Física III - Tema 1.4 Campo Eléctrico
Summary
TLDRThis video explains the fundamental concepts of electric fields in physics, specifically focusing on the electric field generated by point charges. It covers the electric field's mathematical model, how it is calculated using Coulomb's law, and the superposition of fields from multiple charges. The video also delves into the representation of electric field lines, showing how they indicate the direction and strength of the field, and provides rules for drawing them. The content offers a comprehensive understanding of electric fields, ideal for students studying Physics 3.
Takeaways
- 😀 Electric fields are spaces surrounding electric charges where a test charge experiences an electric force.
- 😀 The electric field is a vector quantity represented by 'E' and its units in the SI system are Newtons per Coulomb (N/C).
- 😀 A test charge (q₀) is used to detect the presence of an electric field by experiencing a force in the field.
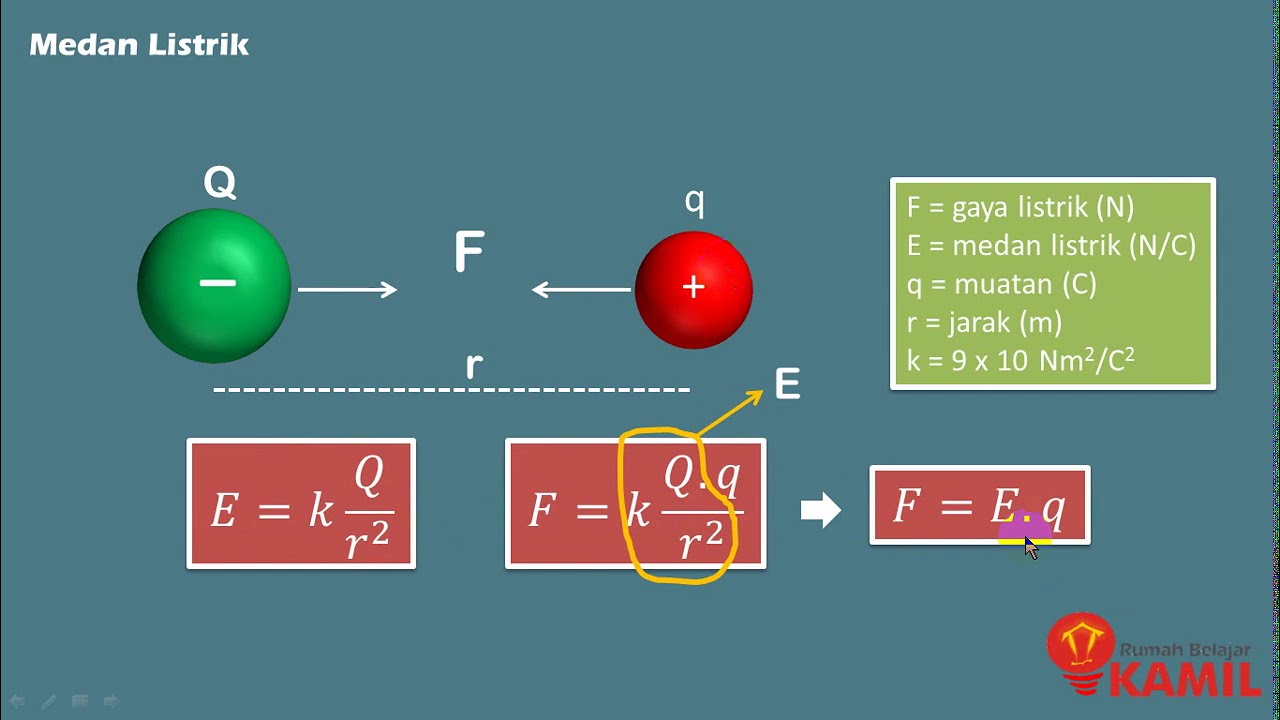
- 😀 The electric field due to a point charge Q at a distance r is calculated using the formula: E = k * |Q| / r² * r̂.
- 😀 The electric field can be calculated for multiple charges by summing the individual fields produced by each charge.
- 😀 Electric field lines represent the direction of the electric field and show the path a positive test charge would take.
- 😀 For a positive charge, electric field lines point outward, and for a negative charge, they point inward.
- 😀 Electric field lines for a dipole (positive and negative charges) move from the positive charge to the negative charge.
- 😀 The density of electric field lines represents the strength of the electric field, with closer lines indicating stronger fields.
- 😀 The electric field around a charge becomes radial and symmetrical at large distances, resembling the field of a point charge.
Q & A
What is an electric field?
