How The Giant Squid Axon Changed Neuroscience
Summary
TLDRThis video script explores how early neuroscientists studied the brain, focusing on the use of the giant squid axon as a model for understanding action potentials. It highlights the innovative work of Hodgkin and Huxley in the mid-1900s, who used squid axons to discover how neurons send electrical signals. Through the use of voltage clamps and chemicals like tetrodotoxin, they unraveled the roles of sodium and potassium ions in signal transmission. This groundbreaking research helped advance our understanding of the nervous system and earned them the Nobel Prize in 1963.
Takeaways
- 🧠 Scientists have been studying the brain and nervous system for centuries, with new technologies like optogenetics transforming research today.
- 🐙 Squid, especially the giant squid axon, played a key role in early neuroscience discoveries when other advanced tools were unavailable.
- 🦑 Hodgkin and Huxley used the giant axon of a squid to study action potentials, leading to major breakthroughs in understanding neuron signal transmission.
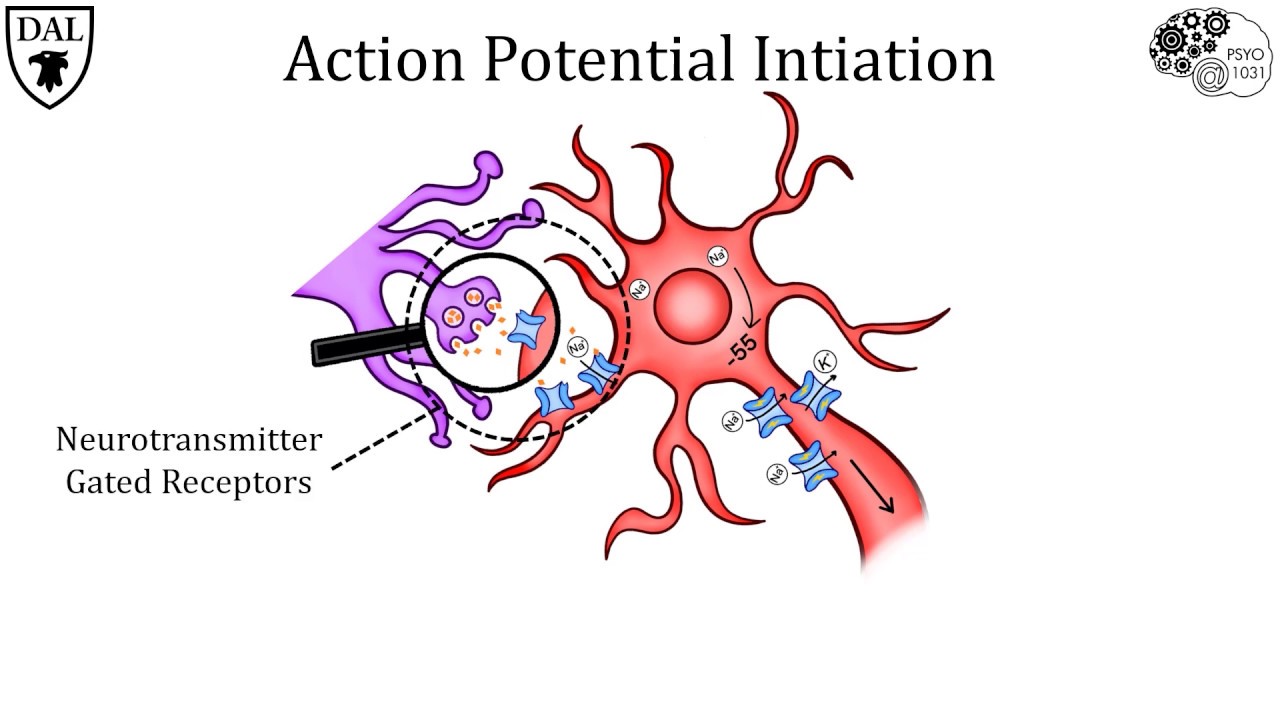
- 💡 Action potentials are electrical signals that neurons send using ionic currents to change the cell's electrical potential.
- ⚡ When a neuron receives a signal, the voltage inside the cell spikes, creating an action potential that travels along the axon.
