Photosynthesis Part 2: The Calvin Cycle | Animated Music Video |
Summary
TLDRThe video delves into the Calvin cycle, a crucial part of photosynthesis where plants synthesize food. It explains how sunlight powers the light reactions to produce ATP and NADPH, which are then utilized in the Calvin cycle to convert carbon dioxide into glucose. The process unfolds in three phases: Carbon Fixation, PGA Reduction, and the Regeneration of RuBP. Throughout the cycle, molecules like G3P are generated, ultimately leading to the formation of glucose. The repetitive nature of the cycle highlights its vital role in sustaining plant life and energy production.
Takeaways
- 🌱 The Calvin cycle synthesizes sugars from carbon dioxide in a cyclic process that operates independently of sunlight.
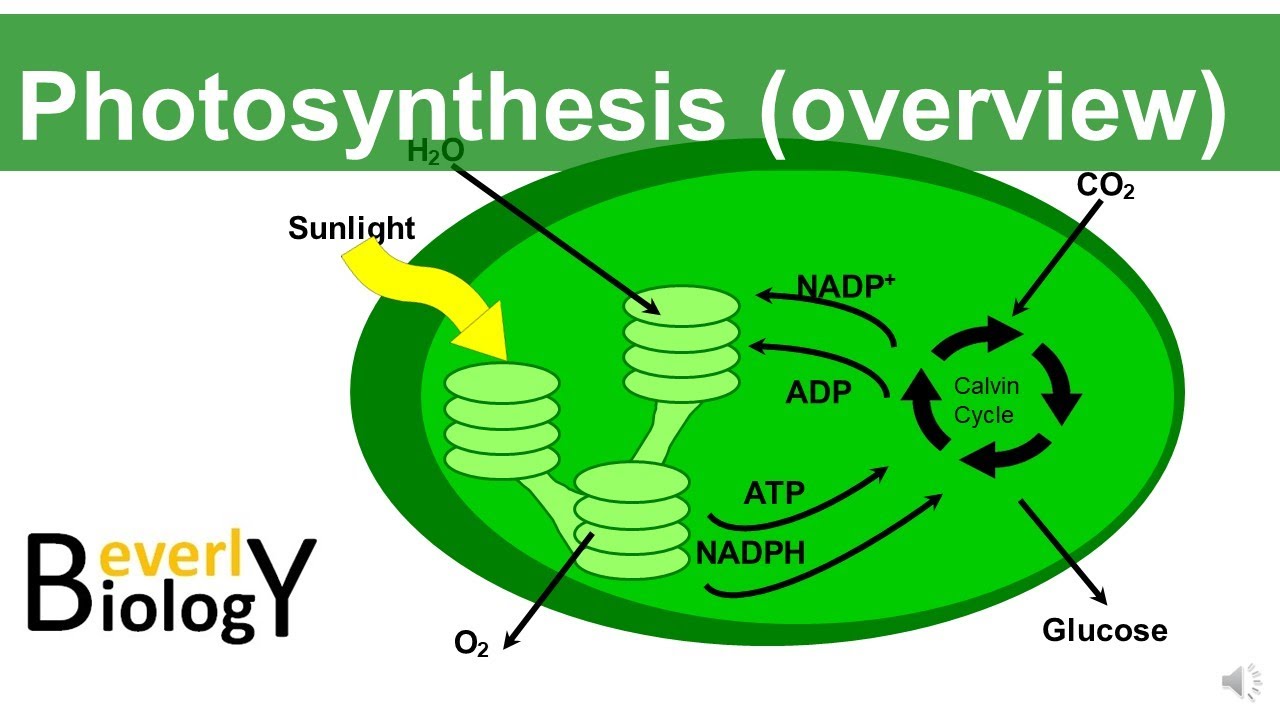
- ☀️ Photosynthesis consists of two main parts: light reactions (which generate ATP and NADPH) and the Calvin cycle.
