Cement Quality Control pt. 1 – Chemical Composition, Fineness
Summary
TLDRIn this video, Tyler Lee discusses cement testing, focusing on the chemical composition and fineness of Portland cement. The most common method for analyzing cement's chemical makeup is X-ray fluorescence, which provides the oxide composition of cement ingredients. He introduces Bogue's equation to predict cement compounds like C3S and C2S. He also mentions the LOI test to measure pre-hydration and the Blaine method to assess particle fineness. This detailed explanation sets the stage for part two, where hydration, set time, and strength gain will be discussed.
Takeaways
- 🧪 Portland cement is the most tested and evaluated material in concrete.
- 📄 Mill certifications provide an average chemical composition over 30 days, but daily batches may vary.
- 🔬 X-ray fluorescence (XRF) is the most common method for testing the chemical composition of cement by analyzing oxides.
- 🧱 Oxides in cement are like building blocks and can be used to predict compounds like C3S, C2S, C3A, and C4AF.
- 📉 The Bogue equation is used to estimate these compounds from oxide data but has limitations, especially with limestone.
- 📐 X-ray diffraction (XRD) provides more accurate measurements of cement compounds but still has noise and overlap issues.
- 🔥 The Loss on Ignition (LOI) test measures prehydration by heating the cement and checking weight changes.
- 🌡️ LOI tests can also indicate how much limestone is present, as limestone releases CO2 when heated.
- 🔬 Fineness of cement is crucial as it affects workability, strength gain, and heat of hydration.
- 🌬️ The Blaine air permeability test measures the particle size distribution by pushing air through packed cement.
Q & A
What is the main focus of part one of the two-part series on cement?
-Part one focuses on the chemical composition and fineness of cement.
Why is cement considered the most tested ingredient in concrete?
-Cement is the most tested ingredient because it is crucial for concrete's performance, requiring evaluation of its chemical composition, fineness, set time, heat of hydration, and strength gain.
What is a mill certification, and why should users be cautious when relying on it?
-A mill certification is a document summarizing cement properties over the last 30 days. Users should be cautious because the actual material received may differ slightly from the average shown in the certification.
How does X-ray fluorescence (XRF) help in evaluating cement’s chemical composition?
-XRF bombards atoms with X-rays, causing them to fluoresce. This technique identifies the oxides in cement, which are the building blocks for various compounds, providing insight into the material's composition.
What is the purpose of the Bogue equation in cement analysis?
-The Bogue equation predicts the amounts of key cement compounds (C3S, C2S, C3A, C4AF) based on oxide analysis. It is widely used in the industry to estimate compound content, though it is not always perfectly accurate.
How does X-ray diffraction (XRD) differ from XRF in analyzing cement?
-XRD measures the spacing of atoms within materials, providing a more direct measurement of cement phases (C3S, C2S, C3A, C4AF), making it more accurate than XRF for certain analyses.
What is the LOI (Loss on Ignition) test, and what does it indicate about cement?
-The LOI test measures weight loss when cement is heated to high temperatures. It helps determine how much pre-hydration or moisture exposure the cement has undergone.
Why is the presence of limestone in cement a challenge for the LOI test?
-Limestone is ground into the cement after the clinker is produced, and during heating, it releases CO2, which affects weight loss measurements, complicating the interpretation of the LOI test results.
How does cement fineness impact concrete properties?
-Cement fineness affects workability, strength gain, and heat release in concrete. Finer particles increase reactivity and heat release, while coarser particles improve workability.
What is the Blaine method, and how does it measure cement fineness?
-The Blaine method uses air permeability to measure cement fineness. Air is forced through a packed bed of cement particles, and the pressure response is used to estimate the material's surface area, which indicates particle size distribution.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
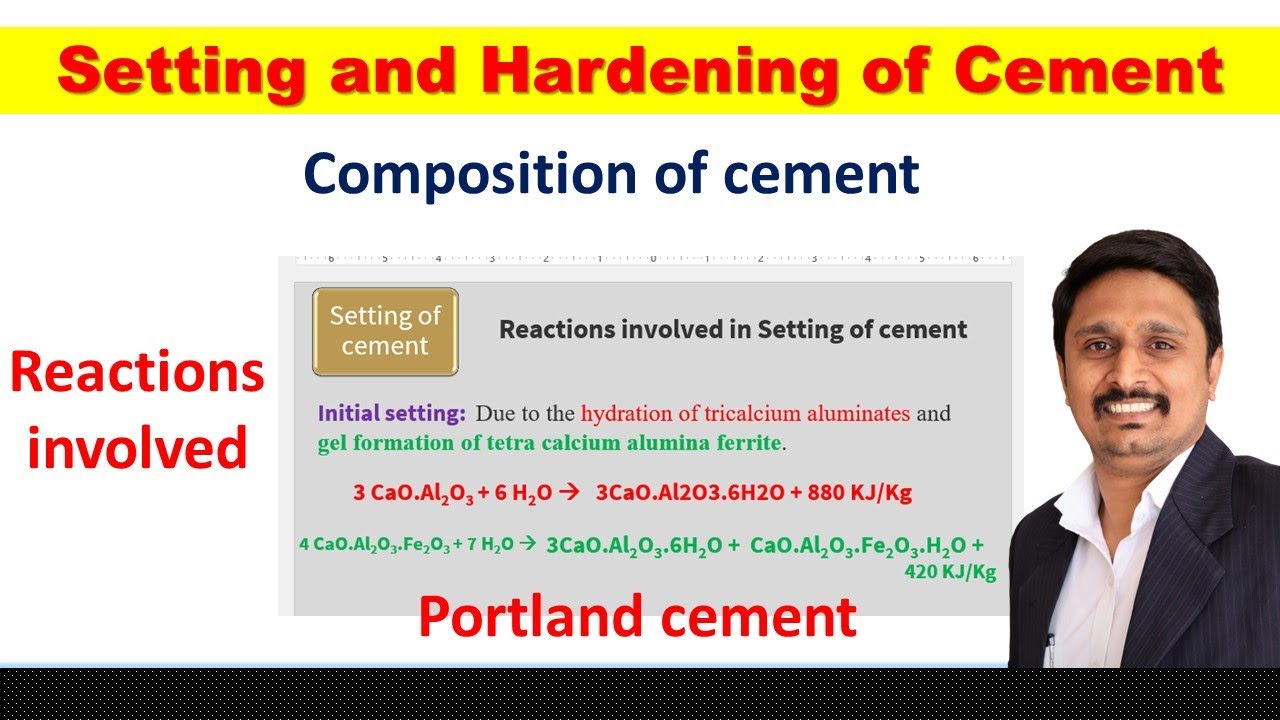
cement | composition | setting and hardening | reactions involved in setting and hardening

Cement Manufacturing

History of Cement
Cement Manufacturing Process with the Portland Cement Association

Shrinkage Cracking in Concrete | Chemical, Autogeneous, and Drying Shrinkage explained!

CMT - Particle Size Distribution Analysis of Coarse Aggregate
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)