PEMBAHASAN SOAL-SOAL FISIKA HOTS SMA (1)
Summary
TLDRThis video explains the dynamics of a system involving two blocks, A and B, connected by a rope, with block A on a rough surface and block B hanging. It illustrates how to analyze forces such as weight, normal force, friction, and tension acting on the blocks. The problem is solved by applying Newton's laws of motion, particularly equilibrium conditions where the net force is zero. The video calculates the tension in the rope (Ta and Tb) and determines the mass of block B by breaking down forces in horizontal and vertical components.
Takeaways
- 🔧 Block A has a mass of 10 kg and is connected to Block B by a rope on a rough surface with a static friction coefficient of 0.2.
- ⚖️ The system is in equilibrium, meaning the sum of forces (ΣF) in both the x and y directions is zero.
- ⬇️ The weight of Block A is 100 N, calculated as mass (10 kg) multiplied by gravity (10 m/s²).
- 🛠 The normal force on Block A is equal to its weight (100 N) since no other forces are acting in the y-direction.
- ⚙️ The frictional force (F_gesek) acting on Block A is calculated using the formula F_gesek = μ_s * N, which results in 20 N.
- ➡️ The tension in the rope (T_A) pulling Block A to the right equals the frictional force, thus T_A = 20 N.
- 🔗 Block B has its own weight (W_B) and tension in the rope (T_B) acting upward.
- 📐 The forces on Block C include tension (T_C), which is resolved into components T_C cos(37°) and T_C sin(37°).
- 🔄 Using equilibrium equations, T_C is found to be 25 N and T_B is calculated to be 15 N.
- ⚖️ Finally, the mass of Block B is calculated using the relationship T_B = W_B = m_B * g, resulting in a mass of 1.5 kg for Block B.
Q & A
What is the mass of block A in the problem?
-The mass of block A is 10 kg.
What is the coefficient of static friction between block A and the table?
-The coefficient of static friction (μs) between block A and the table is 0.2.
How is the normal force on block A determined?
-Since block A is on a horizontal surface, the normal force (N) is equal to its weight, which is 100 N (calculated as mass × gravity: 10 kg × 10 m/s²).
What is the formula used to calculate the static friction force on block A?
-The static friction force (fₛ) is calculated using the formula: fₛ = μs × N, where μs is the coefficient of static friction and N is the normal force.
What is the value of the static friction force acting on block A?
-The static friction force acting on block A is 20 N (calculated as 0.2 × 100 N).
What is the tension force in the string connecting block A and block B (Tₐ)?
-The tension force Tₐ in the string is equal to the static friction force, which is 20 N.
How is the tension in the string related to the angle in the problem?
-The tension in the string is broken into components, with the horizontal component being Tₐ and the vertical component involving trigonometric functions of the angle (such as Tₐ cos 37° and Tₐ sin 37°).
What is the value of tension Tₐ based on the trigonometric components of the tension?
-The tension Tₐ in the horizontal direction is 20 N, and it helps calculate the overall tension in the string system by resolving it with cos 37° and sin 37°.
How is the mass of block B determined from the tension TB?
-Block B is in equilibrium, so the upward force (TB) must equal its weight (WB). TB = WB = mass of block B × gravity. Given TB = 15 N and gravity = 10 m/s², the mass of block B is 1.5 kg.
What is the final value for the tension in the string connecting block B to the system (TB)?
-The tension TB in the string is 15 N, as calculated from the balance of forces in the vertical direction.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
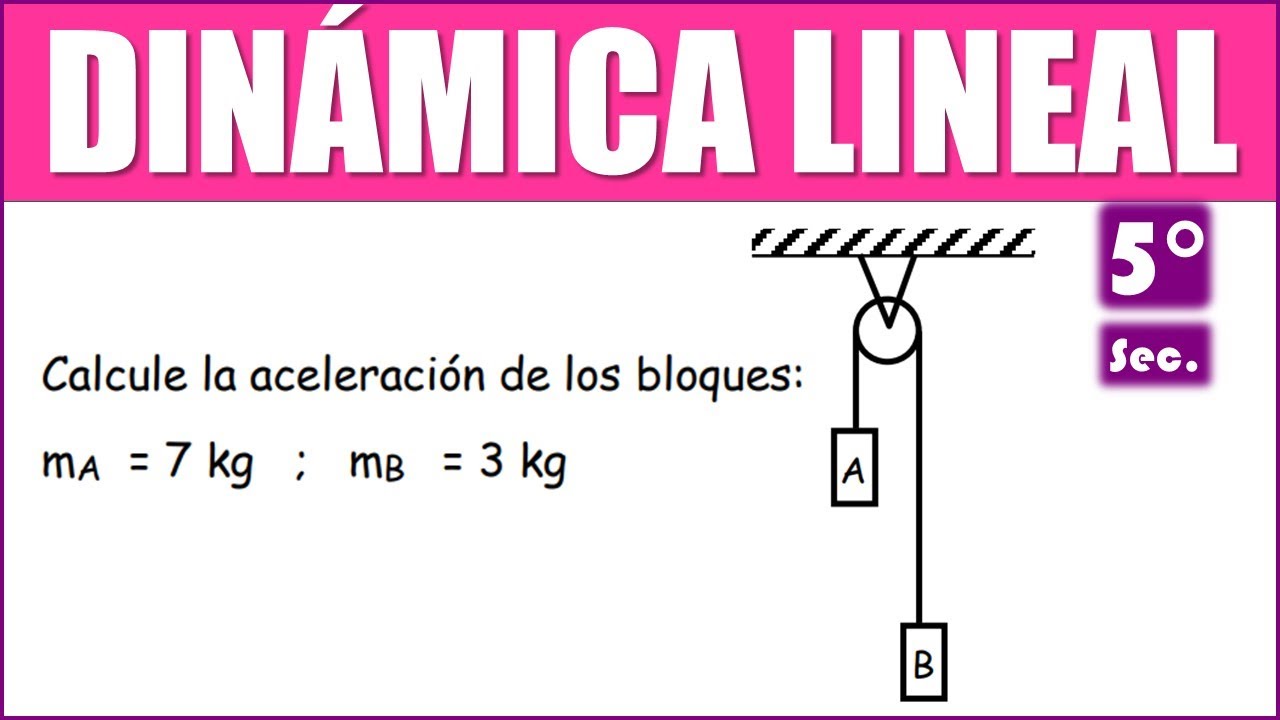
Calcule la aceleración de los bloques: mA = 7 kg ; mB = 3 kg
Types of forces and free body diagrams | AP Physics 1 | Khan Academy

Inline Vs Block Elements | Div & Span Tags Explained | Frontend Bootcamp Hindi | Ep.03

Earthquake Faults—3 basic types...in brief (educational)
How to Draw Block Diagram | Explain with Examples

Work due to Friction equals Change in Mechanical Energy Problem by Billy
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)