APES Video Notes 4.2 - Soil Formation & Erosion
Summary
TLDRThis video covers soil formation and erosion, a key topic in environmental science. It explains that soil forms through weathering of parent material (rock) and erosion, with organic matter like humus contributing from above. Soil is made of sand, silt, clay, and organic material and is vital for plant growth, water filtration, nutrient recycling, and providing habitats. The video also discusses soil degradation, including topsoil loss, compaction, and nutrient depletion, while emphasizing factors like climate, parent material, and organisms that influence soil formation.
Takeaways
- 🌱 Soil is a mix of geological and organic components, including sand, silt, clay, humus, nutrients, water, and air, all essential for plant growth.
- 🪨 Soil forms when parent material, or bedrock, undergoes weathering and erosion, breaking down rocks into smaller particles which form soil.
- 🌬️ Weathering is the breakdown of rocks through physical, chemical, or biological processes, while erosion is the transportation of these particles.
- 🌾 Soil supports plant growth by providing nutrients like nitrogen, potassium, and phosphorus, while also anchoring roots.
- 💧 Soil plays a critical role in water filtration, trapping pollutants and allowing clean water to pass through and recharge groundwater sources.
- 🍂 Decomposers like earthworms, fungi, and bacteria recycle nutrients by breaking down dead organic matter, contributing to soil health.
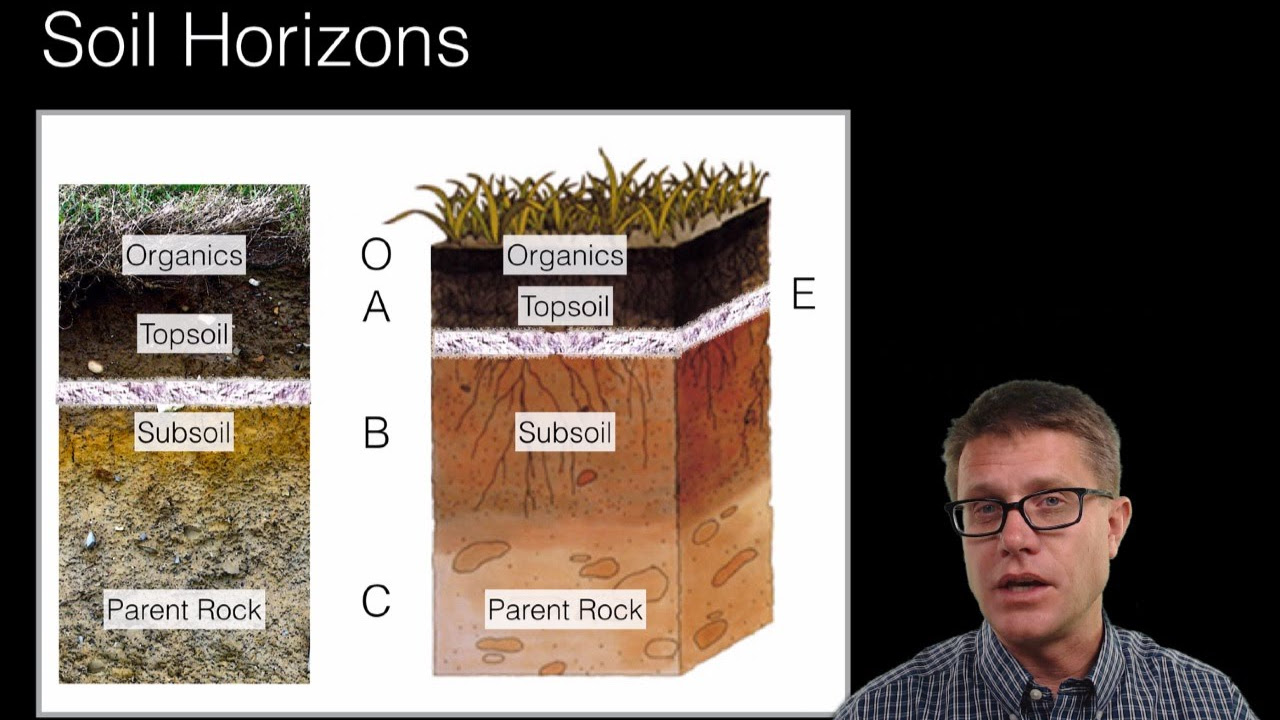
- 🌍 Soil horizons include layers such as the O horizon (organic material), A horizon (topsoil with humus), B horizon (subsoil with clay), and C horizon (least weathered rock).
- 🔄 Soil formation is influenced by factors like parent material, topography, climate, and the activity of soil organisms, which all affect the rate of breakdown and nutrient content.
- 🚜 Soil degradation occurs through processes like loss of topsoil, compaction, and nutrient depletion, which can result from agricultural practices like tilling and overgrazing.
- 🔬 In designing an experiment to study soil formation, key factors to consider include the independent variable (e.g., climate) and the dependent variable (e.g., rate of soil formation).
Q & A
What is soil, and why is it important in ecosystems?
-Soil is a mix of geological (rock-based) and organic components (from living or once-living organisms). It is important because it supports plant growth, filters water, recycles nutrients, and provides habitats for organisms.
What are the three main particles that make up soil?
-The three main particles that make up soil are sand, silt, and clay.
What is humus, and what role does it play in soil?
-Humus is the main organic component of soil, consisting of decomposed organic matter like dead plants and animal waste. It contributes to the soil's nutrient levels and helps retain moisture.
How does soil contribute to water filtration?
-Soil acts as a filtration system by trapping pollutants in its pore spaces as water trickles through. This allows clean water to pass through and recharge groundwater sources and aquifers.
What is the difference between weathering and erosion?
-Weathering is the breakdown of rocks into smaller pieces, while erosion is the transport and deposition of these pieces by wind, water, or other forces.
What factors affect the rate of soil formation?
-Factors affecting soil formation include parent material, topography, climate, precipitation, and the activity of soil organisms like decomposers.
What is the role of decomposers in soil formation?
-Decomposers such as earthworms, fungi, and bacteria break down organic matter, contributing to the formation of humus and increasing soil depth and fertility.
What are soil horizons, and what is the significance of the O horizon?
-Soil horizons are distinct layers of soil. The O horizon, or organic layer, is composed of dead leaves, roots, and animal waste. It provides essential nutrients and helps retain moisture in the soil.
How does soil degradation occur, and what are its consequences?
-Soil degradation occurs through processes like the loss of topsoil, compaction, and nutrient depletion. It leads to reduced soil fertility, decreased plant growth, and increased vulnerability to erosion.
What is the suggested science skill to practice regarding soil formation, as mentioned in the video?
-The suggested science skill is to design an investigation to measure the effect of climate on soil formation. This involves identifying the independent variable (climate) and the dependent variable (soil formation rate).
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Penjelasan lapisan tanah dan konservasi tanah X-10 Kelompok 6

Soil Formation: Factors and Processes | Biogeography | Dr. Krishnanand

Pedosfer #Kurikulum Merdeka

PEDOSFER : PROSES PEMBENTUKAN TANAH
Soil and Soil Dynamics

TENAGA EKSOGEN DAN PEMBENTUKAN TANAH #litosfer #geography #erlanggaofficial #tanah #education
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)