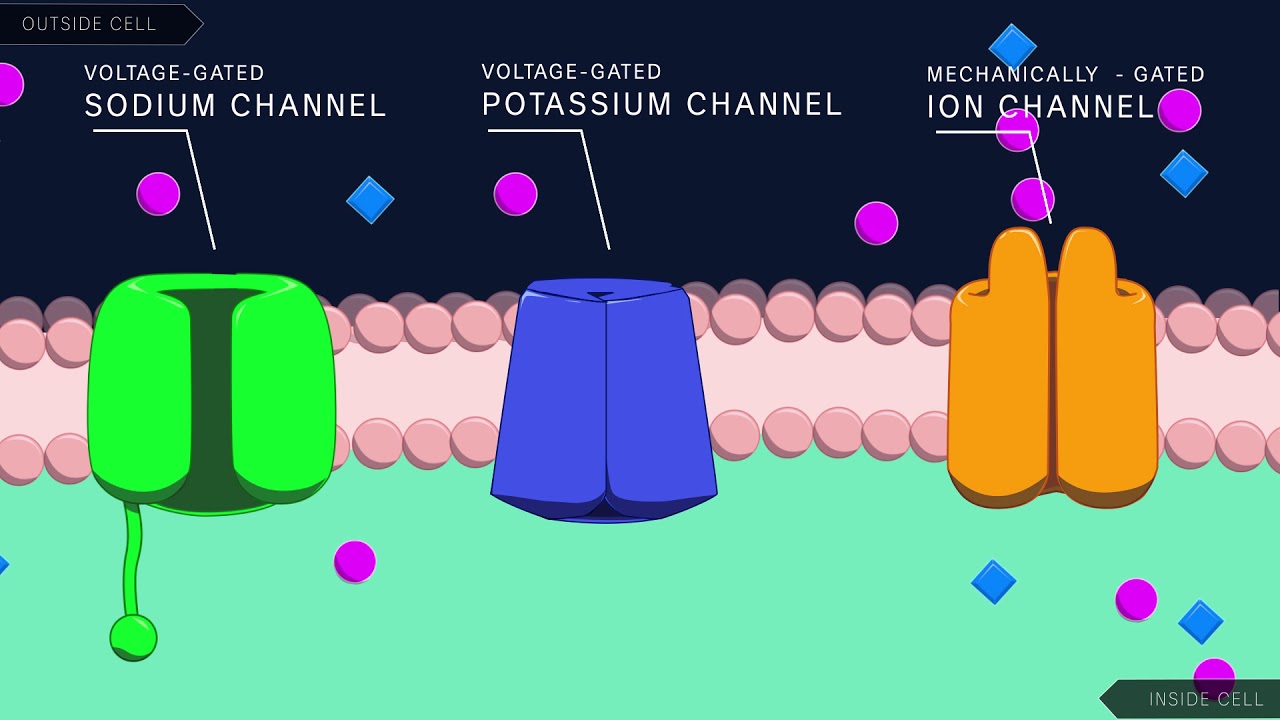
- 📉 Hodgkin and Huxley developed the voltage clamp technique to study ion flow and measure neuron activity by controlling the voltage across the cell membrane.
- 🔬 Their experiments with chemicals like tetrodotoxin helped identify the roles of sodium and potassium ions in neuron depolarization and hyperpolarization.
- 🏆 The research on action potentials and ionic channels won Hodgkin and Huxley the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1963.
- 🐟 Squid aren’t the only marine creatures aiding neuroscience; animals like the California Sea Hare and African Killifish are also used in brain and aging research.
- 👩🔬 The International Youth Neuroscience Association (IYNA) is dedicated to inspiring young scientists to explore neuroscience.
Q & A
What tools do modern scientists use to study brain function?
-Modern scientists use tools like optogenetics, green glowing mice, and advanced imaging techniques, among others, to study how the brain works.
Why did neuroscientists in the mid-1900s study squids instead of humans to learn about brain activity?
-In the mid-1900s, neuroscientists lacked advanced tools to study human brains, so they used squids, specifically their giant axons, because these axons were large enough to easily insert electrodes for studying electrical signals.
What is the significance of the giant squid axon for neuroscience research?
-The giant squid axon, which is much larger than typical human axons, allowed scientists to measure electrical potentials and study how neurons send signals, making it a valuable model for early neuroscience experiments.
How do neurons transmit electrical signals?
-Neurons transmit electrical signals, called action potentials, by changing the electrical potential along their axons. This process involves the movement of ions in and out of the cell, which creates a spike in electrical activity.
What role did the voltage clamp play in Hodgkin and Huxley's research?
-The voltage clamp allowed Hodgkin and Huxley to measure the amount of electrical current needed to keep the voltage constant during an action potential, helping them track how ions moved in and out of the neuron.
What are the phases of an action potential in a neuron?
-An action potential has two main phases: depolarization, where sodium ions flow into the cell causing a spike in voltage, and hyperpolarization, where potassium ions flow out, causing the voltage to drop below the resting potential.
What discovery won Hodgkin and Huxley the Nobel Prize in 1963?
-Hodgkin and Huxley won the Nobel Prize for discovering how sodium and potassium ions move in and out of neurons during an action potential, leading to a better understanding of how neurons send electrical signals.
Why do squids have giant axons, and how do they benefit from them?
-Squids have giant axons to rapidly transmit signals to their water jet propulsion system, allowing them to escape from predators quickly. The larger diameter axon allows for faster signal transmission.
How do squids and humans differ in their method of speeding up signal transmission in neurons?
-Humans speed up signal transmission using myelination, which insulates axons, while squids use a large-diameter axon to transmit signals more quickly.
What are some other sea creatures used in modern neuroscience research, and what are they studied for?
-Other sea creatures used in neuroscience research include the California Sea Hare, which is used to study memory, and the African Killifish, which is studied for aging research.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)