Sistema Imunológico Inato e Adaptativo - Aula 28 - Módulo VII - Histologia e Fisiologia Humana
Summary
TLDRIn this biology lesson, Professor Guilherme explains the immune system, detailing its two key defense systems: innate and adaptive immunity. He discusses the body's first line of defense, such as skin and mucous membranes, followed by chemical barriers and phagocytic cells. The lecture emphasizes the role of antibodies and immune responses, including primary and secondary immune responses. The teacher also highlights the importance of immunoglobulins and how they interact with pathogens. This lesson covers crucial concepts in immunology, including vaccination and the immune system's ability to adapt and fight off infections like viruses and bacteria.
Takeaways
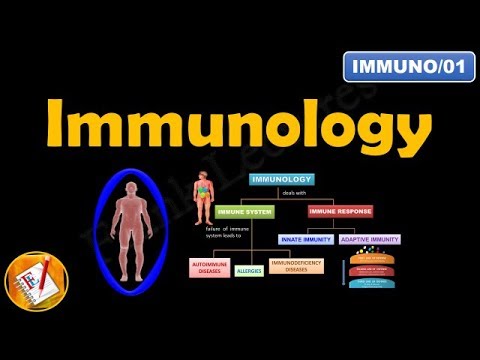
- 😀 The immune system is crucial for defending the body against infectious agents like viruses, bacteria, fungi, and toxins.
- 😀 There are two main types of immune systems: innate (non-specific) and adaptive (specific).
- 😀 The innate immune system includes physical barriers like skin and mucous membranes, which prevent the entry of microorganisms.
- 😀 Chemical barriers, like stomach acid and enzymes in tears, are part of the innate immune system and help eliminate harmful microorganisms.
- 😀 Phagocytic cells, such as macrophages and neutrophils, are a key component of the innate immune system, engulfing and destroying pathogens.
- 😀 The adaptive immune system becomes more specialized over time, responding specifically to pathogens the body has encountered before.
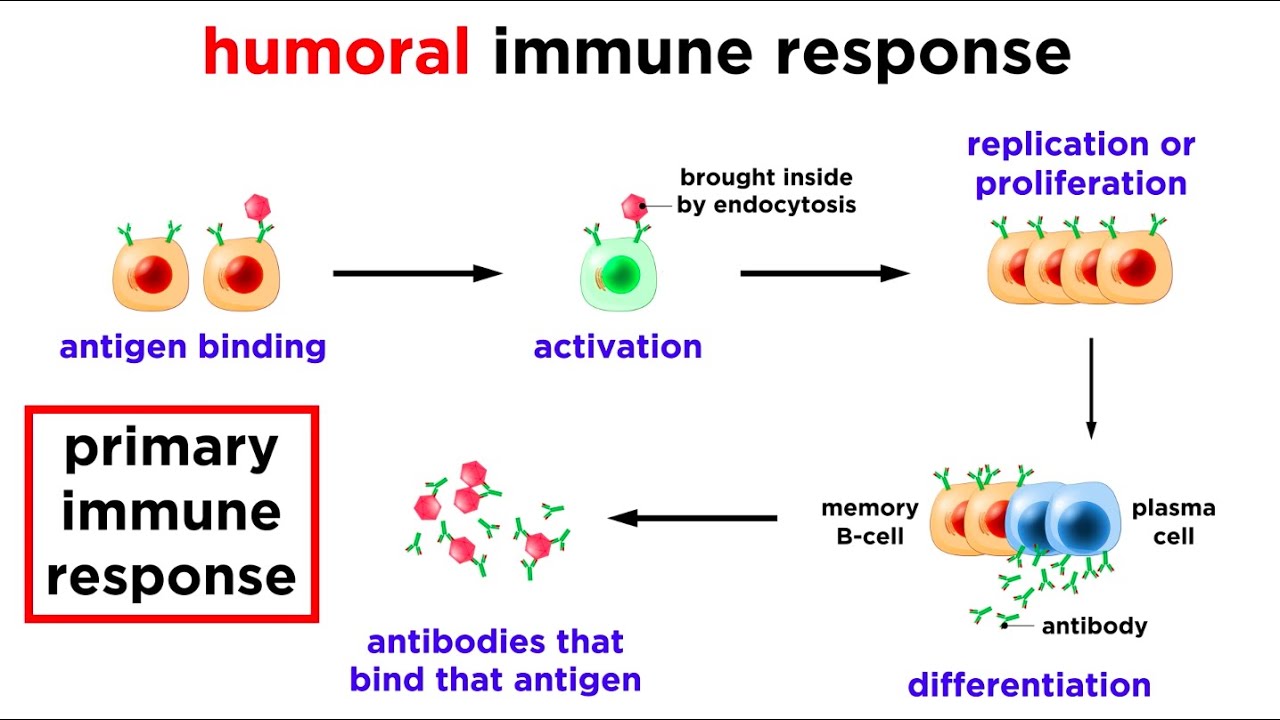
- 😀 Antibodies (also called immunoglobulins) are proteins produced by B lymphocytes that target specific antigens on pathogens.
