Kids Explain Intersectionality
Summary
TLDRThe transcript covers the concept of intersectionality, explaining how individuals have multiple facets to their identity that can influence their experiences, such as race and gender. It highlights that people may face overlapping discrimination, like sexism and racism simultaneously. The conversation emphasizes that everyone's identity is complex and made up of different parts that contribute to who they are. Through an analogy, it illustrates how people are more than just one aspect of themselves, leading to an understanding that identity is multidimensional. The discussion ends on a positive note with an engaging and relatable example.
Takeaways
- 🧠 Intersectionality is a concept that acknowledges how people's lives are multidimensional.
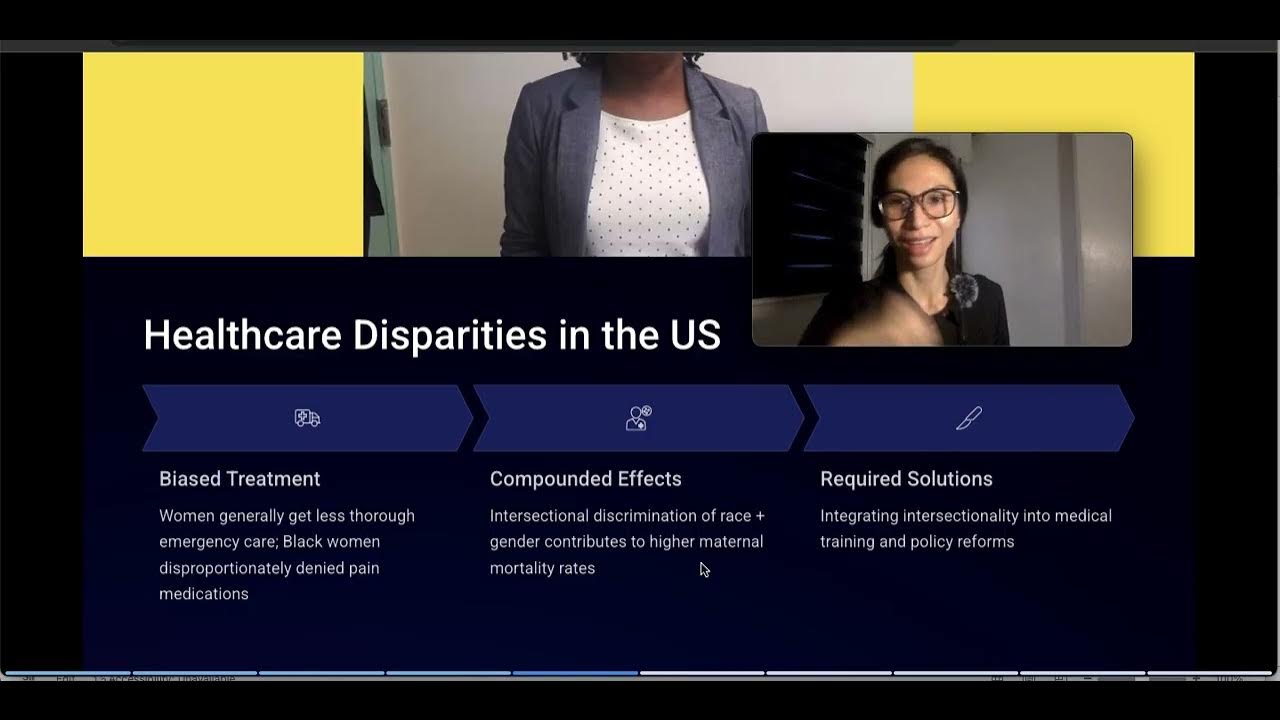
- 👩👩👧👦 Example: A Black woman may experience both racism and sexism simultaneously.
- ❓ Intersectionality asks us to think about how experiences of sexism or racism are not the same for everyone.
- 💡 Being conscious of multiple identity factors is crucial in understanding people's experiences.
- 🗣 The speaker uses a personal example: People think she is white because she is light-skinned, but she is actually First Nations.
- 🧩 Intersectionality is compared to a puzzle, where every part of a person contributes to who they are.
- 🤔 The speaker struggles to fully understand intersectionality at first but later grasps it by thinking about how many parts make up a person.
- 📸 People are not just one-dimensional; their whole identity must be considered.
- 👏 The speaker thanks the explainer and emphasizes that understanding intersectionality is 'cool.'
- 🎮 The conversation touches on societal expectations, such as boys-only clubs, comparing this to how people face different barriers.
Q & A
What is the concept of intersectionality?
-Intersectionality is a concept that helps us recognize that people live multidimensional lives, where different aspects of their identity, such as race and gender, can overlap and lead to unique experiences of discrimination or privilege.
Can you give an example of how intersectionality works?
-An example is a black woman who may experience both sexism and racism simultaneously. The discrimination she faces is not just because she is a woman or just because she is black, but because of the combination of both.
Does everyone experience sexism or racism in the same way?
-No, people do not experience sexism or racism in the same way because different factors, such as race, gender, and other identities, intersect to create unique experiences for each person.
Why is it important to consider intersectionality?
-It is important because it allows us to understand how various aspects of a person's identity contribute to their overall experience. Without considering intersectionality, we might overlook the complexities of their lived experiences.
What does the speaker mean by 'people aren't just the one picture'?
-The speaker is emphasizing that people are not defined by just one part of their identity. Their entire personality and experiences are shaped by multiple factors, making them more complex than a single characteristic.
How does the speaker relate intersectionality to a puzzle?
-The speaker compares intersectionality to a puzzle, where every part of a person—from their toes to the top of their head—comes together to form who they are. Each piece of the puzzle represents different aspects of their identity.
What does the example about light-skinned and First Nations identity demonstrate?
-It shows that people can be perceived differently based on their appearance, which may not always reflect their actual identity. In this case, the speaker is often mistaken for white because of their light skin, but they identify as First Nations.
What is the speaker trying to explain about the exclusivity of certain clubs?
-The speaker is giving an example of how certain societal rules or norms can exclude people based on arbitrary criteria, such as gender or possessions (like Pokemon cards), which reflects how discrimination and inequality can operate in society.
What does the speaker mean by 'the whole picture has to need your whole entire personality'?
-The speaker is saying that to fully understand a person, you need to consider all aspects of their identity and personality. No single trait defines a person; it’s the combination of all traits that makes them who they are.
How does the listener respond to the explanation of intersectionality?
-At first, the listener struggles to fully grasp the concept, but after further explanation, they express understanding, acknowledging that the idea of all parts of one's identity coming together makes sense to them.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)