Newton and Free Body Diagrams
Summary
TLDRIn this lesson on dynamics, the focus is on drawing Free Body Diagrams (FBDs) and understanding Newton's Laws of Motion. Students learn to represent the forces acting on an object, emphasizing that only external forces are included. Examples include a book on a desk and a sled being pushed, illustrating concepts like gravity, normal force, and friction. The lesson then covers Newton's three laws: the law of inertia, the relationship between force, mass, and acceleration, and the action-reaction principle. Together, these concepts provide a foundational understanding of how forces influence motion.
Takeaways
- 😀 Free body diagrams (FBDs) illustrate all external forces acting on an object, excluding internal forces.
- 😀 Forces in FBDs are represented as vector arrows pointing away from the object, indicating direction and magnitude.
- 😀 In simple scenarios, like a book on a desk, the forces include gravity and the normal force from the desk.
- 😀 When pushing a box, forces such as gravity, normal force, applied force, and friction come into play.
- 😀 Newton's first law (law of inertia) states that an object remains at rest or in uniform motion unless acted upon by an unbalanced force.
- 😀 Inertia is directly related to mass; larger masses have greater inertia and resist changes in motion more effectively.
- 😀 The second law of motion (F = ma) indicates that acceleration is directly proportional to net force and inversely proportional to mass.
- 😀 A Newton (N) is defined as 1 kg·m/s², making it a derived unit based on base units of mass and acceleration.
- 😀 The third law states that for every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction, illustrated by examples like punching a wall.
- 😀 Real-world applications of these laws, such as the importance of wearing seatbelts, highlight the relevance of physics in everyday life.
Please replace the link and try again.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Introduction to Free Body Diagrams or Force Diagrams

Forces and Dynamics - free body diagrams - (IB Physics, AP, GCSE, A level)

Fisika SMA - Hukum Newton (1) - Jenis-Jenis Gaya, Menguraikan Gaya Pada Benda (I)

06 03 Fisika Dasar 1- Diagram Gaya Benda Bebas
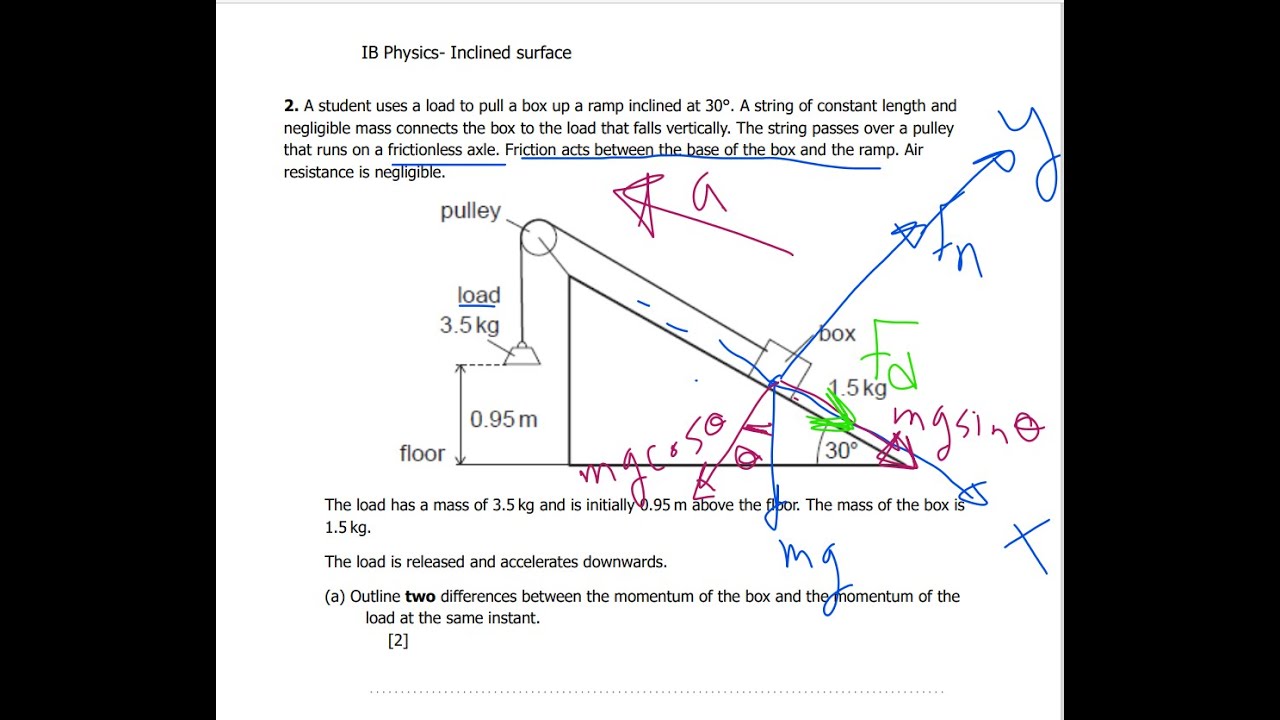
IB Physics-Theme-A2- A student uses a load to pull a box up a ramp inclined

3_LEYES DE NEWTON
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)