(OLD VERSION) The Demand Curve Shifts
Summary
TLDRIn this video, Tyler explores the dynamics of the demand curve, emphasizing how shifts occur due to changes in market demand. He explains that an increase in demand results in a higher quantity demanded at every price, while a decrease signifies a lower willingness to pay. Key factors influencing demand include income changes, population shifts, prices of substitutes and complements, consumer expectations, and evolving tastes. Tyler clarifies the distinction between changes in quantity demanded and changes in demand, ensuring viewers grasp these critical economic concepts for better understanding market behavior.
Takeaways
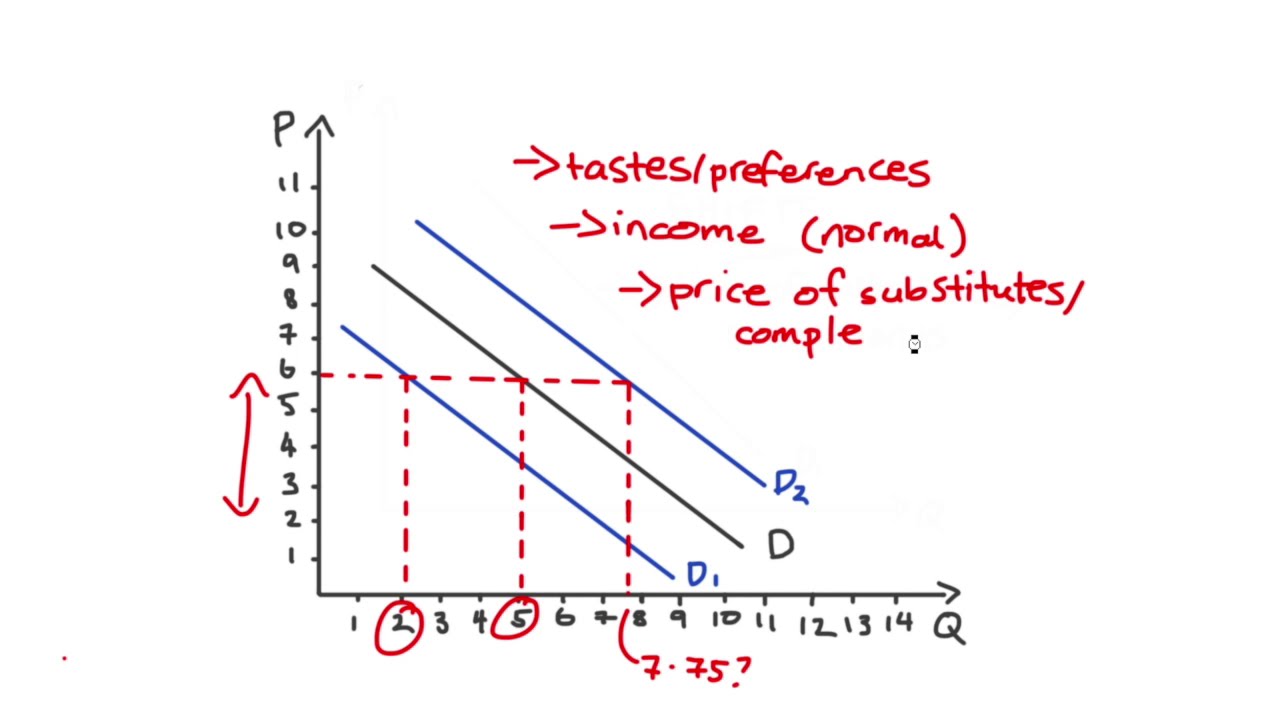
- 😀 A demand curve illustrates the quantity demanded at various prices, showing the relationship between price and quantity.
- 📈 An increase in demand shifts the demand curve outward, indicating a higher quantity demanded at every price.
- 📉 A decrease in demand shifts the demand curve inward, reflecting a lower quantity demanded at every price.
- 💰 Factors that can cause an increase in demand include changes in income, population, and consumer preferences.
- 🛒 Normal goods see increased demand when incomes rise, while inferior goods experience decreased demand as incomes increase.
- 👶 Population changes impact demand; more people can lead to increased demand for certain goods, like diapers.
- 🔄 The price of substitutes affects demand; an increase in the price of one good can raise demand for its substitute.
- 🥨 Complementary goods see decreased demand if the price of one good rises, affecting the demand for the other.
- 🔮 Consumer expectations about future prices can shift demand today, often leading to increased purchases in anticipation.
- 🍔 Understanding the distinction between 'change in quantity demanded' (movement along the curve) and 'change in demand' (shift of the curve) is crucial in economics.
Q & A
What is a demand curve?
-A demand curve is a graphical representation that shows the quantity demanded of a good at different prices, illustrating the relationship between price and quantity demanded.
What happens to the demand curve when there is an increase in demand?
-When there is an increase in demand, the demand curve shifts outward (to the right), indicating a higher quantity demanded at every price level.
How can an increase in income affect the demand for goods?
-An increase in income typically leads to an increase in demand for normal goods (e.g., luxury items) and a decrease in demand for inferior goods (e.g., cheap fast food).
What are some examples of factors that can shift the demand curve?
-Factors that can shift the demand curve include changes in income, population changes, prices of substitutes and complements, consumer expectations, and changes in consumer tastes.
What is the difference between normal goods and inferior goods?
-Normal goods see an increase in demand as consumer income rises, while inferior goods see a decrease in demand when income increases, as consumers tend to buy better alternatives.
How does the population size influence demand?
-An increase in population generally leads to an increase in demand for various goods because there are more potential buyers in the market.
What occurs to the demand for a good when the price of its substitute rises?
-When the price of a substitute rises, the demand for the original good increases, as consumers will switch to the less expensive option.
What does a decrease in demand indicate?
-A decrease in demand is indicated by a leftward shift of the demand curve, meaning that at each price level, the quantity demanded is lower.
What are complements, and how do they affect demand?
-Complements are goods that are often used together. An increase in the price of one complement typically decreases the demand for the other complement.
What is the difference between a change in quantity demanded and a change in demand?
-A change in quantity demanded refers to a movement along a fixed demand curve due to a price change, while a change in demand refers to a shift of the entire demand curve due to factors other than price.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)