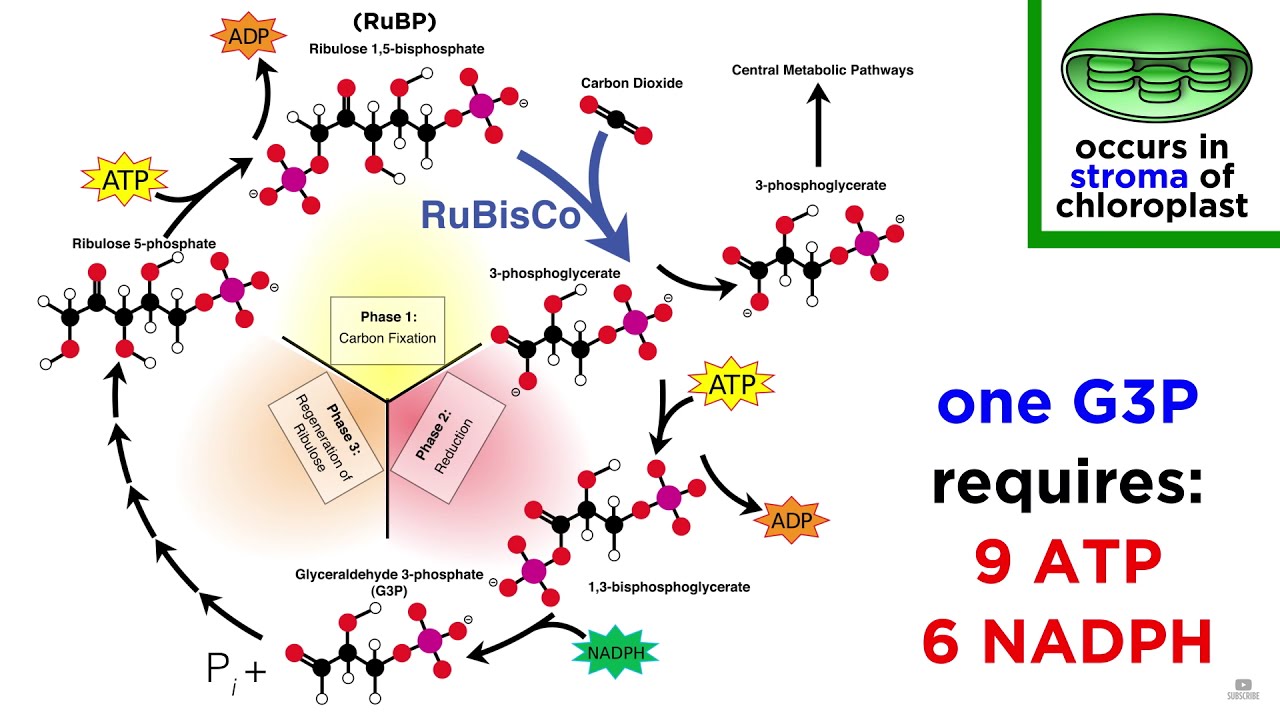
- 💡 The Calvin cycle occurs in the stroma of the chloroplast, where CO2 is fixed into a starting compound called RuBP.
- 🔗 Carbon fixation is the first phase of the Calvin cycle, facilitated by the enzyme rubisco, forming an unstable six-carbon compound.
- 🔄 The unstable six-carbon compound quickly splits into two molecules of PGA (phosphoglycerate), marking the start of sugar formation.
- ⚡ In the second phase, ATP and NADPH convert PGA into G3P (glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate), a three-carbon sugar.
- 🍬 Two G3P molecules combine to form glucose (C6H12O6), demonstrating how the cycle produces essential sugars for the plant.
- 🔄 The Calvin cycle must complete six turns to produce one molecule of glucose, requiring a total of 36 carbons from 12 G3P.
- 🔄 The regeneration of RuBP is crucial for the cycle to continue, involving the enzymatic rearrangement of G3P molecules.
- 🌍 Overall, the Calvin cycle allows plants to convert CO2 into glucose and other organic molecules, vital for their energy needs.
Q & A
What is the Calvin cycle?
-The Calvin cycle is a part of photosynthesis that synthesizes sugar from carbon dioxide, occurring independently of sunlight.
What are the two main parts of photosynthesis?
-The two main parts of photosynthesis are the light reactions and the Calvin cycle.
What products are generated during the light reactions?
-The light reactions generate ATP and NADPH using radiant energy from the sun.
What is RuBP and its role in the Calvin cycle?
-RuBP, or ribulose bisphosphate, is a five-carbon sugar that acts as the starting compound for the Calvin cycle, binding with carbon dioxide.
How does carbon dioxide enter the plant for the Calvin cycle?
-Carbon dioxide enters the plant through the stomata in the leaves and diffuses into the stroma of the chloroplast.
What is the first phase of the Calvin cycle called?
-The first phase of the Calvin cycle is known as Carbon Fixation, where carbon dioxide binds to RuBP.
What happens to the unstable six-carbon compound formed in the Calvin cycle?
-The unstable six-carbon compound splits into two three-carbon molecules called phosphoglycerates (PGA).
What are G3P and its significance in the Calvin cycle?
-G3P, or glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate, is a three-carbon sugar produced in the Calvin cycle, which can be used to form glucose.
How many times must the Calvin cycle spin to produce one molecule of glucose?
-The Calvin cycle must spin six times to produce one molecule of glucose, yielding a total of 36 carbons from 12 G3P molecules.
What occurs during the third phase of the Calvin cycle?
-During the third phase, RuBP is regenerated from G3P, allowing the cycle to start again.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)