Hoe weet je welke sport het beste bij je past?
Summary
TLDRThe video script delves into the world of sports and genetics, exploring how the composition of fast and slow muscle fibers can determine an individual's athletic prowess and suitability for certain sports. Eline Lievens, a movement scientist, explains that the ratio of these fibers is largely genetically determined and can be accurately measured using a new, painless MRI scanning method she developed. This method is particularly beneficial for aspiring top athletes, allowing them to understand their strengths and weaknesses and potentially predict their success in specific sports. The video also touches on the importance of tailored training approaches based on an athlete's muscle fiber type, emphasizing that a one-size-fits-all training regimen may not be the most effective strategy. By knowing one's muscle fiber type, athletes can strategically use their abilities in competitions and optimize their training routines to prevent injuries and enhance performance.
Takeaways
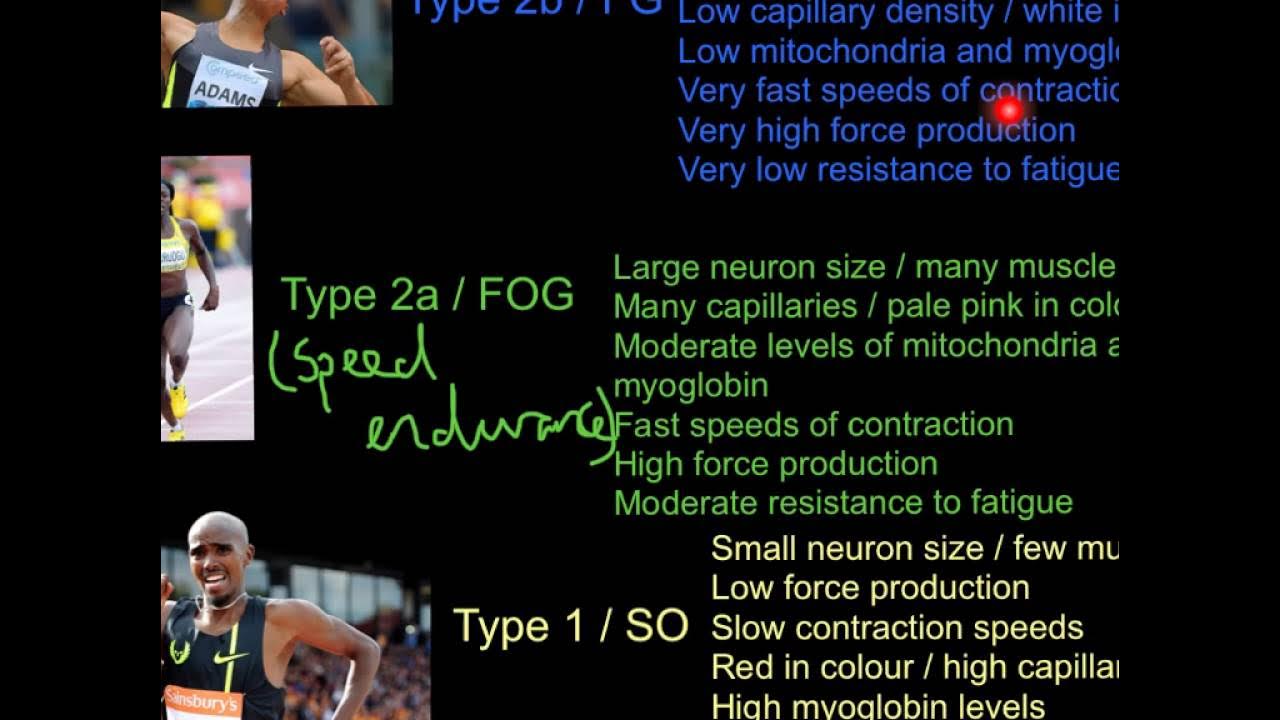
- 🏃♂️ The human muscles consist of two types of muscle fibers: fast and slow, which determine the type of sports one is suited for.
- 💪 Fast muscle fibers are explosive and suitable for activities like sprinting and weightlifting, while slow muscle fibers are for endurance sports like marathons.
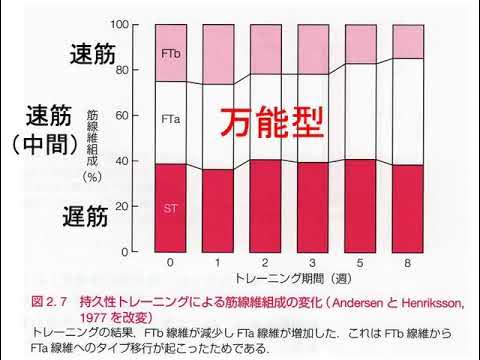
- ⚖️ The ratio of fast to slow muscle fibers is largely genetically determined and cannot be significantly altered by training.
