VCE PE - Glycogen Sparing
Summary
TLDRThe video discusses glycogen sparing and the role of carbohydrates and fats as energy sources during exercise. It explains how the body primarily uses fat at low intensities and shifts to carbohydrates at higher intensities, with a key crossover point around 65% VO2 Max. Enhanced aerobic fitness through training increases VO2 Max, allowing athletes to utilize fat more efficiently and conserve glycogen for critical moments in a race. This adaptation not only helps maintain energy levels but also provides a competitive edge during the final sprint.
Takeaways
- 😀 The primary fuel sources for performance are carbohydrates and fats, with protein being used only in extreme situations.
- 😀 At low exercise intensities, the body predominantly utilizes fat, while carbohydrates become the primary fuel source at high intensities.
- 😀 The crossover point where carbohydrate and fat contribution is 50/50 typically occurs at around 65% of an individual's VO2 max.
- 😀 Training can increase an individual's VO2 max, allowing them to perform at higher intensities with less effort.
- 😀 An increase in VO2 max means that the same absolute intensity (e.g., running speed) can feel easier and requires less carbohydrate energy.
- 😀 An untrained individual may use about 80% carbohydrates and 20% fat at higher intensities, leading to quicker depletion of carbohydrate stores.
- 😀 In contrast, a trained individual may achieve a 50/50 split in energy contribution at the same running speed, leading to better fat utilization.
- 😀 The body has approximately 2,000 calories of stored carbohydrates and around 100,000 calories of stored fat, making fat depletion unlikely during exercise.
- 😀 Maintaining energy levels during endurance activities can be improved by utilizing fat as a fuel source and conserving glycogen for later use.
- 😀 Overall, increasing aerobic fitness allows for better glycogen sparing, benefiting performance towards the end of a race.
Q & A
What are the primary food fuels used for performance in exercise?
-The primary food fuels used for performance are carbohydrates and fats, while protein is generally only used in extreme circumstances when glycogen and fat stores are depleted.
How does the body utilize fats and carbohydrates at different exercise intensities?
-At low exercise intensities, the body predominantly uses fat. As intensity increases, the reliance shifts towards carbohydrates, with a 50/50 split occurring around 65% of VO2 Max.
What is VO2 Max and how does it relate to exercise intensity?
-VO2 Max is the maximum rate of oxygen consumption during intense exercise. It serves as a benchmark for determining exercise intensity, with higher VO2 Max values allowing for greater performance efficiency.
What changes occur in energy source utilization after aerobic training?
-After aerobic training, an individual's VO2 Max can increase, allowing them to perform at higher intensities with a greater reliance on fat for energy, thereby sparing glycogen.
What happens to carbohydrate stores during prolonged exercise?
-An untrained individual may deplete their carbohydrate stores (around 2,000 calories) in about 2.5 hours of exercise, whereas a trained individual can sustain exercise for close to 4 hours by using fats more effectively.
How does the contribution of energy from carbohydrates and fats change in trained versus untrained individuals at the same running pace?
-An untrained individual running at a steady pace may get about 80% of their energy from carbohydrates and 20% from fat, while a trained individual may achieve a 50/50 split in energy contribution.
What is glycogen sparing and why is it important for endurance athletes?
-Glycogen sparing refers to the body's ability to conserve carbohydrate stores by using more fat for energy during exercise, which is crucial for endurance athletes to maintain energy levels throughout longer events.
How does aerobic fitness affect the perceived intensity of exercise?
-With improved aerobic fitness, individuals can perform at the same pace with less perceived effort, as they can rely more on fat and less on carbohydrates for energy.
What is the significance of maintaining the same running speed with an increased VO2 Max?
-Maintaining the same running speed with a higher VO2 Max indicates that the exercise intensity feels easier due to improved aerobic capacity, allowing for better energy utilization.
What are the potential caloric contributions from carbohydrates and fats at a running pace of 14 km/h for trained individuals?
-At a running pace of 14 km/h, trained individuals may derive approximately 500 calories from carbohydrates and 500 calories from fats, totaling 1,000 calories required for that energy demand.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

SEMINÁRIO 9 - INTEGRAÇÃO METABÓLICA E HORMONAL DURANTE A PRÁTICA DO EXERCÍCIO FÍSICO

5. Carbohydrate Metabolism During Exercise
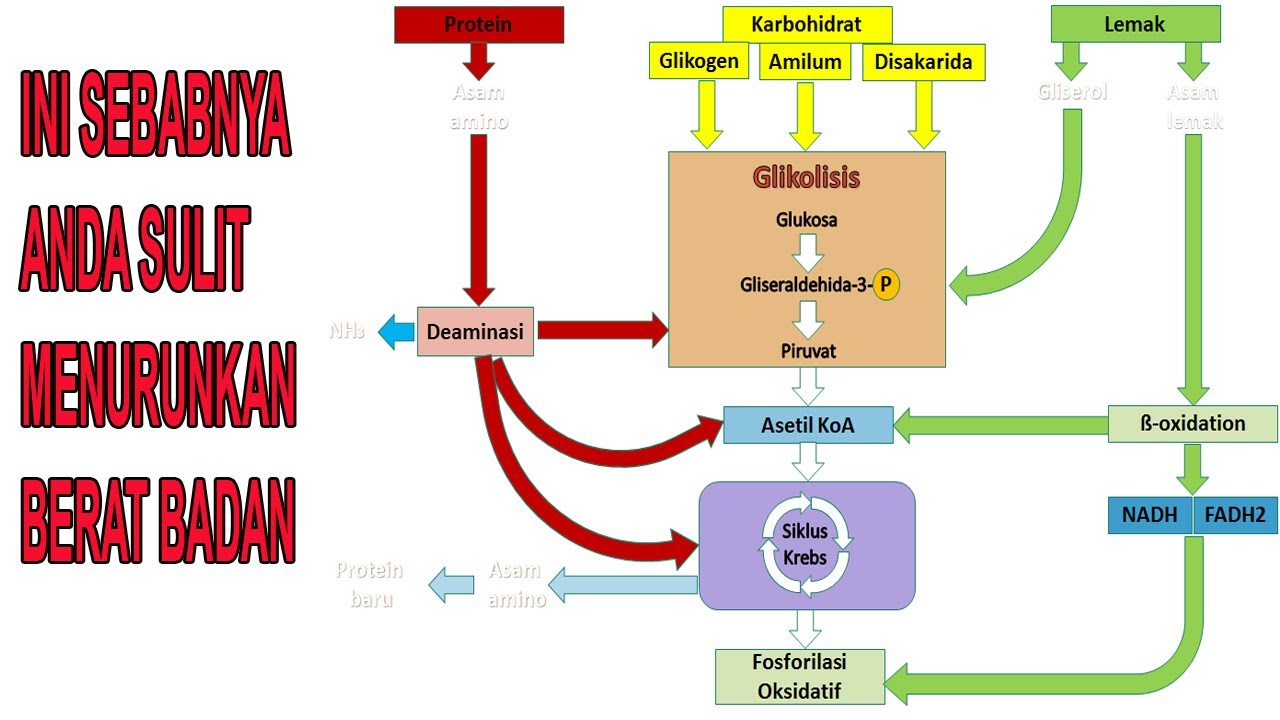
CARBOHYDRATE, FAT AND PROTEIN METABOLISM PATHWAYS

Carbohydrates | Organic Chemistry | Chemistry | FuseSchool
Carbohydrates

How The Body Uses Food - You Are What You Eat - How Are Carbohydrates, Protein, Fat Used In The Body
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)