[HD] THE CENTRAL DOGMA -synra edition- English Narration
Summary
TLDRThis video delves into the fundamental workings of life at the cellular level, focusing on the central dogma of molecular biology, which describes the flow of genetic information from DNA to proteins. It highlights key processes such as transcription, where RNA polymerase copies DNA into messenger RNA, and translation, where ribosomes decode mRNA to assemble amino acids into proteins. Through these intricate processes, our bodies continuously synthesize proteins essential for life, showcasing the remarkable coordination of biomolecular entities that sustain health and functionality.
Takeaways
- 🧬 Our bodies are composed of approximately 60 trillion cells, each engaging in complex biochemical interactions to sustain life.
- 🔬 The Rican Omics Science Center investigates the biological programs that regulate fundamental life processes, aiming to enhance human health and safety.
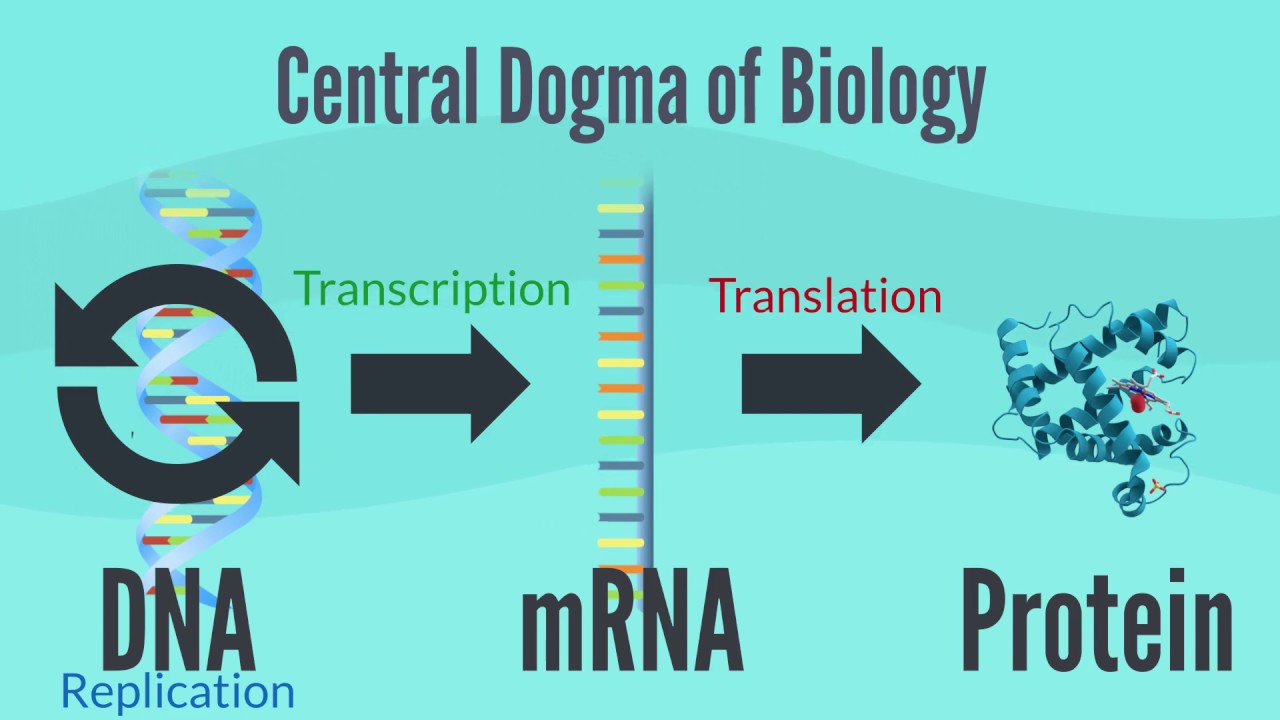
- 📜 The central dogma of molecular biology describes the flow of information from DNA to proteins, highlighting a critical process in cellular function.
- ⚙️ Molecular machines within our bodies retrieve and convert genetic information into essential proteins, showcasing intricate biological mechanisms.
- 🔍 Inside a lymphocyte, organelles such as mitochondria and the Golgi apparatus work together to generate energy and process proteins.
- 📦 The nucleus contains DNA organized into chromatin, which unwinds to expose sequences critical for protein synthesis.
- 🛠️ Transcription factors guide RNA polymerase to specific DNA footholds, initiating the process of copying DNA into RNA.
- ✂️ Newly transcribed RNA undergoes processing, including capping, splicing, and the removal of non-coding regions, to become messenger RNA (mRNA).
- 🔗 mRNA exits the nucleus through nuclear pores and consists of codons that encode specific amino acids for protein synthesis.
- 🌐 The ribosome decodes mRNA and synthesizes proteins by linking amino acids carried by transfer RNA (tRNA), following the instructions provided by the mRNA.
Q & A
What is the primary focus of the Rican Omics Science Center?
-The Rican Omics Science Center aims to uncover the programs that govern the fundamental workings of life, enhancing our knowledge to advance human health and safety.
What does the central dogma of molecular biology describe?
-The central dogma of molecular biology describes the flow of genetic information from DNA to RNA and then to proteins, which is fundamental to all biological processes.
How do molecular machines operate inside human cells?
-Molecular machines in human cells work together to retrieve genetic information from the nucleus and transform it into proteins essential for life.
What is the size of a lymphocyte, and why is it significant?
-A lymphocyte has a diameter of about 10 micrometers, making it only a fraction of the diameter of a human hair. Its size is significant because it allows it to function effectively within the body's complex cellular environment.
What role do mitochondria play in cells?
-Mitochondria are known as the powerhouses of the cell; they generate energy, enabling cellular functions.
What is the function of the Golgi apparatus?
-The Golgi apparatus processes newly synthesized proteins, preparing them for their specific functions within the cell.
What happens during the transcription process?
-During transcription, RNA polymerase, guided by transcription factors, copies information from DNA into RNA, building the RNA strand one nucleotide at a time.
What modifications occur to RNA after transcription?
-After transcription, RNA undergoes several modifications, including capping, splicing to remove non-coding regions, and obtaining a poly-A tail to protect it from degradation.
What is the significance of codons in messenger RNA?
-Codons are sequences of three nucleotide bases in messenger RNA that specify particular amino acids, serving as a blueprint for protein synthesis.
How do ribosomes contribute to protein synthesis?
-Ribosomes decode the information on messenger RNA and synthesize proteins by linking amino acids together based on the sequence of codons.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Genetics - Replication Methods and Central Dogma - Lesson 16 | Don't Memorise

Genetica molecular. Replicación, transcripción y traducción. 4º ESO - Bio[ESO]sfera
Central Dogma of Biology

Trascrizione e traduzione

Central dogma of molecular biology | Chemical processes | MCAT | Khan Academy

Dogma Central Biologi Molekuler
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)