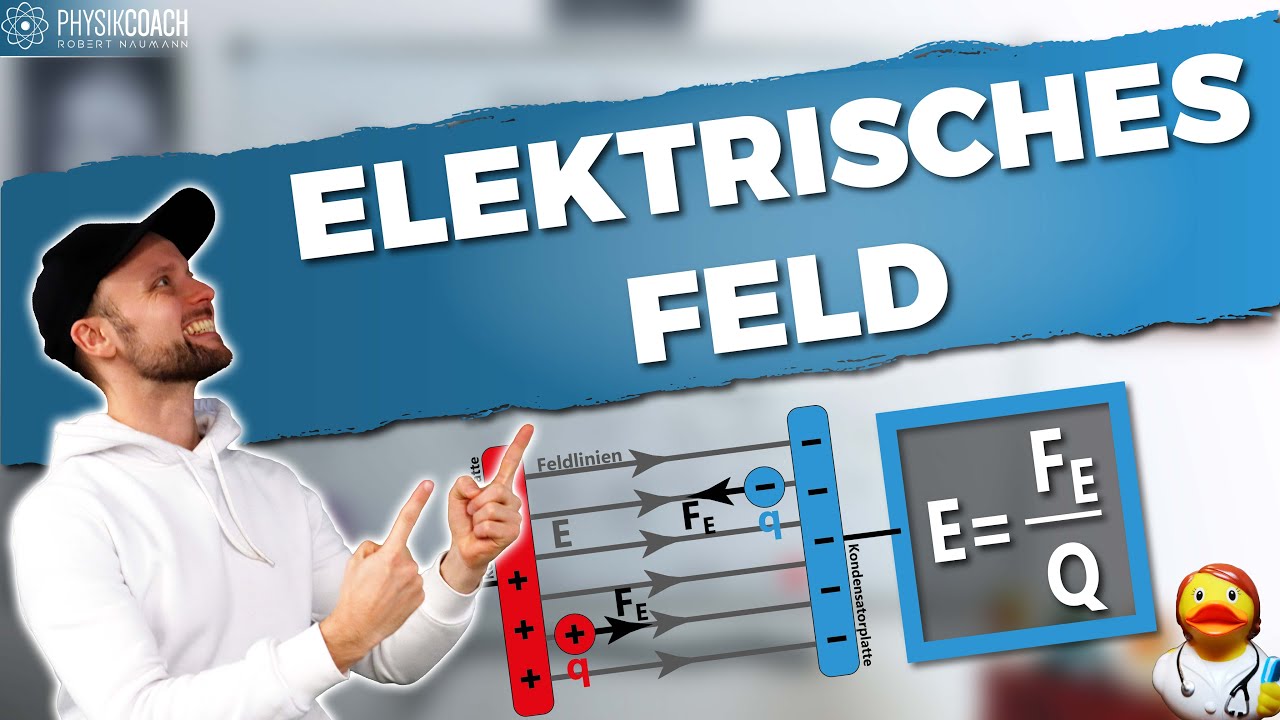
-An electric field is a region around a charge where another charge experiences an electric force. It is a vector quantity, with both magnitude and direction.
What does the symbol 'E' represent in the context of electric fields?
-'E' represents the electric field, a vector quantity that indicates both the direction and strength of the electric force at a point in space.
How is the electric field mathematically defined?
-The electric field is mathematically defined as the force per unit charge, given by the formula E = F / q₀, where F is the force on a test charge q₀.
What is the unit of the electric field in the International System (SI)?
-The unit of the electric field in the International System is Newtons per Coulomb (N/C).
How is the electric field generated by a point charge calculated?
-The electric field generated by a point charge Q at a distance r is given by the formula E = k * |Q| / r² * r̂, where k is Coulomb’s constant and r̂ is the unit vector in the direction of the field.
What is Coulomb’s constant (k) and its value?
-Coulomb’s constant (k) is a proportionality factor in Coulomb's law, and its value is approximately 9 × 10⁹ N·m²/C².
How do you calculate the total electric field from multiple charges?
-The total electric field from multiple charges is calculated by summing the electric fields produced by each charge, using the formula E_total = Σ E_i, where E_i represents the electric field from each individual charge.
What is the role of the test charge (q₀) in determining the electric field?
-The test charge (q₀) is used to measure the electric field. It experiences a force when placed in the field, and the electric field is calculated as the force per unit charge acting on this test charge.
What do electric field lines represent?
-Electric field lines represent the direction of the electric field. They show the path that a positive test charge would follow under the influence of the field.
How do electric field lines behave around positive and negative charges?
-Electric field lines point outward from positive charges and inward toward negative charges. For a dipole, they radiate from the positive charge and enter the negative charge.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)