Y1 34) Price Controls (Minimum/Maximum Prices) and Market Failure
Summary
TLDRThis video discusses price controls, focusing on minimum prices (price floors) and maximum prices (price ceilings) as solutions to market failures. It explores the implementation of minimum pricing for alcohol in places like Scotland to combat overconsumption and its unintended consequences, such as black markets and increased inequality. The video also examines maximum prices set to enhance equity in essential goods, like housing, highlighting the risks of shortages and poor quality. Ultimately, it emphasizes the complexities and challenges of applying these controls effectively without causing further market distortions.
Takeaways
- 😀 Price controls are government interventions designed to correct market failures by establishing minimum and maximum prices.
- 🍺 Price floors (minimum prices) aim to reduce the consumption of goods with negative externalities, like alcohol.
- 📉 Implementing a minimum price above the equilibrium can lead to a contraction in demand and an overall reduction in quantity consumed.
- 💰 Minimum prices can disproportionately affect low-income individuals, increasing income inequality as they bear a larger financial burden.
- 🚫 A rise in minimum prices may encourage black market activity as consumers seek cheaper alternatives, leading to potential health risks.
- 👷♂️ Excessively high minimum prices can result in unintended consequences, including job losses in affected industries and government failure.
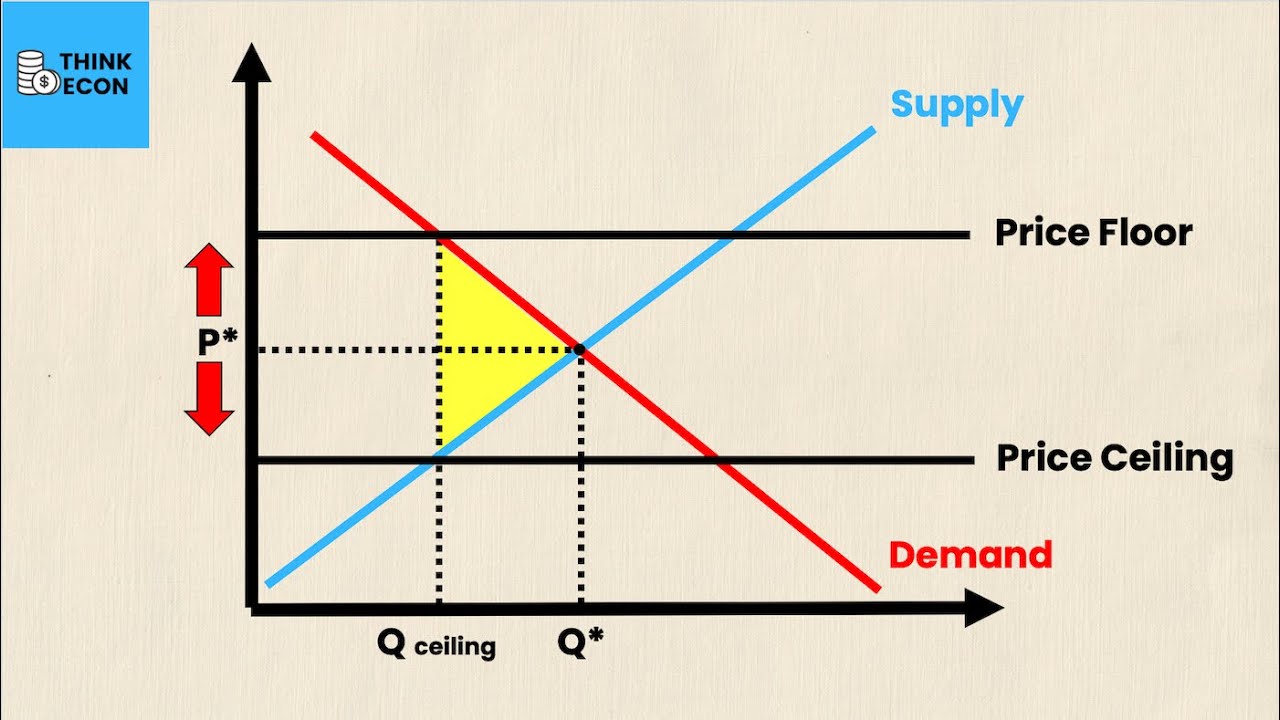
- 🏠 Price ceilings (maximum prices) are intended to make essential goods, such as housing, more affordable to promote equity.
- 📊 While maximum prices can lower costs, they often create shortages as demand exceeds supply, leading to inefficiencies in the market.
- 💼 The emergence of a black market is a common consequence of price ceilings, where landlords may charge higher prices than the set maximum.
- 🔍 Effective enforcement of price ceilings can be challenging and costly for governments, further complicating the intended outcomes of these policies.
Q & A
What is the purpose of implementing a minimum price or price floor?
-A minimum price is set to discourage the consumption of demerit goods, such as alcoholic drinks, by internalizing negative externalities and reducing overconsumption.
How does a minimum price affect the equilibrium in the market?
-By establishing a minimum price above the equilibrium, demand contracts, leading to a decrease in the quantity consumed and produced, moving towards a socially optimal output.
What are some potential drawbacks of a minimum price?
-Drawbacks include price inelastic demand potentially limiting the reduction in quantity, regressive impacts on low-income individuals, the risk of black market emergence, and possible negative consequences for producers.
What is the relationship between minimum price and income inequality?
-Minimum pricing can exacerbate income inequality as it disproportionately affects low-income individuals who spend a higher percentage of their income on the regulated good.
What are the unintended consequences of a high minimum price?
-A high minimum price can lead to government failure, including decreased producer activity, unemployment, and possibly encouraging illegal market transactions.
What is the function of a maximum price or price ceiling?
-A maximum price is implemented to make essential goods, like rent, more affordable by preventing prices from rising above a certain level, thus promoting equity.
What challenges arise from setting a maximum price?
-Setting a maximum price can create shortages due to increased demand and decreased supply, leading to black market activities and a misallocation of resources.
How does a maximum price lead to black market activities?
-When a maximum price creates excess demand, landlords may charge higher prices on the black market, exploiting those who are unable to find affordable housing.
What impact does a price ceiling have on the quality of goods?
-With a price ceiling, the quality of goods, such as rented accommodation, may decline as landlords may not have the financial incentive to maintain or improve properties.
What are the enforcement challenges associated with price ceilings?
-Enforcement of price ceilings can be difficult, as it requires monitoring and regulation to ensure compliance, which can lead to further government inefficiencies.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Price Ceilings and Floors- Micro Topic 2.8

Micro: Unit 1.4 -- Government Intervention: Price Controls, Quotas, and Subsidies

Penawaran, Permintaan, dan Efisiensi Pasar: Surplus Konsumen, Produsen, Deadweight Loss (Part 30)

Episode 15: Price Floors and Price Ceilings
Price Ceiling and Price Floor | Think Econ

💱 Price System | Free Market vs. Government Intervention
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)