Hukum Pascal dan Archimedes | IPA | SayaBisa
Summary
TLDRThe video discusses the principles behind submarines, combining Pascal's and Archimedes' laws. Pascal's law explains how pressure in a closed system is transmitted equally in all directions, forming the basis of hydraulic systems. Archimedes' principle explains buoyancy, where a submerged object displaces water, resulting in an upward force. Using examples and problems, the video illustrates how these laws apply in real-life situations like hydraulic machines and floating objects. In the end, it reveals that the technology discussed is a submarine, which can both float and submerge by leveraging these principles.
Takeaways
- 🚢 The video is about principles used in submarines that involve both Pascal's and Archimedes' laws.
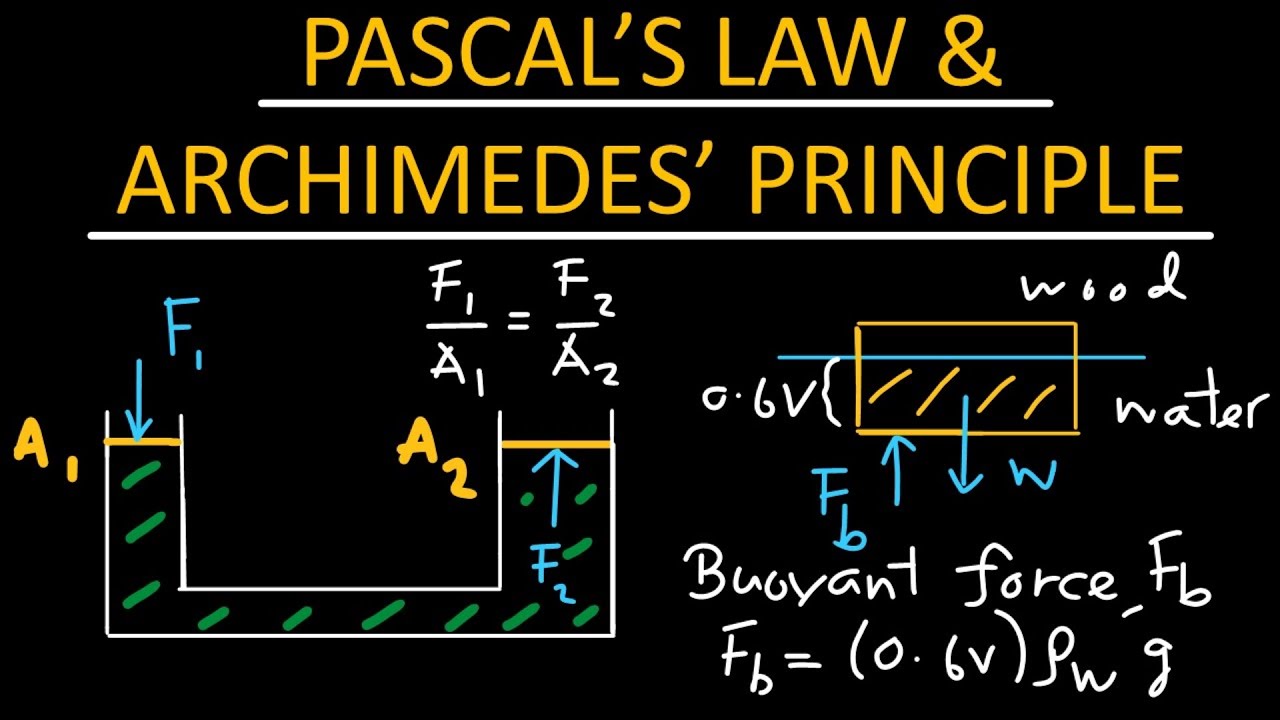
- 📏 Pascal's Law states that pressure in a closed system is equal in all directions, making it a key principle in hydraulic systems.
- 🔧 A hydraulic machine with a small surface area can exert significant force due to Pascal's Law, as pressure is constant across surfaces.
- 🔢 Pascal's Law is demonstrated with an example of a hydraulic machine lifting a car, where force is calculated using pressure equations.
- 🧑🔬 Archimedes' Principle explains buoyancy, where objects submerged in fluid are pushed upward by a force equal to the displaced fluid's weight.
- 🌊 When an object is submerged in water, it displaces water and feels an upward buoyant force, making it float or feel lighter.
- 📚 The weight of an object in water is the original weight minus the buoyant force acting on it.
- ⚖️ Whether an object floats, sinks, or remains suspended in water depends on the relationship between its density and the density of the fluid.
- 🧩 If an object's density is lower than the fluid's, it will float; if the densities are equal, the object will suspend; if higher, the object will sink.
- 🛠️ The video ultimately reveals that submarines are an example of technology that uses both Pascal's and Archimedes' principles.
Q & A
What is the primary function of Pascal's Law as described in the video?
-Pascal's Law states that pressure applied to an enclosed fluid is transmitted equally in all directions, and it forms the foundation of hydraulic systems.
How can Pascal’s Law be illustrated using a connected vessel system?
-Pascal's Law can be illustrated using a connected vessel system where pressure applied on one surface of the fluid is transmitted equally to another surface. The force applied on one side results in an equal force on the other side due to the equal distribution of pressure.
In the video, what example is used to explain a practical application of Pascal’s Law?
-The video uses a hydraulic machine that lifts a car to explain Pascal's Law. The problem involves calculating the force required on one piston of the hydraulic system based on the surface areas of the pistons and the weight of the car.
What formula is used to calculate pressure in Pascal’s Law?
-The formula for pressure in Pascal's Law is Pressure = Force / Area. This is used to calculate the pressure in the hydraulic system, ensuring the force is distributed equally across the surfaces.
How is Archimedes’ principle explained in the video?
-Archimedes' principle is explained using the concept of buoyancy. When an object is submerged in water, it displaces an amount of water equal to its volume. The displaced water exerts an upward buoyant force on the object, allowing it to float.
What is an example of Archimedes' principle provided in the video?
-An example provided is a wooden box floating in a pool. Half of the box is submerged, and the video calculates the buoyant force acting on the box by multiplying the submerged volume by the water's density and gravitational acceleration.
How can the weight of an object in water be calculated using Archimedes' principle?
-The weight of an object in water is calculated by subtracting the buoyant force from the object's actual weight. This makes the object appear lighter in water.
What are the three possible outcomes when an object is submerged in water according to Archimedes' principle?
-The three outcomes are: (1) the object floats if its density is less than the liquid’s density, (2) it hovers or remains suspended if the densities are equal, and (3) it sinks if its density is greater than the liquid’s density.
What real-life technology combines Pascal's and Archimedes' principles, as discussed in the video?
-The technology combining both Pascal's and Archimedes' principles is the submarine. Submarines use hydraulic systems (Pascal's principle) for control and adjust buoyancy (Archimedes' principle) to submerge and surface.
Why does an object appear lighter when submerged in water?
-An object appears lighter in water because the buoyant force, equal to the weight of the water displaced by the object, counteracts part of the object’s weight, reducing the net force acting on it.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Kelas XI Bab 3 Fluida Statis Part 1 Massa Jenis

MICROTEACHING FISIKA SMA KELAS XI - HUKUM ARCHIMEDES

10 01 Fisika Dasar 1- Fluida Statik
Understanding Pascal's Law and Archimedes' Principle - Physics

TEKANAN ZAT CAIR (Tekanan Hidrostatis, Hukum Archimedes, Hukum Pascal)

Diavoletto di Cartesio – Laboratorio
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)