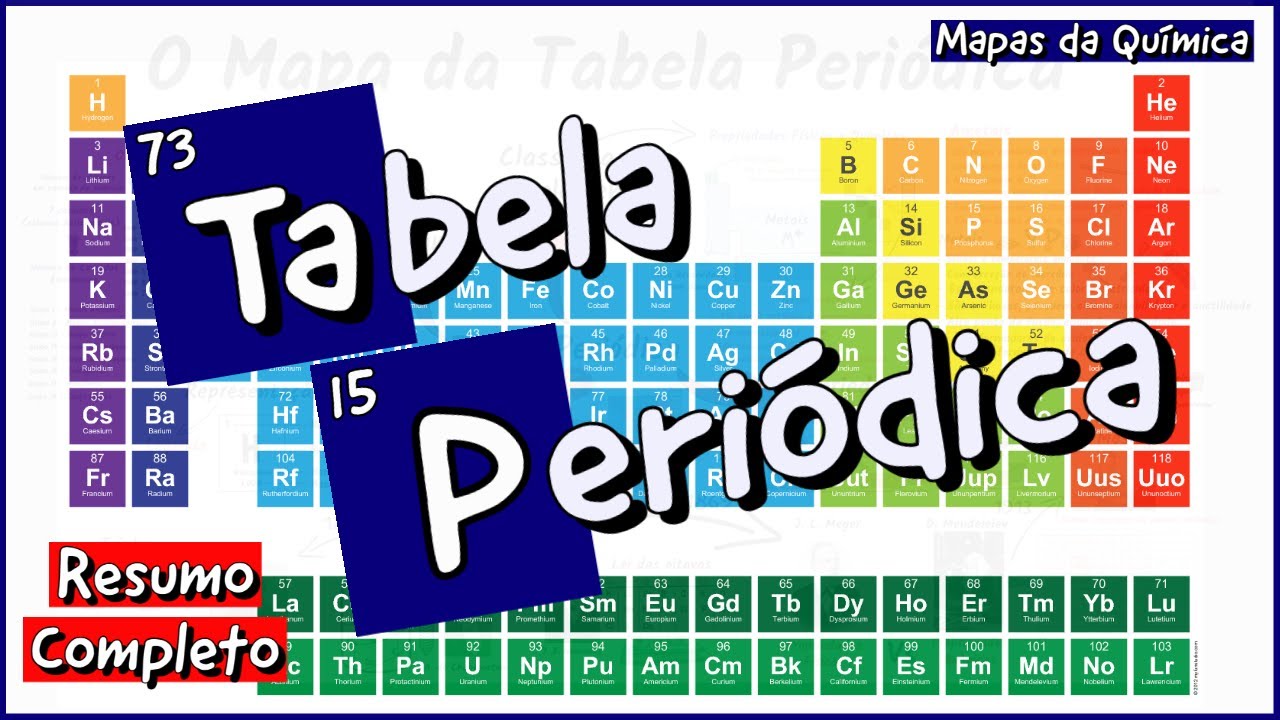
TABEL PERIODIK MODERN | MENENTUKAN GOLONGAN DAN PERIODE
Summary
TLDRThis video provides an insightful overview of the modern periodic table, highlighting its structure and organization based on atomic numbers. It explains the significance of groups and periods, detailing how elements are classified into 18 groups and seven periods. The video also discusses electronic configurations, emphasizing the role of valence electrons in determining the chemical properties of elements. Special attention is given to lanthanides and actinides, which are positioned separately due to their unique characteristics. Overall, it serves as an educational guide to understanding the periodic table's layout and the relationship between electronic structure and element behavior.
Takeaways
- 😀 The modern periodic table organizes elements by increasing atomic number, reflecting their periodic properties.
- 😀 Groups in the periodic table are vertical columns, numbered from 1 to 18, with similar chemical properties due to the same number of valence electrons.
- 😀 Periods are horizontal rows numbered from 1 to 7, representing the number of electron shells in the elements.
- 😀 The modern method of group numbering contrasts with the traditional method, which used Roman numerals and labeled main and transition groups.
- 😀 Elements are categorized into four blocks (s, p, d, and f) based on their electron configurations.
- 😀 Valence electrons in the outermost shell determine an element's chemical behavior, with elements in the same group sharing similar properties.
- 😀 Group 1A elements have one valence electron, while Group 2A elements have two, affecting their reactivity.
- 😀 Groups 3A to 8A have increasing numbers of valence electrons, culminating in Group 8A, which has eight (except for helium).
- 😀 To determine an element's group and period, analyze its electron configuration and count the valence electrons.
- 😀 An example illustrates how to classify an element based on its electron configuration, identifying its group and period accordingly.
Q & A
What is the modern periodic table based on?
-The modern periodic table is organized based on the increasing atomic number of elements.
How many groups and periods are in the modern periodic table?
-The modern periodic table consists of 18 groups and 7 periods.
What are the main groups in the periodic table, and how are they labeled?
-The main groups are labeled 1A to 8A, where 1A includes alkali metals and 8A includes noble gases.
What distinguishes main groups from transition groups in the periodic table?
-Main groups (1A-8A) have a specific naming convention based on their properties, while transition groups (1B-8B) are labeled with Roman numerals and letters.
What are the four blocks of the periodic table based on electron configurations?
-The four blocks are Block S (groups 1A and 2A), Block P (groups 3A to 8A), Block D (transition metals), and Block F (lanthanides and actinides).
How can you identify the group of an element using its electron configuration?
-You can identify the group by looking at the last electron's sublevel; for example, if it ends in s or p, it indicates a main group.
What is the significance of valence electrons in the periodic table?
-Valence electrons determine the chemical properties of elements, with elements in the same group having the same number of valence electrons.
How do periods correspond to the structure of elements in the periodic table?
-Periods indicate the number of electron shells, with elements in the same period having the same highest occupied energy level.
What are the characteristics of elements in the same group?
-Elements in the same group typically have similar chemical properties due to their identical number of valence electrons.
How can the period of an element be determined from its electron configuration?
-The period can be determined by identifying the highest occupied energy level in the electron configuration.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)