Fungsi Permintaan
Summary
TLDRThis educational video introduces business mathematics, focusing on linear functions in the business context. It covers three key applications: demand and supply functions, break-even points, and depreciation. The presenter explains the demand function, illustrating its inverse relationship with price through examples and graphical representations. Viewers learn to determine price and quantity limits, predict demand, and derive demand functions from given data points. The engaging presentation concludes with a promise to continue exploring supply functions in the next video, making it an essential resource for understanding essential business concepts.
Takeaways
- 📊 The video focuses on the application of linear functions in business, specifically demand and supply models, break-even points, and depreciation.
- 🛒 Demand and supply are influenced by price (P) and quantity (Q), with demand showing an inverse relationship with price.
- 📉 The demand function is generally represented as Qd = A - B * P, where A is the intercept and B is a negative slope.
- 🔄 The law of demand states that as the price of a good increases, the quantity demanded decreases, and vice versa.
- 📈 Demand curves typically slope downwards from left to right, indicating this inverse relationship.
- 📏 It’s essential to properly label axes when graphing demand curves, whether using horizontal or vertical orientations.
- ⚖️ Certain conditions, like perfectly inelastic demand, result in vertical demand curves where quantity remains constant regardless of price.
- ❓ Example problems are provided to illustrate how to determine price and quantity limits based on a demand function.
- 🔍 The video also explains how to find the demand function when price and quantity data are given, emphasizing the use of linear equations.
- 🎥 The lesson concludes with an invitation to the next video, which will cover supply functions.
Q & A
What is the main focus of the video?
-The video focuses on the application of linear functions in business, specifically discussing demand and supply functions, break-even points, and depreciation.
What are the three types of applications of linear functions in business mentioned in the video?
-The three types are: 1) Demand and Supply functions, 2) Break Even Point, and 3) Depreciation.
How is demand represented in a linear function?
-Demand is represented by the function Q_d = a - bP, where 'a' is the intercept (a positive value) and 'b' is the slope (a negative value).
What does the law of demand state?
-The law of demand states that if the price of a good increases, the quantity demanded decreases, and vice versa.
How does a price change affect the demand curve?
-A price increase typically results in a movement along the demand curve to a lower quantity demanded, while a price decrease results in a movement to a higher quantity demanded.
What happens to the demand curve when the price is zero?
-When the price is zero, the quantity demanded will reach its maximum, as consumers are willing to take as much of the good as is available for free.
What does it mean if the demand function results in a negative quantity?
-A negative quantity is not feasible, as it indicates an impossible situation where the demand cannot be less than zero; thus, the quantity demanded must always be non-negative.
What are the limitations of using demand functions in predicting market behavior?
-Demand functions provide predictions based on established relationships, but they can be inaccurate due to market fluctuations, consumer preferences, and other external factors.
How can producers utilize the demand function in their business strategies?
-Producers can use the demand function to forecast how many goods to supply at different price points, helping to avoid overproduction or stock shortages.
What was the example given to illustrate the calculation of demand?
-An example was given where the demand function is Q_d = 50 - 5P, allowing the determination of price and quantity limits for various scenarios.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Calculus made EASY! 5 Concepts you MUST KNOW before taking calculus!
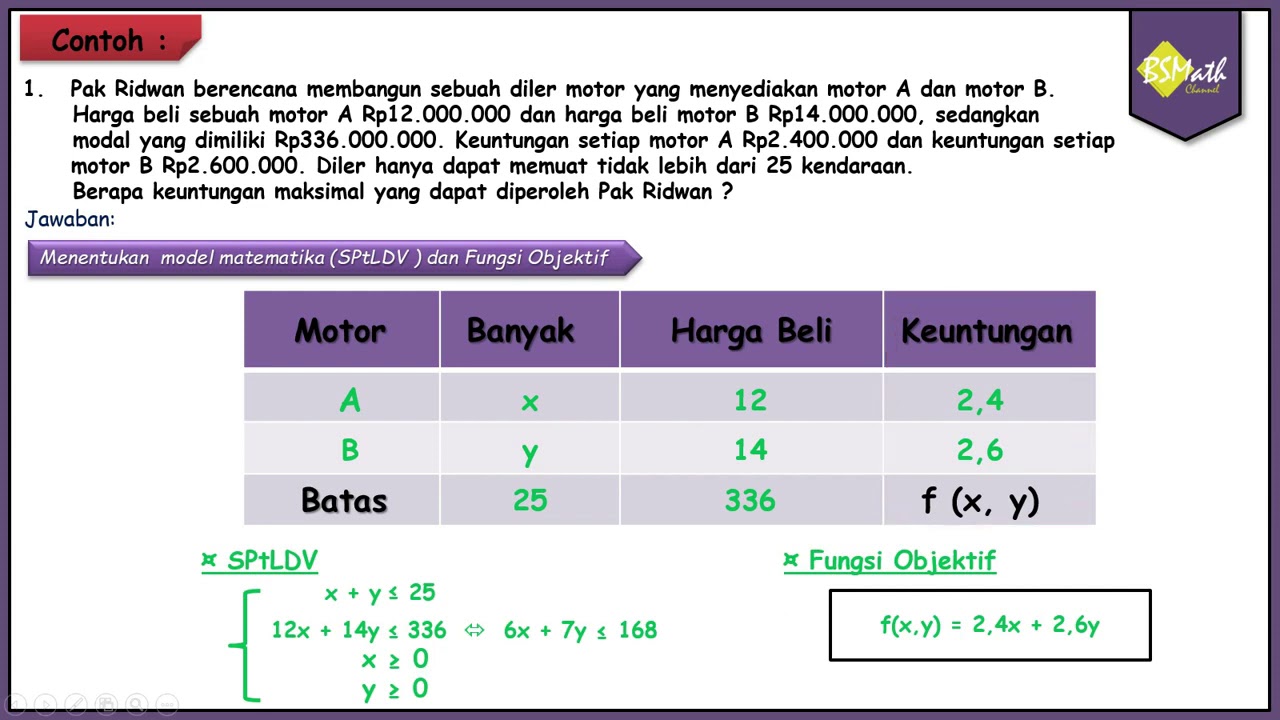
Menyelesaikan Permasalahan Program Linear Menentukan Nilai Optimum dengan Metode Uji Titik Pojok

Sesi 3 Matematika Bisnis; Penerapan Fungsi Linier dalam Bidang Ekonomi

FASE 4 - VIDEOAULA 1 - MATEMÁTICA - DESAFIO CRESCER SAEB (3ª SÉRIE)
Matematika Teknik 4. Fungsi

Matematika Keuangan dan Bisnis - Ep.03 Pengenalan Fungsi
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)