Generate Electricity - How Solar Panels Work!
Summary
TLDRThis video explains how solar panels work, detailing the photovoltaic effect where light is converted into electricity. It covers the structure of solar cells, their efficiency, and the differences between monocrystalline, polycrystalline, and thin-film cells. The video also touches on solar energy systems, including grid-connected and off-grid setups, and the importance of charge controllers and inverters. Additionally, it discusses solar panel designs for optimal performance, solar farms, and energy storage, while offering insights into the challenges of using solar energy effectively.
Takeaways
- 🔆 Solar panels convert light (sunlight or artificial light) into electricity using the photovoltaic effect.
- 💡 A solar cell generates electricity by absorbing photons, which knock electrons free, creating a flow of current.
- ⚡ Solar cells are composed of a silicon layer with phosphorus on top and boron at the bottom, forming a PN junction that generates electricity.
- 🔋 Solar modules are made of multiple cells connected in series or parallel to increase voltage or current.
- 🌞 Solar panels work best when aligned perpendicularly to sunlight, but this requires careful planning for optimal orientation and tilt.
- 🔌 Solar energy can be stored in batteries, used directly, or fed back to the electrical grid through systems like net metering.
- 🛠️ Charge controllers regulate the charging of batteries to prevent overcharging and discharging back into the panel.
- 🔁 Monocrystalline solar cells are more efficient but costlier than polycrystalline cells due to their more refined structure.
- 🌍 Commercial and large-scale solar farms often connect multiple solar panels to inverters and transformers to feed power into the grid.
- 💻 Advanced software like PV case can simulate solar installations, including design and shading analysis, to optimize system performance.
Q & A
What is the basic principle behind how solar panels generate electricity?
-Solar panels generate electricity using the photovoltaic effect, where light (photons) strikes a solar cell and knocks electrons loose, creating a flow of electricity.
What materials are used in the construction of a basic solar cell?
-A basic solar cell consists of a metal conductive plate, a thin silicon layer (which acts as the semiconductor), and an anti-reflective coating. The silicon is typically doped with boron on the bottom and phosphorus on the top to form a PN junction.
Why are anti-reflective coatings used on solar cells?
-Anti-reflective coatings are used to reduce the amount of light that is reflected away from the solar cell. This helps capture more sunlight and increase the cell's efficiency.
How does connecting solar cells in series and parallel affect the voltage and current?
-When solar cells are connected in series, the voltage adds together, but the current remains the same. When connected in parallel, the current adds together, but the voltage remains the same.
What is the purpose of a charge controller in a solar power system?
-A charge controller regulates the voltage and current coming from the solar panels to the battery. It prevents overcharging and protects the battery from discharging back into the solar panel at night.
What are the main differences between monocrystalline and polycrystalline solar cells?
-Monocrystalline cells are made from a single, pure crystal structure, making them more efficient (15-19%) but more expensive. Polycrystalline cells consist of multiple silicon crystals, which makes them cheaper but slightly less efficient (13-17%).
Why do solar panels lose efficiency as they heat up?
-As solar panels heat up, some of the energy from sunlight is wasted as heat rather than being converted into electricity. This increase in temperature causes a decrease in efficiency, as the excess energy heats the cells.
How does net metering work in a solar power system?
-Net metering allows excess electricity generated by solar panels to be sold back to the electrical grid. During sunny periods, the excess power is fed into the grid, and at night or on cloudy days, electricity is bought from the grid.
What is the depletion region in a solar cell, and why is it important?
-The depletion region is the area where the P-type and N-type materials meet in a solar cell. It's important because it creates an electric field that separates the free electrons from the holes, allowing electricity to flow when light hits the cell.
What is the role of an inverter in a solar power system?
-An inverter converts the direct current (DC) produced by solar panels into alternating current (AC), which is the form of electricity used by most household appliances and the electrical grid.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

¿Cómo funciona la ENERGÍA SOLAR? Efecto Fotoeléctrico y Fotovoltaico ☀️⚡ Con @dateunvlog

Como Energia Solar é Convertida em Eletricidade? | Ep. 29

Cara Kerja Panel Surya

Química - Fontes de energia e suas classificações (QEF0065)

PROSES PEMBUATAN PANEL SURYA UNTUK PEMBANGKIT LISTRIK DI PABRIK MODERN
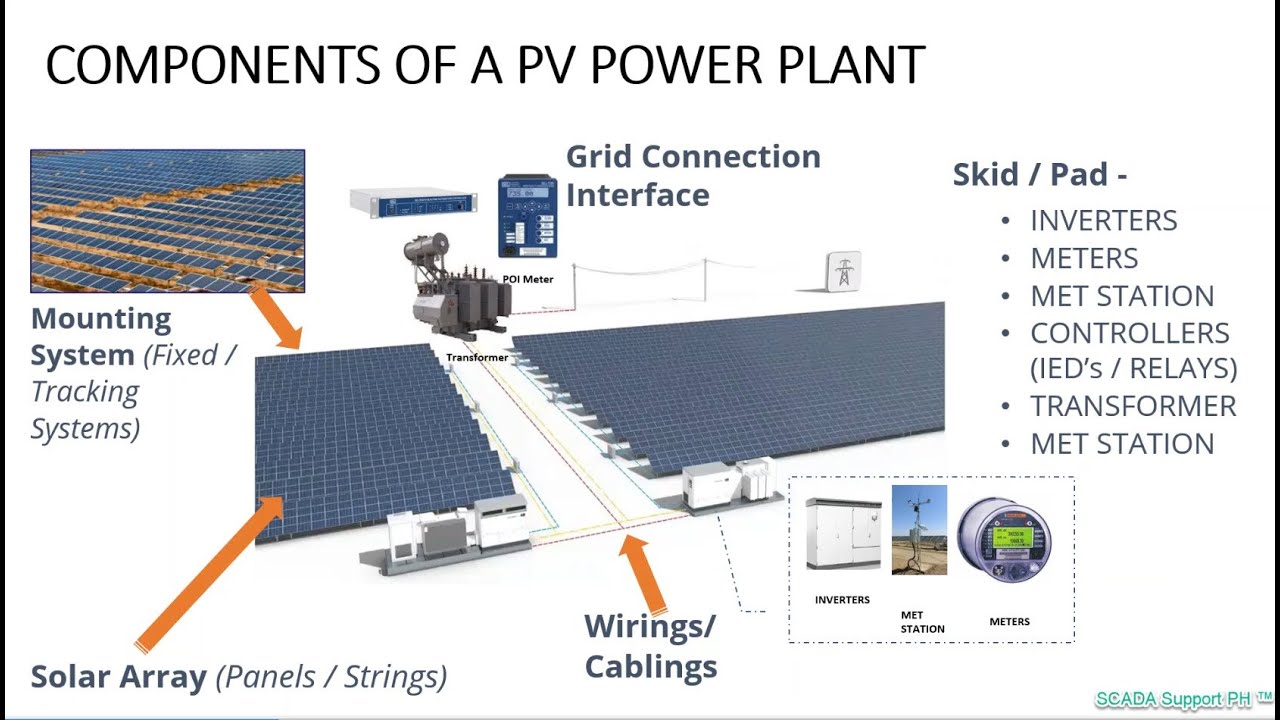
Solar Photovoltaic (PV) Power Plant
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)