- 😀 The immune system has a primary and secondary response. The primary response is slower and produces fewer antibodies, while the secondary response is faster and more intense due to immune memory.
- 😀 Immunoglobulins like IgE are important for defense against allergens and larger parasites, while IgG is the most common antibody, aiding in pathogen recognition and neutralization.
- 😀 Vaccination helps stimulate the adaptive immune system, making it recognize and defend against specific pathogens, such as the flu virus.
- 😀 Immunoglobulin IgM is the first to be produced during an infection, and IgG is the main antibody involved in long-term immunity, including passing immunity from mother to child via the placenta.
Q & A
What are the two main types of immune defense systems?
-The two main types of immune defense systems are the innate immune system and the adaptive immune system. The innate system is present from birth and provides a general, non-specific defense against a wide range of pathogens. The adaptive immune system, on the other hand, is more specific and develops over time in response to exposure to specific pathogens.
What are the first and second lines of defense in the innate immune system?
-The first line of defense in the innate immune system includes physical barriers such as the skin and mucous membranes. These prevent the entry of microorganisms into the body. The second line of defense involves chemical substances and cells such as acid in the stomach and enzymes like lysozyme in tears, which break down pathogens.
How does the skin function as a barrier in the immune system?
-The skin functions as a barrier by being composed of multiple layers of cells that prevent the proliferation of microorganisms. Its structure is crucial in preventing harmful agents from entering the body.
What is the role of mucous membranes in the immune defense?
-Mucous membranes line various body cavities and secrete mucus, which traps foreign particles like dust, pollen, and pathogens. Cilia in the mucous membranes then help to move these trapped particles out of the body, contributing to defense against infections.
What are phagocytic cells and what is their role in the immune system?
-Phagocytic cells, such as neutrophils and macrophages, are responsible for engulfing and destroying pathogens. They play a key role in the innate immune system by eliminating microorganisms through a process called phagocytosis.
What is the difference between innate immunity and adaptive immunity?
-Innate immunity is non-specific and provides immediate defense against a broad range of pathogens. Adaptive immunity, in contrast, is specific to particular pathogens and improves over time through exposure and immunological memory.
What is the role of antibodies in the immune response?
-Antibodies, also known as immunoglobulins, are proteins produced by B lymphocytes that specifically target and neutralize foreign invaders like viruses and bacteria. They bind to antigens on the surface of pathogens, marking them for destruction by other immune cells.
How does the immune system respond to reinfection by the same pathogen?
-During reinfection, the immune system responds more rapidly and effectively due to immunological memory. The adaptive immune system, which has previously recognized and fought off the pathogen, produces a quicker and more intense response, preventing symptoms from appearing.
What is the significance of IgG antibodies in immune defense?
-IgG antibodies are the most abundant type of antibodies in the blood and are crucial for fighting infections. They facilitate the process of phagocytosis by marking pathogens, making them easier for immune cells to identify and destroy.
What is the difference between primary and secondary immune responses?
-The primary immune response occurs when the body encounters a pathogen for the first time. It is slower and produces fewer antibodies. The secondary immune response is faster and more efficient due to the presence of memory cells that remember the pathogen from previous encounters.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)