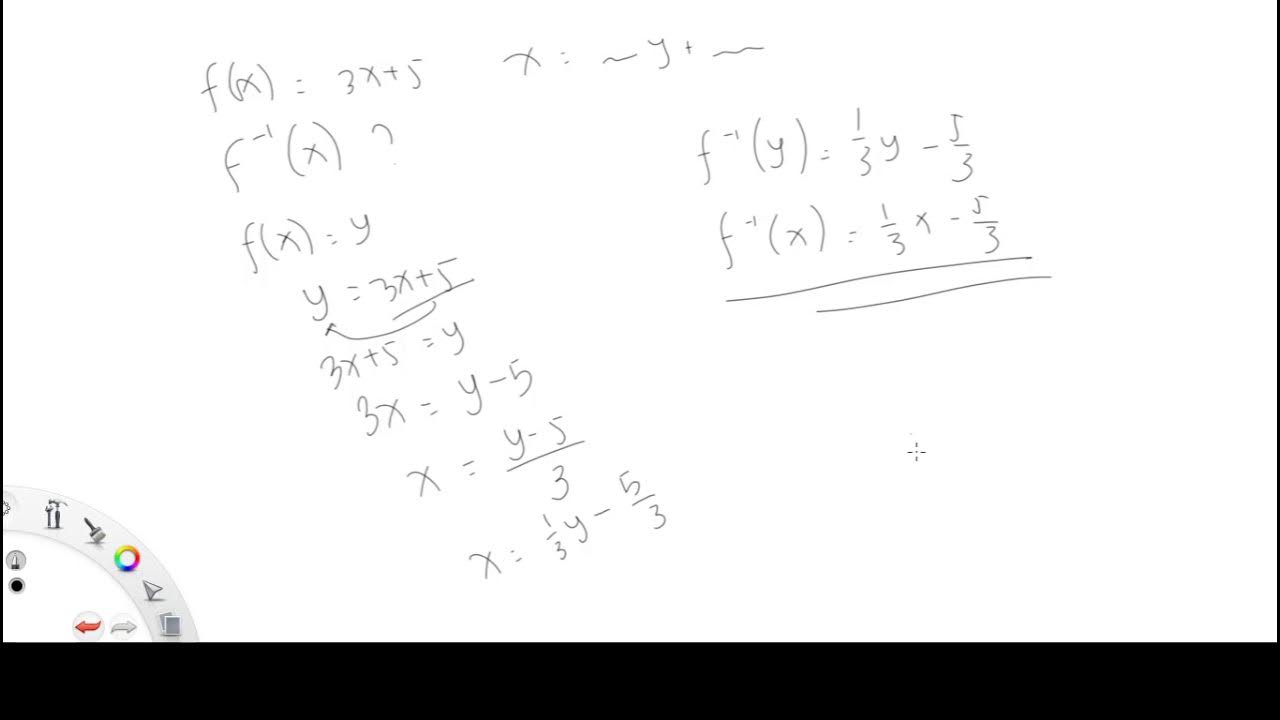Aljabar Linier Pertemuan 2_Sistem Persamaan Linier part 1/4
Summary
TLDRThe transcript covers a lecture on linear algebra, specifically focusing on linear systems of equations (SPL). The instructor explains the basic concepts of linear equations, their structure, and the differences between linear and non-linear equations. The session emphasizes the importance of linear equations in algebra, with examples showing how linearity is determined by variables and their powers, and how systems of equations are formed and solved. The lecture introduces key concepts like variables, coefficients, constants, and how they interact within linear equations, offering foundational understanding for future topics in the course.
Takeaways
- 📚 The lecture focuses on linear algebra, specifically the concept of linear equations.
- 🧮 Linear equations are foundational for understanding more advanced mathematical concepts.
- 🔢 Linear equations are defined as having variables with the highest power of one.
- 📈 Linear equations create straight lines when graphed, as the term 'linear' suggests.
- 🆓 There are two types of variables in these equations: dependent and independent variables.
- 🔀 Independent variables can be chosen freely, while dependent variables are determined based on the values of independent variables.
- ⚙️ A linear system consists of at least two linear equations working together.
- ✔️ The solution to a system of linear equations involves finding variable values that satisfy all equations simultaneously.
- ❌ Equations that involve exponents, square roots, or trigonometric functions are not considered linear equations.
- 📝 Examples of linear and non-linear equations are provided to help differentiate between the two.
Q & A
What is the primary topic of the lecture?
-The primary topic of the lecture is Linear Algebra, specifically focusing on linear equations and systems of linear equations (SPL).
What is the definition of a linear equation?
-A linear equation is one where the variables have a maximum exponent of 1, resulting in a straight line when graphed. The variables cannot have roots, powers greater than 1, or other non-linear operations.
What is a system of linear equations (SPL)?
-A system of linear equations (SPL) consists of two or more linear equations that are related to each other. The solution to the system is the set of values that satisfy all equations simultaneously.
What is the difference between a dependent variable and an independent variable?
-A dependent variable is influenced by the values of independent variables, while an independent variable is free to vary and is not dependent on other variables.
What is the significance of having more than one equation in a system?
-Having more than one equation in a system creates a relationship between the equations, forming a system that can have one solution, multiple solutions, or no solution at all.
What are some examples of linear equations mentioned in the lecture?
-Examples of linear equations include y = 3x + 5 and x + y = 7, where the variables have exponents of 1, resulting in straight lines on a graph.
Why is the equation y = 3√x not considered a linear equation?
-The equation y = 3√x is not considered linear because the variable x is raised to the power of 1/2, which makes it non-linear, as a linear equation must have variables with exponents of 1.
What is the general form of a linear equation with two variables?
-The general form of a linear equation with two variables is Ax + By = C, where A and B are coefficients, and C is a constant.
What is the graphical representation of a linear equation?
-A linear equation is represented as a straight line on a graph. The slope of the line is determined by the coefficients of the variables.
Can a linear system have more than two variables?
-Yes, a linear system can have multiple variables. For example, a system can have variables X1, X2, ..., Xn with corresponding equations that form a system of linear equations.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)