Bivariate Analysis for Categorical & Numerical | Statistics Tutorial #20 | MarinStatsLectures
Summary
TLDRThis video provides a comprehensive overview of the relationship between categorical (X) and numeric (Y) variables, focusing on the distinction between paired and independent groups. It discusses methods of analysis suitable for each type, emphasizing paired designs like before/after experiments and independent comparisons such as smokers versus non-smokers. Key statistical tests, including the paired t-test and one-way ANOVA, are outlined, highlighting their appropriate contexts. The video aims to equip viewers with foundational knowledge to navigate statistical analyses effectively.
Takeaways
- 📊 Understanding the relationship between a categorical variable (X) and a numeric variable (Y) is crucial for statistical analysis.
- 📈 Side-by-side box plots are effective visual tools for comparing groups in this context.
- 🤝 Paired groups involve the same individuals in different conditions, while independent groups consist of different individuals in each condition.
- 🧪 Examples of paired designs include before-and-after experiments and crossover designs where the same individual receives both treatments.
- 👥 Independent groups examples include comparisons such as smokers versus non-smokers, where individuals cannot belong to both groups.
- ⚖️ Pairing reduces biological variability, allowing for clearer comparisons based on the treatment rather than individual differences.
- 🔍 Subjectivity in matching individuals can complicate paired analyses, making it difficult to find appropriate matches.
- 🚦 Ensuring comparability in independent groups is essential; confounding factors like age or occupation must be controlled.
- 🔄 Randomization helps balance characteristics across groups in independent designs, improving the validity of findings.
- 📅 The choice of statistical tests depends on whether groups are paired or independent and how many groups are being compared.
Q & A
What is the primary focus of the discussion in the transcript?
-The primary focus is on the relationship between categorical variables (X) and numeric variables (Y), emphasizing how to analyze these relationships using appropriate statistical methods.
How can data be visualized when analyzing categorical and numeric variables?
-Data can be visualized using side-by-side box plots, which allow for comparison of distributions between different groups.
What is the difference between paired and independent groups?
-Paired groups involve the same individuals being measured under different conditions, while independent groups consist of different individuals in each group, with no overlap between them.
Can you provide an example of a paired design?
-A simple example is a before-and-after experiment where the same individuals are measured before receiving a treatment and then after.
What is a crossover design in the context of paired groups?
-A crossover design involves administering two different treatments to the same individual at different times, allowing for direct comparison of the treatments within the same person.
What are some advantages of using paired designs?
-Paired designs decrease biological variability by ensuring that comparisons are made within the same individuals, isolating the treatment effect.
What challenges exist when matching individuals in paired designs?
-Matching individuals can be subjective and challenging; finding appropriate matches based on relevant characteristics is not always straightforward.
How can researchers ensure that independent groups are comparable?
-Researchers can use randomization to assign individuals to groups, ensuring that other characteristics are balanced. They can also restrict the analysis to specific characteristics or adjust statistically to account for differences.
What statistical methods are appropriate for comparing two paired groups?
-For comparing two paired groups, the paired t-test (parametric) and the Wilcoxon signed-rank test (nonparametric) are appropriate methods.
What is the purpose of using statistical adjustments in independent groups?
-Statistical adjustments help to control for confounding factors that may affect the outcome, ensuring that the comparison between groups more accurately reflects the treatment effect.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
Bivariate Analysis Meaning | Statistics Tutorial #19 | MarinStatsLectures

UJI CHI-SQUARE TEORI DAN CONTOH KASUS PART 1
Variables and Types of Variables | Statistics Tutorial | MarinStatsLectures

One Way ANOVA (Analysis of Variance): Introduction | Statistics Tutorial #25 | MarinStatsLectures
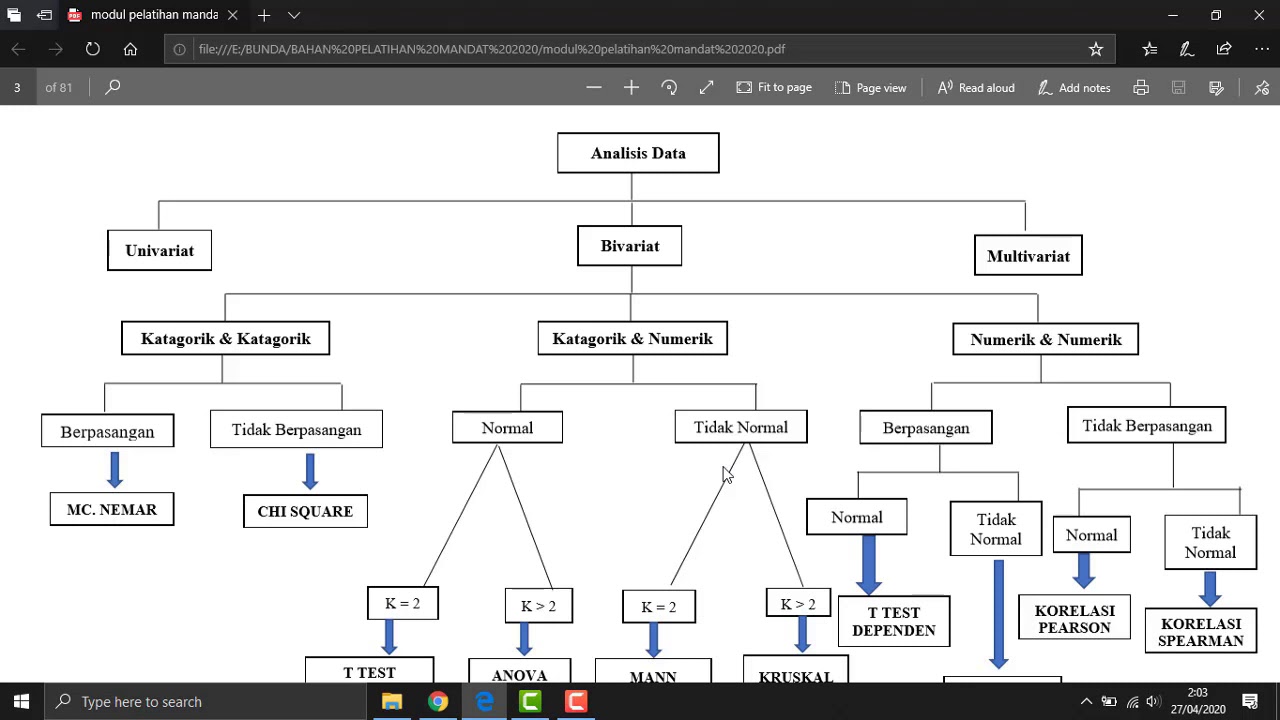
VIDEO 3 Jenis uji statistik AWAL

Uji t dengan Microsoft Excel
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)