01 01 Innate Recognition of Pathogens
Summary
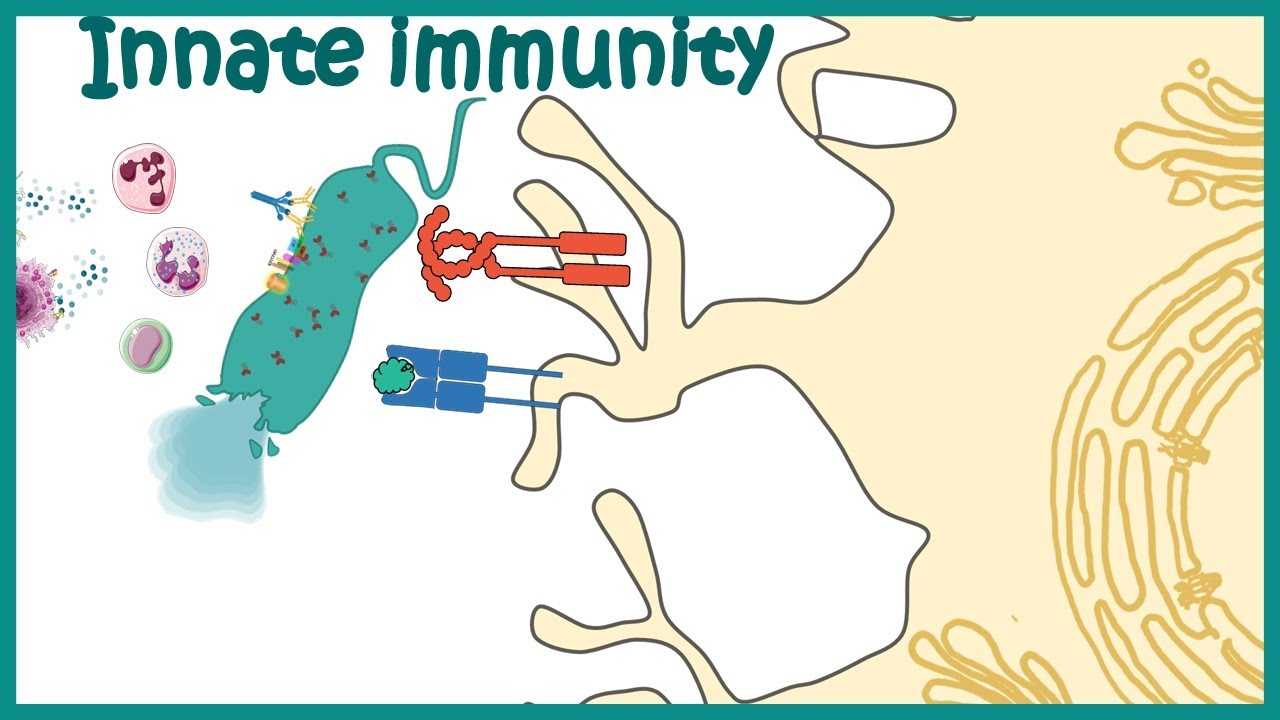
TLDRThe innate immune system serves as the first line of defense against pathogens, with dendritic cells playing a pivotal role. These cells recognize pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs), particularly lipopolysaccharides (LPS) from gram-negative bacteria, through toll-like receptors (TLRs), notably TLR4. The binding of LPS, facilitated by the LPS binding protein (LBP) and CD14, triggers dendritic cell maturation. This process enables dendritic cells to migrate to lymph nodes, where they activate the adaptive immune response, highlighting their essential function in bridging innate and adaptive immunity.
Takeaways
- 😀 The innate immune system is the first line of defense against pathogens.
- 😀 Dendritic cells play a crucial role in recognizing pathogens through pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs).
- 😀 PAMPs are conserved features of pathogens, including components like lipopolysaccharides (LPS) found in gram-negative bacteria.
- 😀 Dendritic cells express toll-like receptors (TLRs) to recognize PAMPs.
- 😀 TLR4 is a specific receptor that recognizes LPS on the surface of dendritic cells.
- 😀 LPS is transported to dendritic cells by the soluble LPS-binding protein (LBP).
- 😀 The binding of LPS to the CD14 protein on dendritic cells facilitates its detection by TLR4.
- 😀 The interaction between TLR4 and LPS triggers the maturation of dendritic cells.
- 😀 Mature dendritic cells migrate to regional lymph nodes to activate the adaptive immune response.
- 😀 This process underscores the importance of dendritic cells in linking the innate and adaptive immune responses.
Q & A
What role does the innate immune system play in the immune response?
-The innate immune system recognizes the presence of pathogens and serves as the first line of defense against infections.
What are dendritic cells and their function in the immune response?
-Dendritic cells are specialized immune cells that circulate through tissues and have the ability to recognize pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs).
What are pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs)?
-PAMPs are conserved features of pathogens, such as lipopolysaccharides (LPS) found in the cell membranes of gram-negative bacteria.
How do dendritic cells recognize PAMPs?
-Dendritic cells recognize PAMPs through a family of receptors known as toll-like receptors (TLRs).
Which toll-like receptor is specifically involved in recognizing LPS?
-TLR4 is the toll-like receptor that recognizes lipopolysaccharides (LPS) on the surface of dendritic cells.
What role does the LPS-binding protein (LBP) play in the immune response?
-The LPS-binding protein transports LPS to the surface of dendritic cells and helps deposit it on the cell surface protein CD14.
What happens when LPS is bound to CD14 on dendritic cells?
-When LPS binds to CD14, TLR4 recognizes it, and this interaction initiates a signaling cascade that leads to the maturation of the dendritic cell.
What is the significance of dendritic cell maturation?
-Maturation of dendritic cells enables them to migrate to regional lymph nodes and activate the adaptive immune response.
What is the adaptive immune response?
-The adaptive immune response is a specific and long-lasting immune response that is activated by the recognition of pathogens, involving B cells and T cells.
Why is the recognition of LPS important in the immune system?
-Recognizing LPS is crucial for the immune system to respond effectively to gram-negative bacterial infections, enabling a rapid and appropriate immune reaction.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)