The Computer System Clock
Summary
TLDRThis video explores the system clock in computer systems, explaining its characteristics and impact on performance. It discusses the difference between analog and digital signals, focusing on how a crystal generates a sinusoidal waveform that is converted into a digital square wave by a pulse generator. The video compares the clock's function to an orchestra conductor, highlighting how clock pulses synchronize the CPU and components. It emphasizes that higher clock frequencies increase instruction execution, improving system performance, and explains how clock speed, measured in Hertz, influences computing power.
Takeaways
- 💡 Clock pulses synchronize the operations of the CPU and its components.
- 🔄 Analog signals, like the sinusoidal waveform from a crystal, are converted into digital square waves for use in computer clocks.
- 🔂 Each cycle of an analog waveform repeats identically over time, maintaining the same frequency.
- 📏 The frequency of a signal, measured in Hertz (Hz), indicates how many cycles occur per second.
- 🔄 A square wave is generated from a sinusoidal waveform using a pulse generator, and its two states (high and low) make it a digital signal.
- 🎼 The clock is like a conductor in an orchestra, synchronizing various components of the computer to work together.
- ⏱️ The leading edge of a clock pulse (transition from low to high) triggers actions like moving data or incrementing registers in the CPU.
- 🛣️ Data moves along paths (buses) in a computer, and clock pulses open, move, and close these paths at specific intervals.
- ⚡ Faster clocks (higher frequency) allow more instructions to be executed in a given time, improving overall performance.
- 📊 A 3.5 GHz clock, for example, produces 3.5 billion pulses per second, allowing the computer to perform 3.5 billion steps in that time.
Q & A
What is the primary purpose of the system clock in a computer?
-The system clock synchronizes the operations of the central processing unit (CPU) and its supporting components by generating regular clock pulses.
How is an analog signal generated within a computer system?
-An analog signal is generated by applying a voltage to a crystal, producing a sinusoidal waveform, which is analog in nature.
Why can't a sinusoidal waveform be used directly as a clock signal in a computer system?
-A sinusoidal waveform is analog and continuously changes its amplitude, which does not meet the digital requirements of a computer clock that needs a signal with distinct high and low states.
How is a sinusoidal waveform converted into a digital clock signal?
-A sinusoidal waveform is fed into a pulse generator, which produces a square wave. This digital square wave has distinct high and low states, making it suitable for use as a system clock.
What is the relationship between the system clock’s frequency and the performance of the computer?
-The higher the clock frequency, the more instructions can be executed by the CPU in a given amount of time, directly affecting the computer's performance.
What is meant by the term 'cycle' in the context of clock signals?
-A cycle refers to one complete repetition of the waveform, from low to high and back to low again. The frequency of the clock determines how many cycles occur in one second.
What is the significance of the leading edge in a digital clock signal?
-The leading edge is the point where the signal rapidly transitions from low to high. Important operations, such as moving data or incrementing registers, occur on this edge.
How does the system clock function similarly to a conductor in an orchestra?
-Just like a conductor uses a baton to synchronize different sections of an orchestra, the system clock uses pulses to synchronize the actions of different components in the computer system.
What happens when the clock frequency increases?
-When the clock frequency increases, more clock pulses are generated per second, allowing the CPU to perform more operations in the same amount of time, improving overall performance.
What does a 3.5 GHz clock frequency indicate in terms of system performance?
-A 3.5 GHz clock frequency means the clock produces 3.5 billion pulses per second, allowing the CPU to perform up to 3.5 billion steps or instructions per second.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Arquitetura de Computadores | O que é? Por que Devo Estudar?
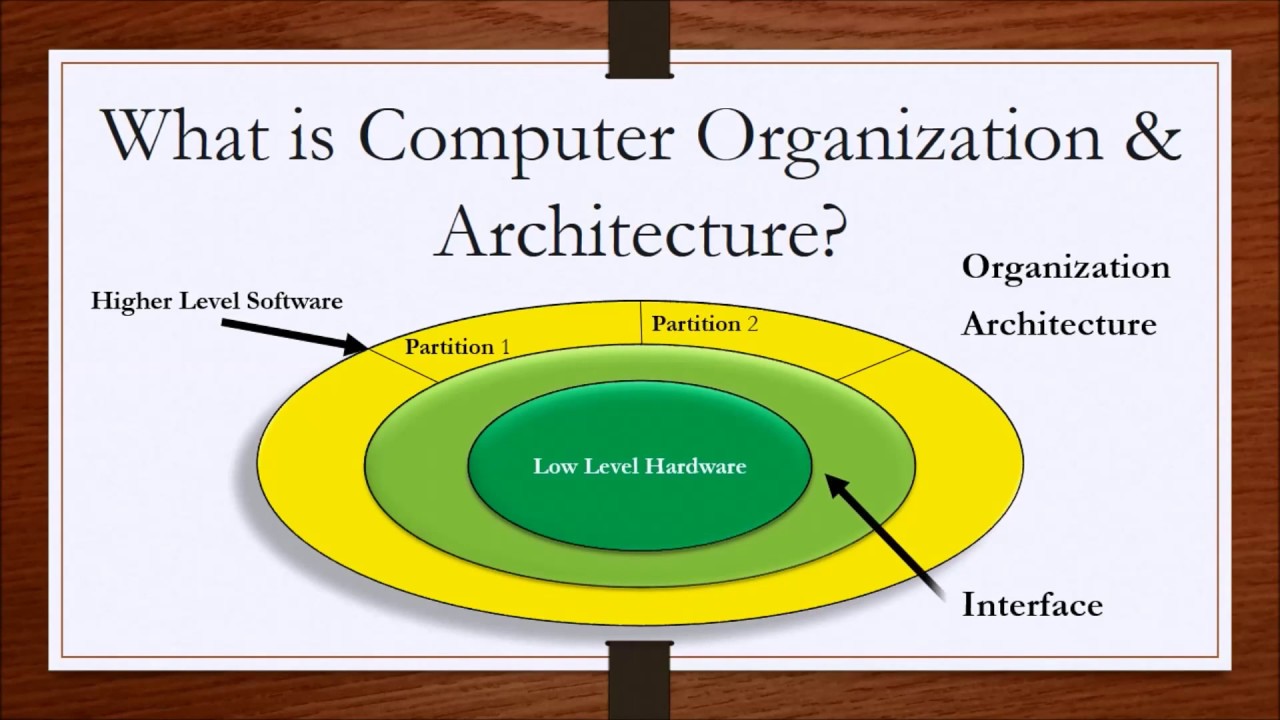
Computer Organization and Architecture Lesson 1 - Introduction
Computer Concepts- Module 3: Computer Hardware Part 3 (4K)

IGCSE Computer Science 2023-25 - Topic 3: HARDWARE (2) - Fetch–Decode–Execute Cycle. Cores, Cache

Overview of Information System Auditing | Information System Auditing Kya Hai | Overview of Auditing

16. OCR A Level (H046-H446) SLR4 - 1.2 Scheduling
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)