Simulasi dan Penjelasan Percobaan Gaya Gerak Listrik (GGL) / Induksi Elektromagnetik Michael Faraday
Summary
TLDRThis educational video explores Michael Faraday's groundbreaking experiment on electromagnetic induction, demonstrating how electric current is generated by moving a magnet through a coil. The video explains key concepts such as magnetic fields, the significance of the coil's turns, and the effects of the magnet's strength and speed on the induced current. Using simulations, viewers witness how the light bulb illuminates when the magnet moves, indicating current flow. The session emphasizes the importance of change in magnetic field lines as the fundamental mechanism behind the induction of electric current, making complex concepts accessible and engaging.
Takeaways
- 😀 Michael Faraday's experiments demonstrate the principles of electromagnetic induction, showing how electric current can be generated by moving a magnet near a coil.
- 🔋 The setup includes a light bulb connected to a coil (kumparan) and a magnet with distinct north and south poles, illustrating the flow of electricity.
- 🔄 When the magnet is moved through the coil, an electric current is induced, causing the light bulb to light up.
- 🚫 No current is produced when the magnet is stationary, emphasizing the importance of movement in generating electricity.
- ⚡ The direction of the induced current changes when the magnet is reversed, demonstrating the relationship between magnet orientation and current flow.
- 📏 The use of a voltmeter allows for the measurement of voltage changes as the magnet moves, indicating the presence of electric current.
- 🏃♂️ Faster movement of the magnet through the coil results in a stronger induced current, highlighting the effect of speed on electromagnetic induction.
- 🌀 The number of coils in the setup plays a crucial role; more coils lead to a higher electromotive force (gaya gerak listrik) and stronger current.
- 🔍 The strength of the magnet also influences the amount of induced current, with stronger magnets generating larger currents.
- 🔑 Key factors influencing induced current include the number of coils, speed of magnet movement, and magnet strength.
Q & A
What is the main topic of the video?
-The main topic of the video is Michael Faraday's experiment on electromagnetic induction, which demonstrates how a magnetic field can generate electric current.
What equipment is used in the experiment?
-The experiment uses a light bulb, a coil (or winding), and a magnet with defined north and south poles.
How does the movement of the magnet affect the light bulb?
-When the magnet is moved into the coil, the light bulb lights up, indicating that electric current is generated. If the magnet is stationary or removed, the current ceases.
What is electromotive force (EMF)?
-Electromotive force (EMF) is the induced voltage generated in the coil due to the changing magnetic field.
How does the speed of the magnet affect induced current?
-The speed of the magnet's movement significantly affects the induced current; faster movement produces a larger current.
What role does the voltmeter play in the experiment?
-The voltmeter is used to measure the direction and magnitude of the induced current, with its needle deflecting based on the pole of the magnet being inserted or removed.
What is magnetic flux, and why is it important?
-Magnetic flux refers to the number of magnetic field lines passing through a given area. It is crucial because changes in magnetic flux are what induce current in the coil.
How does the number of turns in the coil affect induced voltage?
-Increasing the number of turns in the coil enhances the induced voltage (GGL), as more magnetic field lines cut through the coil, leading to a greater current.
What can be concluded about the relationship between magnetic field strength and induced current?
-Stronger magnets generate a larger induced current, demonstrating that the strength of the magnetic field directly influences the amount of current produced.
What key factors influence the generation of induced electromotive force?
-The key factors are the number of turns in the coil, the speed of the moving magnet, and the strength of the magnetic field.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
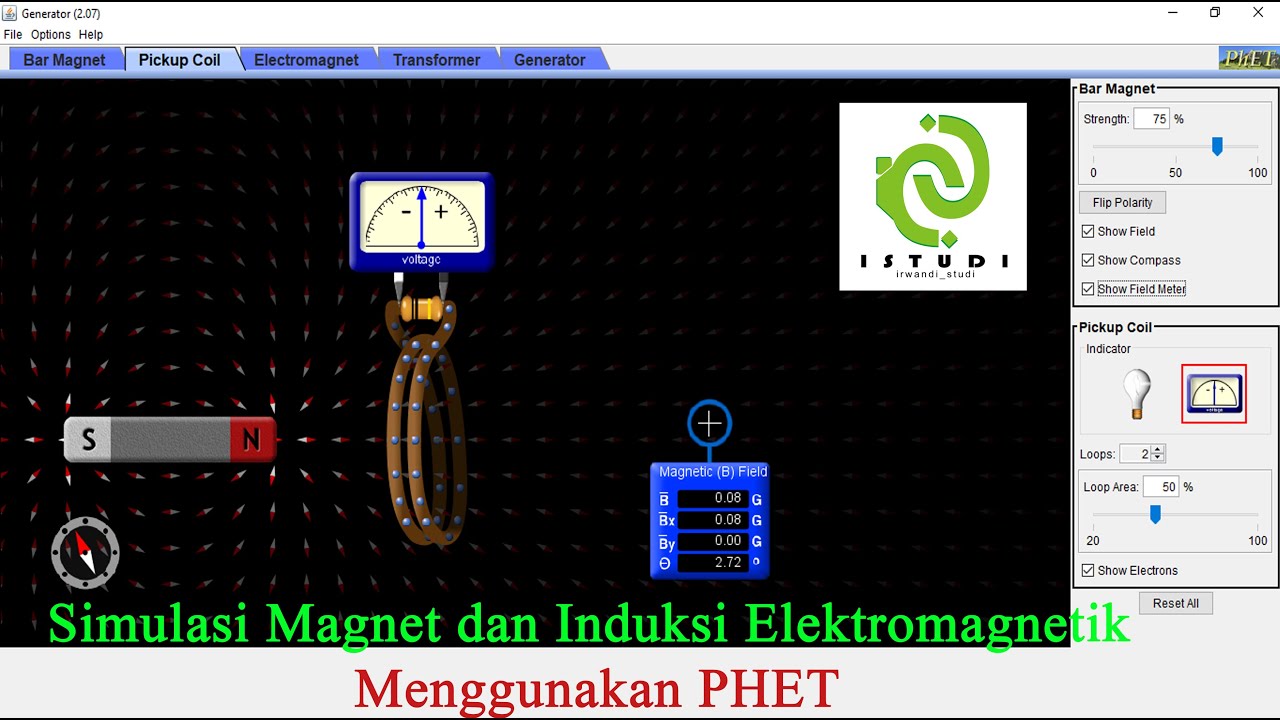
Simulasi Magnet dan Induksi Elektromagnetik Menggunakan PHET

