNA strands?
-Energy for forming the covalent bonds between nucleotides comes from the nucleotide itself. Nucleotides arrive with three phosphate groups, and the removal of two phosphates releases energy to form the bond with the next nucleotide.
What are Okazaki fragments, and why are they formed?
-Okazaki fragments are short sequences of DNA nucleotides that are synthesized discontinuously on the lagging strand during replication. They are necessary because DNA polymerase can only synthesize DNA in the 5' to 3' direction, and the lagging strand runs in the opposite direction.
What is the function of the primase enzyme in DNA replication?
-Primase synthesizes a short RNA primer, which provides a starting point for DNA polymerase to begin adding nucleotides. DNA polymerase requires this primer because it cannot start synthesizing a new strand on its own.
Why is the mutation rate of DNA polymerase not zero, and why is this important?
-The mutation rate of DNA polymerase is low but not zero, which is essential for evolution. Small mutations allow for genetic variation, which drives evolutionary change, but a very high mutation rate could be harmful, leading to genetic disorders.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)