Energy 101
Summary
TLDRThe video explains energy as the capacity to do work, highlighting its various forms such as kinetic, potential, chemical, thermal, and radiant energy. It discusses the conservation of energy according to the first law of thermodynamics and how energy cannot be created or destroyed but can change forms and flow between systems. Additionally, the script outlines the energy supply chain, from primary energy resources like natural gas to the conversion into final energy forms such as electricity, which is then used by technologies to deliver useful energy for consumers.
Takeaways
- ⚡ Energy is defined as the capacity to do work.
- 🔁 The first law of thermodynamics states that energy can neither be created nor destroyed, only transformed.
- 🌍 Energy exists in various forms in nature, including kinetic, potential, chemical, thermal, and radiant energy.
- 🏃 Kinetic energy is associated with mass and motion.
- 🎯 Potential energy is related to position in a force field such as gravitational, electric, or magnetic fields.
- 🧪 Chemical energy is stored in materials and can be released through chemical reactions.
- 🔥 Thermal (heat) energy is linked to random molecular motions and often associated with temperature.
- 💡 Radiant energy is carried by light and electromagnetic radiation.
- 🔄 Energy systems involve a chain from resources to energy services: primary energy, final energy, and useful energy.
- 🔌 End-use technologies convert final energy (like electricity) into useful energy for consumer services.
Q & A
What is the simplest definition of energy?
-Energy is the capacity to do work.
What does the first law of thermodynamics state about energy?
-The first law of thermodynamics states that energy can neither be created nor destroyed, but it can change form and flow from one place to another.
What are some forms of energy found in nature?
-Some forms of energy found in nature include kinetic energy, potential energy, chemical energy, thermal (heat) energy, and radiant energy.
What is kinetic energy?
-Kinetic energy is the energy associated with mass and motion.
How is potential energy defined?
-Potential energy is the energy associated with the position of an object in a force field, such as gravitational, electric, or magnetic fields.
What is chemical energy?
-Chemical energy is the energy stored in certain materials that can be released through chemical reactions.
What is thermal or heat energy?
-Thermal energy, also known as heat energy, is the energy associated with random molecular motions within a medium, often linked to temperature.
What is radiant energy?
-Radiant energy is the energy carried by light and other forms of electromagnetic radiation.
What are the stages of energy transformation from resources to useful energy?
-Energy is extracted and processed as primary energy, converted and distributed as final energy, and then used by end-use technologies to become useful energy, which consumers use in their daily lives.
What is the difference between final energy and useful energy?
-Final energy is the usable form of energy like electricity or fuel, while useful energy is the energy used by end-use technologies to perform energy services.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

What is Kinetic and Potential Energy? [Stored Energy & Energy of Movement]

What the HECK is Energy?
Types of Energy | Energy Forms | Energy Sources and Uses

Energi dan Perubahannya - X OTKP SMKS Hang Tuah I Jakarta

FORMS OF ENERGY ⚡ - Primary Education Grade 5-6 | Different Types | Elementary | Happy Learning Kids
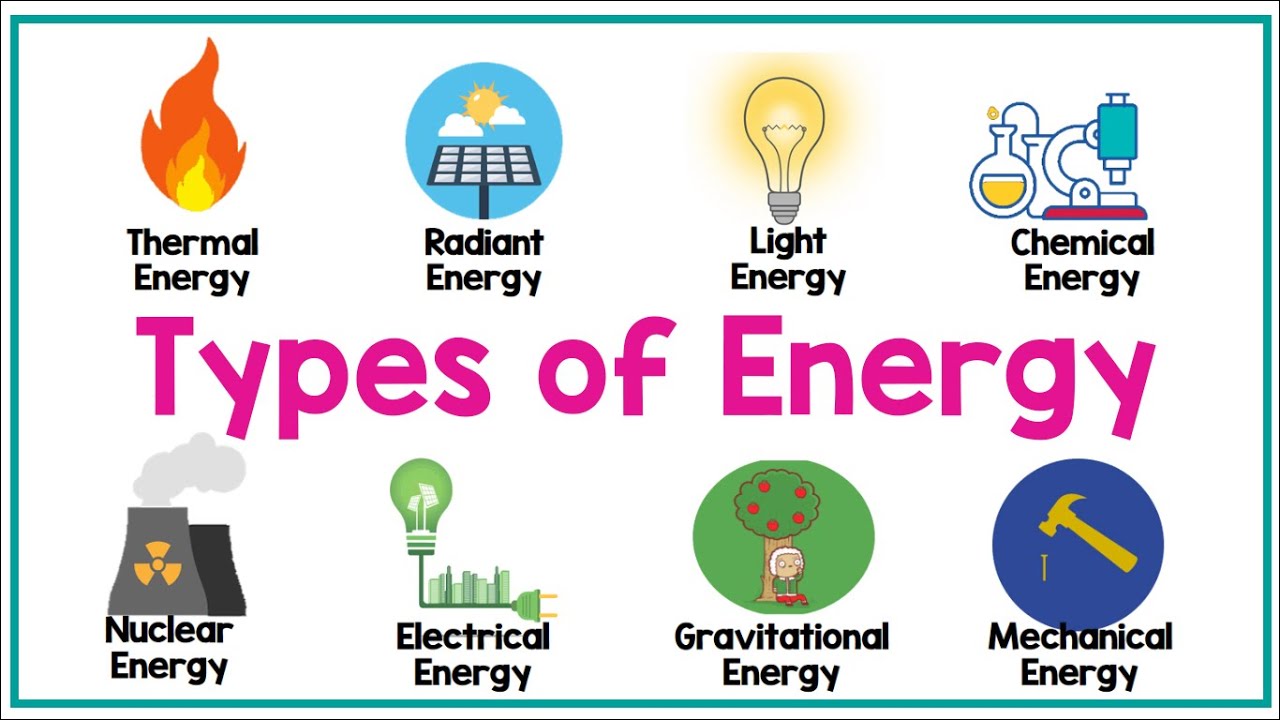
TYPES OF ENERGY | Physics Animation
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)