What is Auxiliary Power Unit (APU) ? | It’s Location and Purpose | Basic Explanation in 5 mins
Summary
TLDRIn this engaging video, aviation enthusiast Rochester explores the Auxiliary Power Unit (APU), explaining its essential role in aircraft operations. He discusses the APU's structure, highlighting its components like the centrifugal compressor and combustion chamber, and clarifies its location within the aircraft's tail cone. Rochester also details how the APU functions, requiring electrical power from the aircraft's batteries, and emphasizes its primary purposes, including providing electrical, pneumatic, and hydraulic power. This informative session sets the stage for deeper discussions in future videos, captivating viewers with the intricacies of aviation technology.
Takeaways
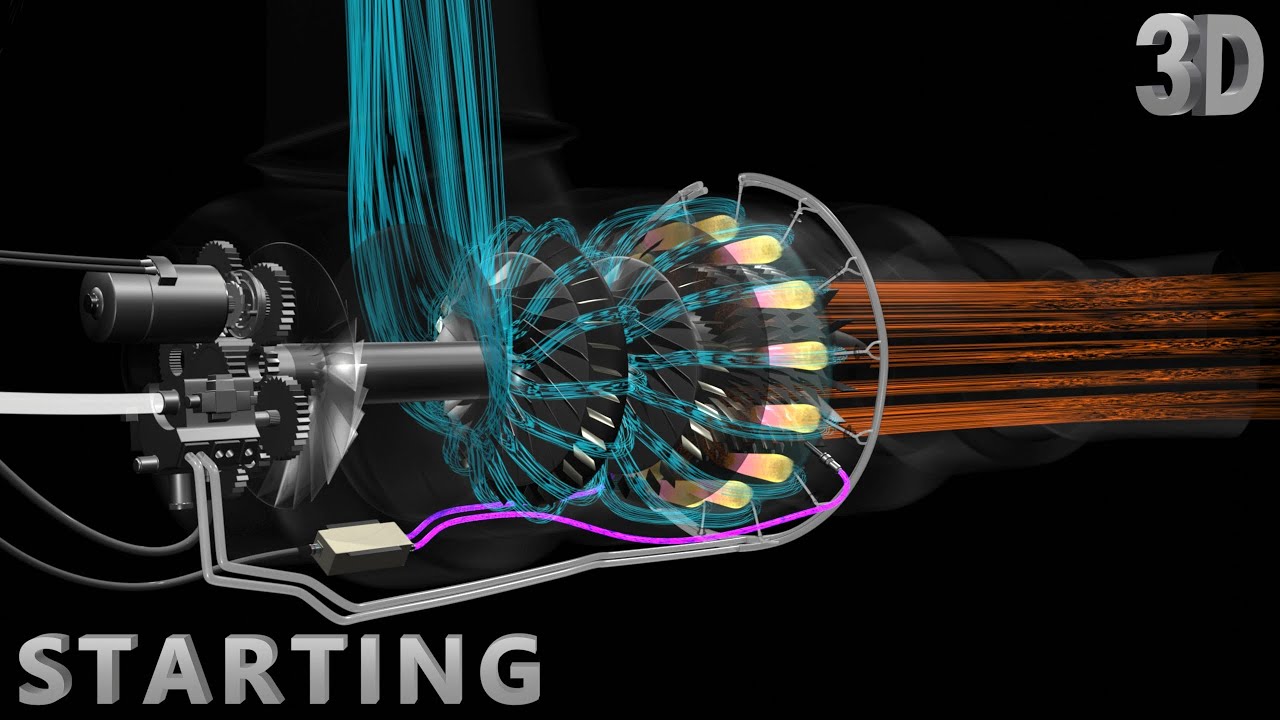
- ✈️ The APU (Auxiliary Power Unit) is a small gas turbine engine essential for aircraft.
- 🔍 The APU features components similar to main engines, including an intake, compressor, combustion chamber, turbine, and exhaust.
- ⚙️ Unlike main engines that use an axial flow type compressor, the APU utilizes a centrifugal flow type compressor.
- 📍 The APU is located in the tail cone of the aircraft, ensuring compactness and efficiency.
- 🌬️ Air intake for the APU occurs through a small flap on the fuselage, which opens upon activation of a switch.
- 🔋 To start the APU, electrical power is required, typically supplied by the aircraft's main batteries.
- ⚡ The primary purpose of the APU is to provide electrical power, pneumatic power, and sometimes hydraulic pressure.
- 🌀 The APU operates at a constant speed, without any throttle control, once it is running normally.
- 🔄 When the APU is operational, its starter converts into a generator, supplying electrical power for ground and in-flight use in some aircraft.
- 🌡️ Pneumatic power is generated from the APU's compressor stage and distributed to the aircraft's air distribution system as needed.
Q & A
What does APU stand for?
-APU stands for Auxiliary Power Unit.
What is the primary function of an APU?
-The primary function of an APU is to provide electrical power, pneumatic power, and sometimes hydraulic pressure for an aircraft.
Where is the APU located in an aircraft?
-The APU is typically located in the tail cone of the aircraft.
What type of engine does an APU use?
-An APU uses a small gas turbine engine, which includes an intake, compressor, combustion chamber, turbine, and exhaust.
What is the main difference between the compressor in an APU and that in a main aircraft engine?
-The main difference is that the APU uses a centrifugal flow type compressor, while the main engines typically use an axial flow type compressor.
How does an APU receive air for operation?
-The APU receives air through a small flap on the fuselage that opens when the APU is activated, allowing airflow into the unit.
What kind of power does the APU provide during flight?
-In some four-engine aircraft, the APU is not certified for in-flight use, but in extended range operations, it can provide electrical, pneumatic, and hydraulic power.
What happens to the starter of the APU during normal operation?
-Once the APU is operating normally, its starter is converted into a generator, which then provides electrical power.
How does the APU provide pneumatic power?
-The APU provides pneumatic power through its compressor stage, which feeds air to the aircraft's air distribution system via a component called the load compressor.
Is throttle control required for the APU during normal operation?
-No, the APU operates at a constant speed during normal operation, so no throttle control is needed.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
How Auxiliary Power Units Work | Part 1 : Starting

Airbus A320 Auxiliary Power Unit (APU) start

Banco de Dados - Aula 15

Gerbang Logika pada CPU | Bab Sistem Komputer | Materi Informatika SMP Kelas 8 | Kumer Fase D

AIRBUS HYDRAULIC SYSTEM how does it work? Explained by Captain Joe

737NG Bleed Air System explained | Real 737 Pilot
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)