Electromagnetic Induction | #aumsum #kids #science #education #children

Electromagnetic induction (& Faraday's experiments)

IPA kelas 9 Semester 2 : Kemagnetan (Part 4 : induksi elektromagnet)
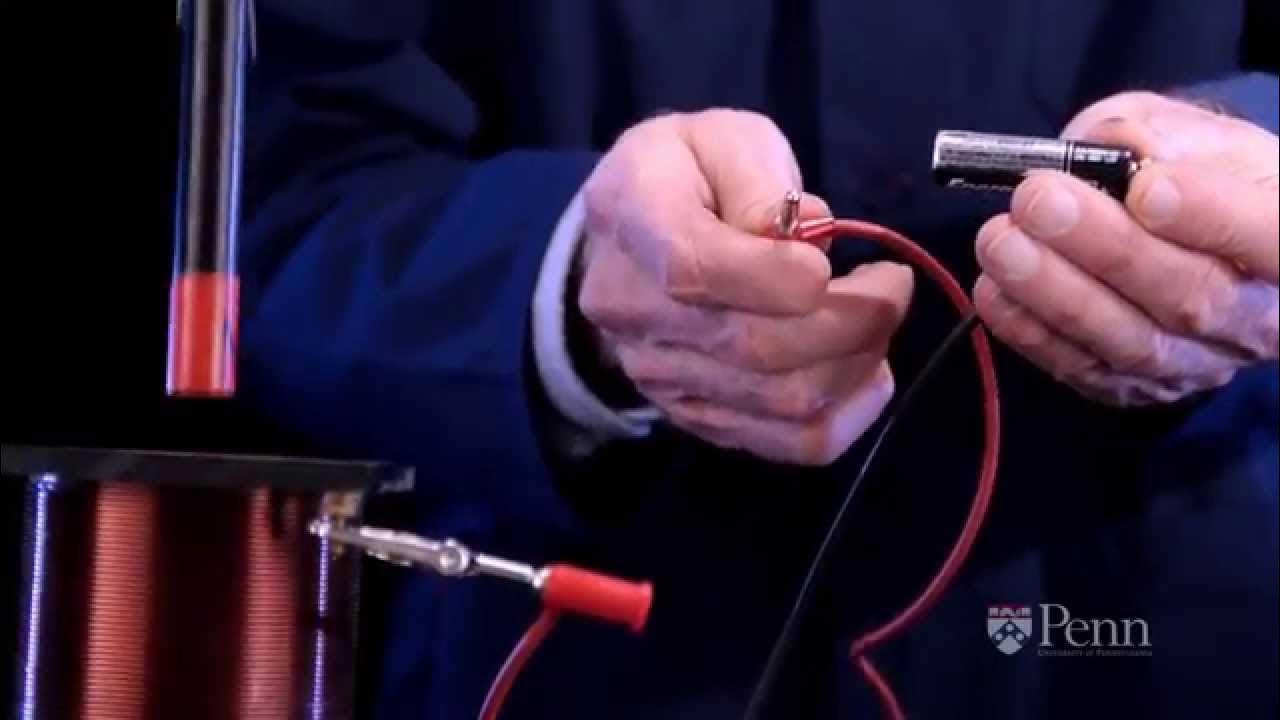

Faraday's Law of Induction Demonstration - Penn Physics
Materi Kemagnetan Kelas 9 (Part-5) Induksi Elektromagnetik
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)