Apa itu DNA I Mengenal material genetik yang disebut DNA
Summary
TLDRThe video explains how genetic traits, such as skin color, blood type, and inherited conditions, are passed from parents to children through DNA. DNA is a long, twisted molecule found in cell nuclei that stores genetic information. It consists of a sugar-phosphate backbone and nucleotide bases (adenine, thymine, guanine, and cytosine), which pair up to form the DNA structure. DNA's key roles are in genetic inheritance (DNA replication) and expressing genetic information (transcription). These processes help determine physical traits and contribute to hereditary patterns observed in families.
Takeaways
- 👫 Offspring can inherit physical traits from both parents, such as skin color, which may be a combination of the parents' skin tones.
- 🧬 DNA is a macromolecule found in the cell nucleus that carries genetic information passed down from parents to their offspring.
- 📏 DNA has a long, twisted structure resembling a coiled ribbon, which condenses into chromosomes located in the cell nucleus.
- 🔬 The body is made up of different types of cells, each containing DNA that stores genetic information.
- 🧱 DNA is composed of three main components: phosphate groups, deoxyribose sugar, and nitrogen bases.
- 🧪 The deoxyribose sugar in DNA is a pentose sugar made up of five carbon atoms.
- 🧩 Nucleotide bases in DNA are categorized into purines (adenine and guanine) and pyrimidines (thymine and cytosine).
- 🔗 Adenine pairs with thymine through two hydrogen bonds, while guanine pairs with cytosine through three hydrogen bonds (AT/GC rule).
- 📚 DNA has two primary roles: inheritance of traits through DNA replication and expression of genetic information through transcription.
- 🧑🔬 Genetic conditions, such as albinism, can be inherited within families due to DNA mutations or variations.
Q & A
Why do some children have physical traits that are a combination of their parents' characteristics?
-Children inherit a mix of genetic information from both parents, which results in them having traits that combine their parents' characteristics, such as skin color, which could be a blend of both.
What determines the skin color of a child whose parents have different skin tones?
-The child’s skin color could be a mix of both parents' tones, resulting in a brown color, or it could be closer to one parent's skin tone if a particular trait is dominant, like lighter skin from the mother or darker skin from the father.
How are blood types inherited?
-Blood types are passed down from parents to their children through genetic inheritance, much like other physical traits.
What is an example of a hereditary condition mentioned in the script?
-An example of a hereditary condition is albinism, a disorder that affects skin pigmentation, causing a person to have very pale skin and hair due to the inability to produce melanin.
What is DNA and where is it located?
-DNA is a macromolecule that contains genetic information. It is located inside the nucleus of cells.
How is the structure of DNA described?
-DNA is described as a long, twisted strand that resembles a spiraling ribbon, which condenses to form structures called chromosomes.
What are the three components that make up DNA?
-The three components of DNA are phosphate groups, deoxyribose sugar, and nitrogenous bases.
What role do the nitrogenous bases play in DNA structure?
-Nitrogenous bases form pairs that are connected by hydrogen bonds, with purines (adenine and guanine) pairing with pyrimidines (thymine and cytosine). Adenine pairs with thymine through two hydrogen bonds, and guanine pairs with cytosine through three hydrogen bonds.
What are the two primary functions of DNA as explained in the script?
-DNA has two main functions: to transmit inherited traits from parents to offspring (through a process called replication) and to express genetic information (a process called transcription).
What is the significance of the variability in nucleotide bases in DNA?
-The variability in nucleotide bases allows DNA to store a wide range of genetic information, which is responsible for the diversity of traits and characteristics in living organisms.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

🧬 Kenapa Kita Mirip Orangtua Kita?

Materi Hereditas Pada Manusia | Kelas 12 SMA

Pewarisan Sifat pada Makhluk Hidup dan Kelainan Sifat yang Diturunkan | IPA Kelas 9 | Materi BAB 3
D3.2 Analysis of Inheritance Patterns [IB Biology SL/HL]
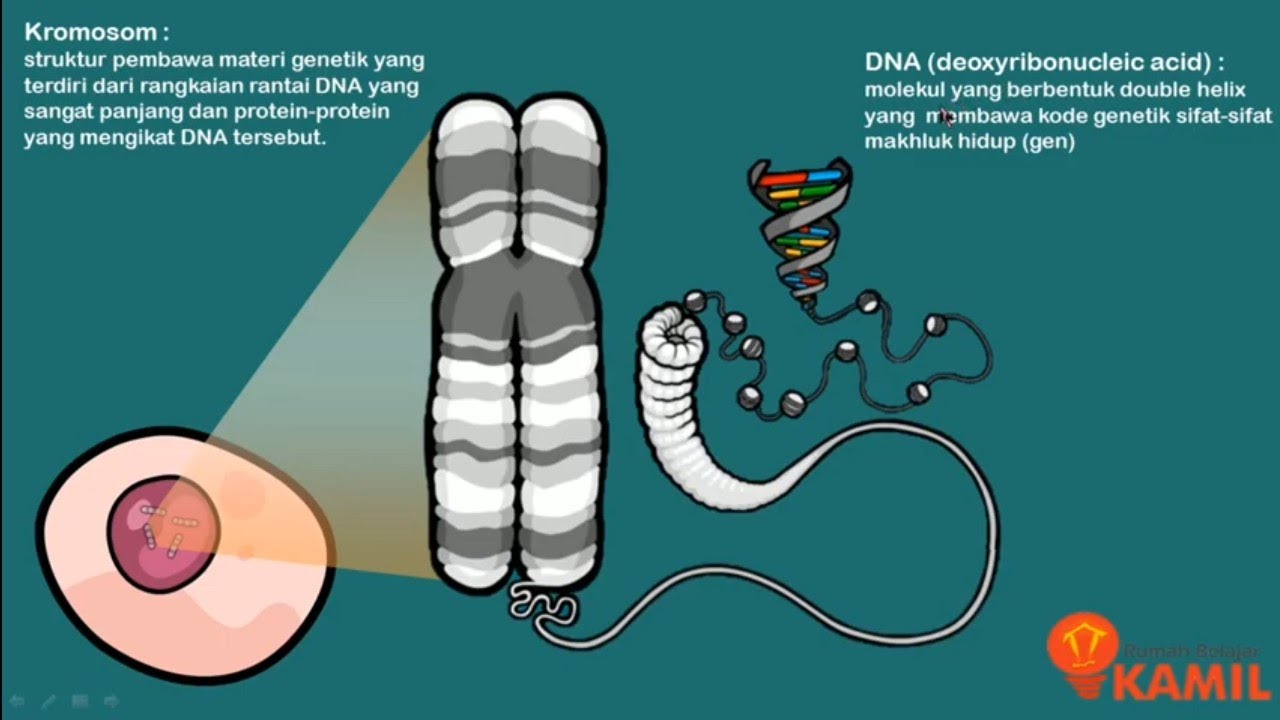
IPA Kelas 9 : Pewarisan Sifat I (Materi Genetik : Kromosom, DNA dan RNA)
17. Inheritance (Part 2) (Cambridge IGCSE Biology 0610 for exams in 2023, 2024 and 2025)
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)