Respirasi Pada Tumbuhan
Summary
TLDRIn this presentation by Group 4, the concept of respiration in plants is explored, highlighting its essential role in absorbing oxygen from the atmosphere to produce carbon dioxide, water, and energy vital for growth. The process occurs during both day and night, alongside photosynthesis. Key stages include oxygen capture, gas diffusion, and the various types of respiration: aerobic and anaerobic. Factors affecting respiration rates, such as temperature, humidity, and plant age, are also discussed. The informative session aims to enhance understanding of plant respiration and its significance in the ecosystem.
Takeaways
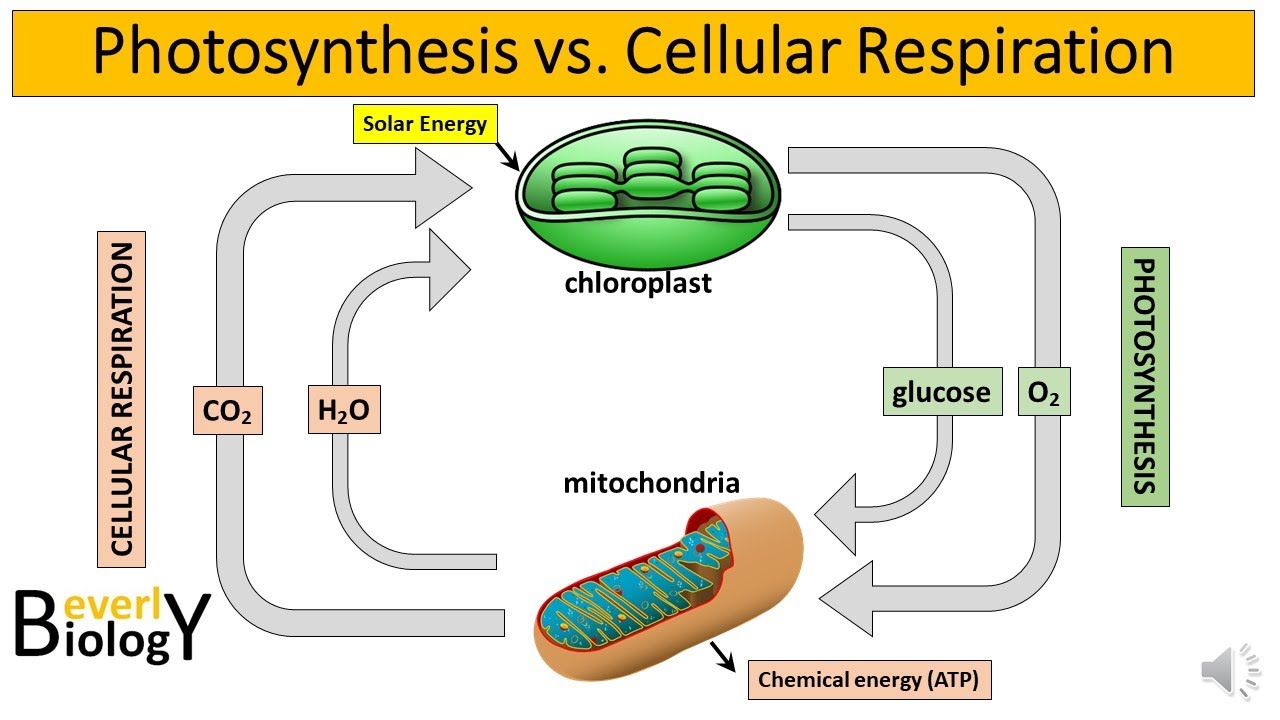
- 🌱 Respiration in plants refers to the absorption of oxygen from the air to produce carbon dioxide, water, and energy necessary for growth.
- 💨 The chemical reaction for respiration is represented as C6H12O6 + O2 → CO2 + H2O + energy.
- ☀️ Plants perform respiration during both day and night, with photosynthesis occurring simultaneously in daylight.
- 🌜 Respiration continues at night when photosynthesis does not take place.
- 🔄 The process of plant respiration includes several stages, starting with oxygen capture from the environment.
- 🌬️ Gas exchange in plants occurs through diffusion, allowing oxygen to enter and carbon dioxide to exit the cells.
- ⚗️ The main stages of respiration are glycolysis, oxidative decarboxylation, the citric acid cycle, and electron transport.
- 🧬 Aerobic respiration requires oxygen, while anaerobic respiration does not.
- 🌡️ The rate of photosynthesis is influenced by several factors, including temperature, substrate type and amount, humidity, and plant age.
- 🌿 Understanding plant respiration is essential for recognizing how plants grow and develop in different environmental conditions.
Q & A
What is respiration in plants?
-Respiration in plants is the process of absorbing oxygen from the atmosphere to produce carbon dioxide, water, and energy, which are essential for plant growth and development.
What is the chemical equation for respiration in plants?
-The respiration process can be represented by the equation: C6H12O6 + O2 → CO2 + H2O + energy.
When does respiration occur in plants?
-Respiration occurs during the day and night. During the day, it happens alongside photosynthesis, while at night, respiration continues when photosynthesis is not taking place.
What are the stages involved in the respiration process of plants?
-The stages of respiration in plants include glycolysis, oxidative decarboxylation, the citric acid cycle, and electron transport.
What is the difference between aerobic and anaerobic respiration in plants?
-Aerobic respiration requires oxygen, while anaerobic respiration does not require oxygen.
How does carbon dioxide produced during respiration exit the plant?
-Carbon dioxide produced during respiration is released from the plant cells through the process of diffusion.
What factors influence the rate of photosynthesis in plants?
-The rate of photosynthesis is influenced by several factors, including temperature, type and amount of substrate, humidity, amount of oxygen, and the type and age of the plant.
What role does oxygen play in plant respiration?
-Oxygen is crucial for aerobic respiration, as it is used to break down glucose to release energy.
What happens during the glycolysis stage of respiration?
-During glycolysis, glucose is broken down into pyruvate, which is a crucial step in the respiration process.
What is the significance of energy produced during respiration?
-The energy produced during respiration is essential for various physiological processes in plants, including growth, nutrient uptake, and overall metabolism.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)