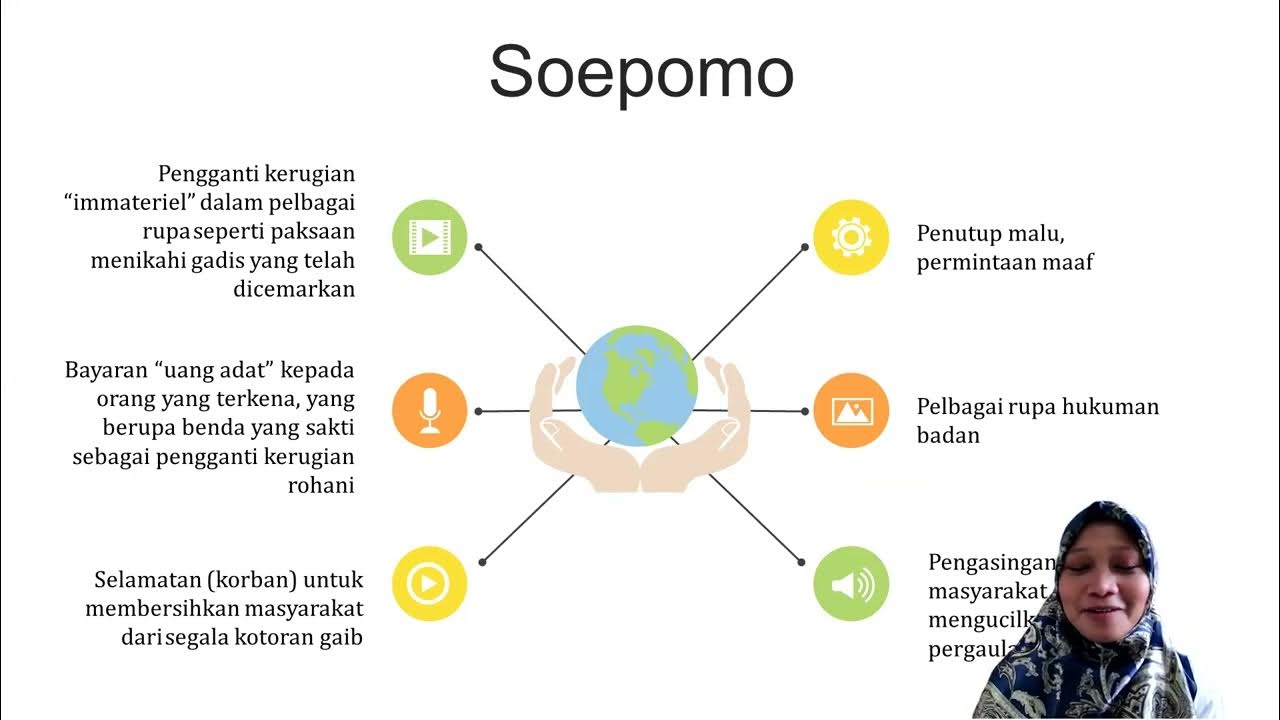
Hukum Keturunan
Summary
TLDRThis lecture covers the laws of kinship from the perspective of customary law. It focuses on lineage, including parent-child relationships, kinship structures, and the societal impact of family ties. Key topics discussed include the types of lineage (upward, downward, and lateral), marriage restrictions based on kinship, inheritance laws, and parental obligations. The speaker also outlines the five categories of children under Indonesian law—legitimate, adopted, out-of-wedlock, illegitimate, and foster children—and compares kinship rules in Islamic law, customary law, and civil law. Listeners are encouraged to analyze these comparisons.
Takeaways
- 👨👩👧👦 The discussion is about kinship laws from the perspective of customary law.
- 👶 The first focus is on lineage, including the relationship between parents and children, and between children and extended family.
- 👥 It also covers the care of orphans and the adoption of children within kinship systems.
- 🩸 Kinship is defined by blood relations, typically involving two or more people related by descent.
- 📜 Three types of lineage are discussed: ascending (parent-child), descending (grandparent-grandchild), and lateral (siblings).
- 🚫 Kinship rules influence marriage laws, such as prohibiting marriage between siblings and between parents and their children.
- 🏠 Inheritance laws also rely on kinship, as blood relations determine rights to inherit property.
- 📖 Indonesia's law, including articles 45 and 46 of Law No. 1 of 1974, mentions parental obligations, such as educating and supporting children until adulthood.
- 👶 There are five types of children recognized in Indonesian law: legitimate, adopted, out-of-wedlock, illegitimate, and foster children.
- 🔍 The speaker encourages a comparison of customary, Islamic, and Indonesian legal perspectives on issues like adoption, inheritance, and guardianship.
Q & A
What is the main focus of the discussed legal topic?
-The main focus is on kinship law, particularly from the perspective of customary law, covering familial relationships, inheritance, and child adoption.
What does 'kinship' refer to in this context?
-'Kinship' refers to blood relations between two or more individuals, such as between parents and children or between siblings.
What are the three lines of descent mentioned?
-The three lines of descent are: 1) vertical descent (parent-child), 2) upward descent (child-parent), and 3) lateral descent (siblings).
Why is lineage important in marriage according to customary and Islamic law?
-Lineage is important in marriage to determine marriage prohibitions, such as preventing marriage between close relatives (e.g., siblings, parents, and children).
What is the relevance of lineage in inheritance matters?
-Lineage is one of the primary factors determining inheritance rights, as inheritance laws often rely on family ties to determine beneficiaries.
What are the five types of children recognized in Indonesian law?
-The five types of children are: 1) legitimate children, 2) adopted children, 3) children born out of wedlock, 4) illegitimate children, and 5) foster children.
What legal obligations do parents have toward their children under Indonesian law?
-According to Indonesian law (Article 45 and 46 of Law No. 1 of 1974), parents are obligated to educate and raise their children until adulthood to the best of their ability.
What obligations do children have toward their parents?
-Children are legally required to take care of and respect their parents.
What is the significance of child adoption in customary and Islamic law?
-Child adoption has legal significance in both customary and Islamic law, affecting inheritance rights, parental obligations, and the child's status within the family structure.
How is the concept of guardianship addressed when a parent dies?
-Guardianship after a parent's death is governed by customary law, Islamic law, and the Indonesian Civil Code, which provide guidelines for assigning responsibility for the child’s welfare.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)