- 🧬 Slow muscle fibers contain more mitochondria, which allows them to produce energy for a longer time compared to fast muscle fibers.
- 📉 Traditional methods of measuring muscle fiber type, such as muscle biopsies, are invasive, painful, and not entirely representative.
- 🛠️ Eline Lievens has developed a new, non-invasive method using MRI scans to measure muscle fiber type without causing pain or requiring recovery time.
- 📚 This new technique allows for a much larger sample size to be measured, providing a more accurate assessment of muscle fiber composition.
- 👟 While sprint or jump tests can give an indication of muscle fiber type, factors like footwear, fatigue, experience, and motivation can influence the results.
- 🎯 The new scanning method is particularly interesting for aspiring top athletes who want to understand their strengths and weaknesses to excel in their chosen sport.
- 🏅 Coaches often use a one-size-fits-all approach to training, but knowing an athlete's muscle fiber type can lead to more personalized and effective training regimens.
- 🤔 Different muscle fiber types may require different training strategies; for example, athletes with fast muscle fibers may need more rest to avoid injury.
- 🧠 Understanding muscle fiber types can also inform tactical decisions during competitions, helping athletes to leverage their strengths against opponents with different muscle compositions.
Q & A
What are the two types of muscle fibers that our muscles are composed of?
-Our muscles are composed of two types of muscle fibers: fast-twitch and slow-twitch fibers.
How does the ratio of fast-twitch to slow-twitch muscle fibers determine an individual's suitability for certain sports?
-The ratio of fast-twitch to slow-twitch muscle fibers determines an individual's natural athletic abilities, with more fast-twitch fibers being beneficial for explosive, short-duration sports, and more slow-twitch fibers being advantageous for endurance sports.
What are some examples of sports that would benefit from having a higher proportion of fast-twitch muscle fibers?
-Sports such as sprinting, weightlifting, BMX racing, and high jumping would benefit from having a higher proportion of fast-twitch muscle fibers due to their explosive and power-intensive nature.
What is the disadvantage of having predominantly fast-twitch muscle fibers?
-The disadvantage of having predominantly fast-twitch muscle fibers is that they fatigue more quickly and cannot sustain activity for as long as slow-twitch muscle fibers.
Why are slow-twitch muscle fibers more prevalent in athletes like marathon runners and triathletes?
-Slow-twitch muscle fibers are more prevalent in marathon runners and triathletes because they have a higher endurance capacity, allowing for sustained energy production over longer periods.
How does the presence of mitochondria in slow-twitch muscle fibers contribute to their function?
-The presence of more mitochondria in slow-twitch muscle fibers allows them to produce energy for a much longer time compared to fast-twitch fibers, making them ideal for endurance activities.
What was the traditional method used to measure an individual's muscle fiber type, and why was it considered unpleasant?
-The traditional method involved taking a muscle biopsy, which involved cutting a piece of muscle from the athlete's leg using a needle. It was considered unpleasant due to the pain involved and the fact that it was not entirely representative or accurate.
How does the new, non-invasive method developed by Eline Lievens measure muscle fiber type?
-The new method involves placing an athlete under an MRI scanner and measuring the muscle fiber type based on the signal from the entire body, providing a much larger sample size and a more accurate representation without causing pain or requiring recovery from an injury.
Is it necessary for every young athlete to undergo an MRI scan to determine their muscle fiber type?
-No, it is not necessary for every young athlete to undergo an MRI scan. The scan is more relevant for aspiring top athletes who wish to understand their strengths and weaknesses to potentially excel in a specific sport.
How can knowing one's muscle fiber type influence training and competition strategies?
-Knowing one's muscle fiber type can help tailor training programs to the individual's natural abilities, allowing for more effective use of their strengths and mitigating the risk of injury. It can also inform tactical decisions during competitions, such as pacing and energy management.
What is the significance of the muscle fiber type in determining how an athlete should train and compete?
-The muscle fiber type is significant as it can indicate whether an athlete is naturally more suited to explosive or endurance activities. This knowledge can be used to optimize training routines, recovery periods, and competitive strategies to maximize performance and reduce the risk of injury.
Why might a 'one-size-fits-all' approach to coaching not be the most effective strategy?
-A 'one-size-fits-all' approach to coaching may not be effective because it does not take into account the individual muscle fiber types and their corresponding needs. Athletes with different muscle fiber compositions may require different training intensities, durations, and recovery times to perform optimally.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)